Types and properties of covering materials for greenhouses
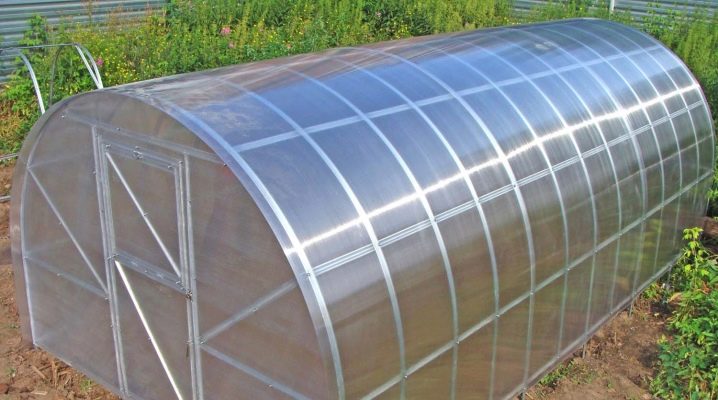

The issue of arranging a greenhouse is fundamental for every gardener and gardener, regardless of practical experience. In particular, this applies to the choice of high-quality and practical covering material. The modern market for such products offers a lot of various raw materials that can be used for the construction of a greenhouse.


Peculiarities
Covering materials of the latest generation make it possible to successfully grow most heat-loving plants even in the most severe climates. However, in order for them to cope with the assigned task as efficiently as possible, they must have certain quality characteristics and properties. For decades, glass or film has been widely used as a covering material for greenhouses. This, to some extent, narrowed the range of possibilities for the multifunctionality of structures.


Today, the product range has expanded significantly. However, each material taken separately has a number of specific positive and negative qualities. Therefore, the choice of this or that raw material must be approached with special care.
For the material of greenhouses and greenhouses, several criteria are important properties.
- Strength, ensuring the resistance of raw materials to temperature fluctuations, mechanical damage, the effects of any atmospheric precipitation, wind and ultraviolet radiation.
- Sufficient light transmission to save on energy consumption, including heating.


- Acceptable weight and flexibility of the material, which will ensure reliable installation of the coating on the frame.
- The ability to scatter sunlight and cut off harmful UV radiation.
- Counteracts the formation of condensation on the surface, which can cause burns on plant foliage.
- Resistance to the formation of harmful microflora on the coating;
- Ease of care, ease of use of the material (especially when the work will be done with your own hands).


In order to decide which material is best for the greenhouse, a kind of compromise is needed between the properties of the material for keeping heat inside, the operating life, cost and installation conditions.
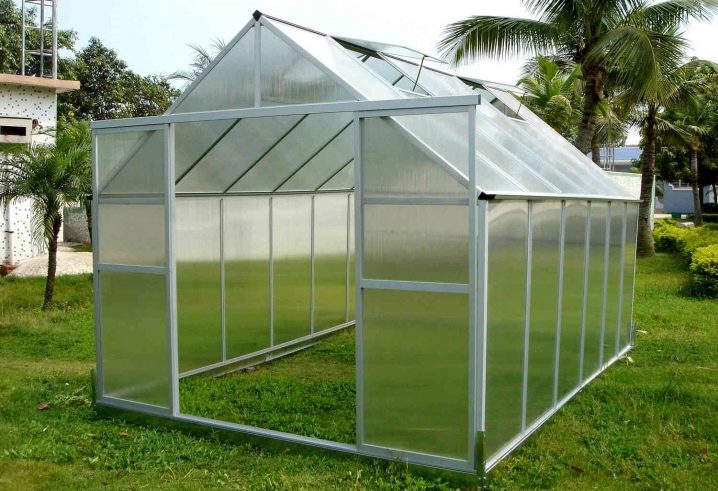

Types and characteristics: pros and cons
Having studied the varieties of this material and individual operating conditions, you can correctly prioritize and purchase exactly the products that will meet the requirements in a specific situation. The development of modern technologies contributes to the fact that new products of this segment appear on the market, and existing ones acquire additional properties.


Polyethylene film
This is a product that, for a fairly long period of time, served as the main material for covering the greenhouse. This was due to the meager range of analogue products. Due to a certain pricing policy that has developed on the market for this product, the film could be changed every season. The raw materials perfectly fulfilled their functional tasks. Today it is mainly used for small greenhouses.If atmospheric factors allowed the material to persist throughout the summer cottage, it is recommended to remove the material for the winter, since it does not withstand a temperature drop of more than -15C. The service life of the product is not always determined by the thickness, and the cost of the product may increase from this parameter.


