How to plant a rose?
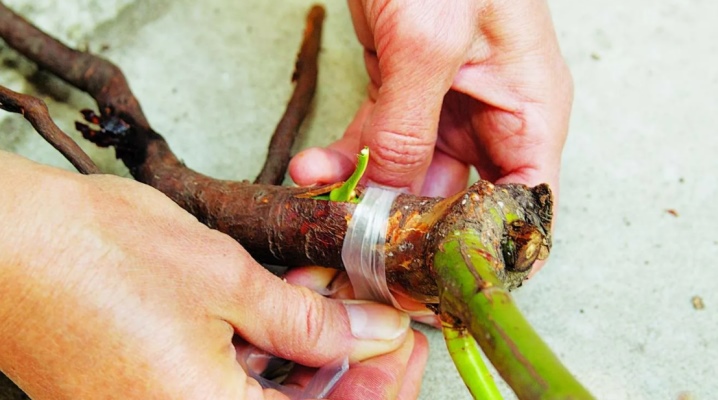

Roses are one of the most spectacular and popular flowers in garden plots and in home greenhouses. Growing them is difficult, as a rule, not always with sufficient frost resistance. To improve such qualities of a plant, experienced florists use different methods of grafting. If you feel the need for this procedure, you need to study all its features. The main thing in this business is patience, since the first time the result is not always one hundred percent satisfied.
The need for a procedure
Before deciding whether to plant a rose, you need to understand the reasons why the procedure is recommended for carrying out. In fact, this is one of the methods of reproduction, when the fibers of a part of one plant grow together with the fibers of another representative of the flora. It was this breeding method that made it possible to admire many hybrid varieties. In addition, it made it possible to improve the qualities of existing ones, for example, to increase their resistance to cold weather, diseases, and other external factors. You can connect either the same variety or completely different ones.


One of the most common crosses is grafting a rose onto a rose hip. There are successful examples of grafting donated roses from a bouquet to a bush. The result is a fundamentally new option with spectacular flowers and lush greenery. In principle, you can plant any flower, but there are nuances that should be taken into account:
- only those buds that have already passed the flowering period are suitable for the procedure;
- only shoots are suitable, the length of which varies from 6 to 7 cm, and the branch should not be bending, strong are preferred;
- if the procedure cannot occur when it was conceived, the cuttings should be folded into a wet cloth, which must be regularly moistened, otherwise the plant will die.
If these nuances are taken into account, there is a need for vaccination, you can proceed to the procedure, during which many other rules arise that must be followed strictly.

Timing
When is the best time to plant a rose is a question that still does not have an obvious answer. Gardeners have different opinions on this matter. It is very important to take into account the characteristics of the variety that you decide to plant. Since the rose belongs to plants that love warmth, this procedure is optimal in summer. Experts agree on one thing - in July and August, vaccination gives the most positive results. True, experienced florists graft the plant in winter, spring, and autumn.
But the chance of a positive outcome of such an experiment is small. Cold negatively affects growth activity, so summer grafting is the right decision. It is believed that from mid-July to mid-August is the period impeccably suited for these activities. In autumn, the procedure is carried out 20 days before the expected frost, no later, in winter - in the last month, in spring - from April to May.


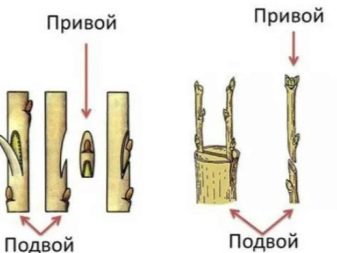
Choice of rootstock and scion
Usually, the buds of the cultivar type are transplanted onto the stock, which can be used as different bases. Most often these are wild shrubs such as rose hips or other types of roses that could not recover after winter. In this case, it is important that the root system is completely healthy. Not only the level of skill determines the success of the procedure, but also the choice of rootstock, scion.
- Rootstock. Ideally, the stock should have excellent healthy roots.It is better if the plant is grown in the area in which the procedure is carried out. If you plan to vaccinate on a rose hip that you do not have yet, it will take up to three years to make it happen. If the bark normally departs from the trunk, and the diameter of the root neck is at least 8 mm, then the base is ready for budding. Shoots with thin shoots and fibrous roots are not able to provide a new plant in a full-fledged way. Rootstock seedlings can be purchased in greenhouses and nurseries, choosing representatives with strong rod-type roots and a powerful root collar. It is very important that the growth forces of the rootstock and the scion match, therefore, a mini-flower from a home greenhouse does not need to be planted on a powerfully developing shrub.
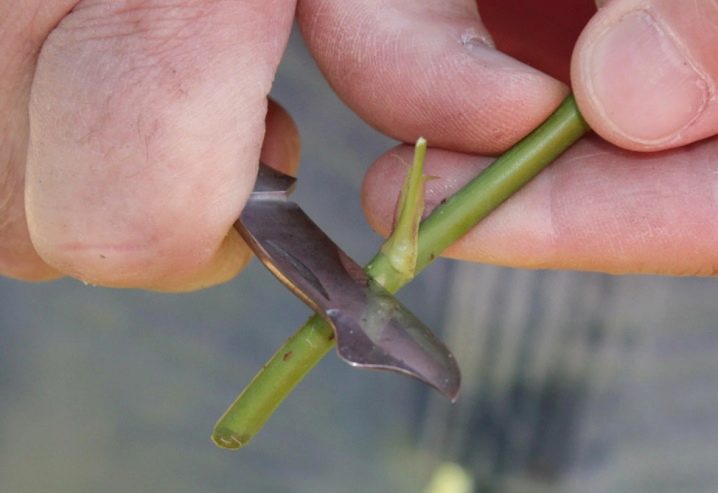
- Graft. The bud should be taken away exclusively from a fully matured plant, the thickness of which is at least 5-6 mm, while the bark must be dense. Check the shoot for a fold - it bends poorly and is ready to break. Dormant buds are grafted in the summer, when the first stage of flowering is completed. Germinating buds are transplanted in the spring. The dormant bud is taken from the middle of an absolutely healthy shoot in order to succeed in budding. In addition to the buds, grafting is carried out in the split, when not the buds, but the cuttings of the plant are used.

It is also important to prepare instruments and materials for the procedure:
- well sharpened knife, there are special options for budding;
- strapping tape;
- clean dry matter;
- transparent type film.
All cutting tools must be disinfected and sharpened if necessary. The risk of tissue damage and infection during grafting should be minimized.

Vaccination methods
It is quite possible to plant a plant at home if you know how to do it yourself correctly. You can do this with your own hands in several ways on a bole, a wild variety, for example, a dog rose, another rose.
On the stem