The film has several advantages. Seedlings or already mature plants are perfectly sheltered from gusts of wind, precipitation, morning frosts and fogs. Thermometer reading and humidity level will always be higher than outside the greenhouse. Conventional polyethylene covering products are still found everywhere as a raw material for covering greenhouses and greenhouses. It is recommended to use products with a transparent color, which will not heat up so much from the sun's rays. The disadvantages of the product include a short service life, a low level of cut resistance.


Reinforced polyethylene film
In the light of technological advances, conventional polyethylene film has undergone significant improvements. The influence of progress has affected the composition of this raw material. The inclusion of special impurities in it made it possible to create a completely new covering material - reinforced polyethylene film. Such products are notable for their availability and low cost.
Reinforcing film is a fabric consisting of three layers, where the middle layer is a polymer mesh. Visually, the product looks like a fishing net, but the cells in this case are filled with polyethylene.


She has her own merits.
- Resistance to negative temperatures. The material withstands frosts down to -40C, does not lose its properties at temperatures up to + 90C.
- Due to the different size of the cells with micropores, the plants under the film breathe well, condensation does not accumulate on the surface from the inside.
- Light-stabilizing and reflective additives act as additional components, which extend the product's service life, reducing the negative effect of sunlight on the material.


- good durability and maintainability of the product;
- the products are not subject to rotting and mold formation, they are easy to install.
The types of reinforced film include products that are a frame made of polypropylene or fiberglass threads, twisted polyethylene.


PVC film
This product resembles cellophane in appearance. However, it does not emit characteristic sounds upon contact and is very thick. The main visual difference of the product from other materials that cover the greenhouse frame is the yellowish color of the roll cut. The positive qualities of products include light transmittance, which is 90% for ordinary light, and no more than 80% for sunlight.


It does not transmit infrared radiation, this confrontation indicator delivers 9%. This quality of the material prevents the greenhouse from cooling down overnight. The disadvantages of the film include low resistance to low temperatures. The coating can withstand frost not exceeding -15C. It is not resistant to dirt: dust settles on the surface of the material, which negatively affects the light transmission capacity.


Glass
Until recently, glass greenhouses were not available to everyone due to the cost of such a structure. But the functionality of such greenhouses justified a serious investment, since the plants inside were protected from adverse weather conditions.
Glass has many advantages, including:
- excellent level of light transmission;
- good thermal insulation characteristics;
- biostability.


Glass greenhouses have the most attractive appearance in comparison with other materials that can be used to cover the structure.


The disadvantages of glass construction include:
- impressive weight;
- fragility of products;
- labor intensity of the device.


There are alternative options for arranging glass greenhouses, which presuppose the use of old window frames with whole glazing for these purposes. For the most hardworking summer residents, this solution will be ideal, since the use of used materials will save money, build an environmentally friendly and durable greenhouse that is not afraid of cold weather, snow, rain and hot and scorching sunlight. You can return the dirty glass to its previous transparency using a regular irrigation hose and clean rags.


Cellular polycarbonate
This material belongs to the group of expensive raw materials. It comes in different sheet sizes. Polycarbonate is a hollow construction with bridges along the product that bear some resemblance to a honeycomb.
The positive features of the material include the following characteristics:
- good level of thermal insulation;
- light transmission (84%);
- resistance to mechanical damage;


- minimum weight;
- beautiful appearance;
- ease of installation.
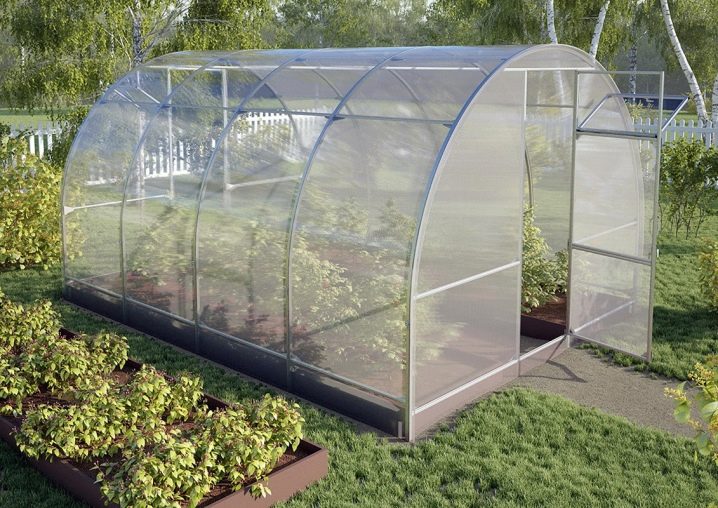

The disadvantages of cellular polycarbonate are:
- deformation when heated or cooled;
- decrease in light transmission over time.


When arranging greenhouses with such products, the ends of the sheets must be additionally protected from moisture using plugs. The polycarbonate construction will last for a long time, and the configuration options, thanks to the ability to bend the sheets, can be very diverse. That is why this material is preferred by landscape designers.

Agrofibre: what is it?
This product is a non-woven fabric similar to non-woven fabric. In its production, polymers are used.


What happens?
There are two types of material that have a specific purpose. There are black and white products. The first option is intended for insulating seedlings and protecting against weeds, the last one for the construction of the greenhouse structures themselves. Agrotextile is represented on the market for similar products in a wide variety of types. The most demanded materials are agrotex, spunbond, lutrasil. All types of products are similar in their characteristics, although the same material may be called differently by each manufacturer.


Agrofibre can have different markings that indicate its density (60, 80, 42). The installation technology of such a material does not require a special frame. With a medium thickness material, you can simply cover the seedlings, fixing the coating along the edges. To equip greenhouses with a frame, you need to purchase material with a high density.


Advantages and disadvantages
Agrotextile has positive features:
- the material does not absorb liquid and allows it to pass through perfectly;
- it provides reliable protection against ultraviolet rays;
- retains heat well inside;
- excellent air permeability;
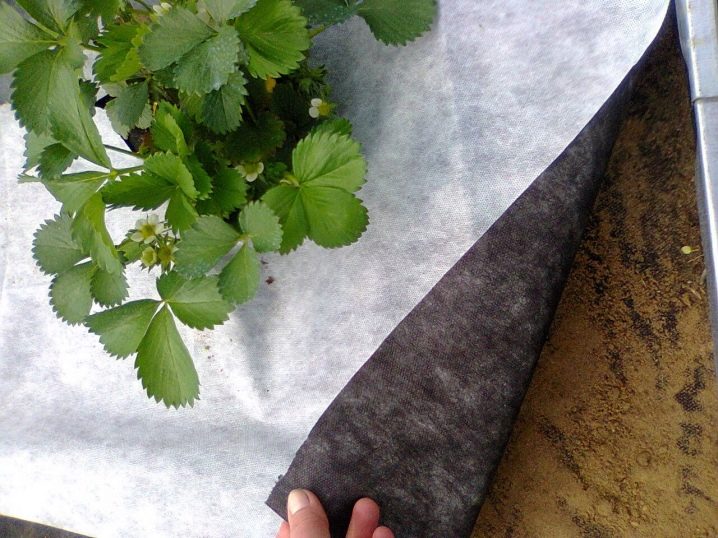

- eliminates the formation of condensation;
- reliably protects plants from insects, birds and precipitation (hail and freezing rain);
- it is easy to use and maintain.


The disadvantages of the product are:
- high price;
- a small level of thermal insulation.


Application: Features
Experienced gardeners, when installing agrofibre on the frame, recommend strengthening fabric cuts in the middle of the canvas, forming from them a kind of ties that will ensure the convenience and efficiency of fastening. To carry out the work, there is no need to purchase a special tool or involve specialists in the process. The ability to tie fabric knots will be sufficient. If slats are attached at the edges, the windage of the structure will be significantly reduced. The canvas that has already become unsuitable for covering greenhouses can be effectively used as a covering product for seedlings or perennial flowering plants. The average rock service life of the material is 4-5 years.


Tips for use and care
Take note of a few guidelines.
- With a lack of funds, the most economical option for covering material for greenhouses will be a polyethylene film. For consumers with average financial capabilities, it would be more logical to opt for glass or polycarbonate.
- If the operation of the greenhouse will be short-term, there is no practical sense in purchasing expensive and durable materials.


- A small structure can be covered with different materials every season. It is better to equip constructions with serious dimensions more thoroughly (for example, using glass, which is unassuming to care for).
- PVC products are very durable, they can be used for about 8 years, however, like ordinary polyethylene film, it will need to be dismantled at the end of the season.


The device of a greenhouse presupposes the knowledge that it is not worth planting the same plant in one place every year. Agrofibre and cellular polycarbonate have recently been in the greatest demand among gardeners. These materials are of high quality and efficiency in providing an optimal microclimate inside the greenhouse.


How to choose a greenhouse, see the video below.





























































The comment was sent successfully.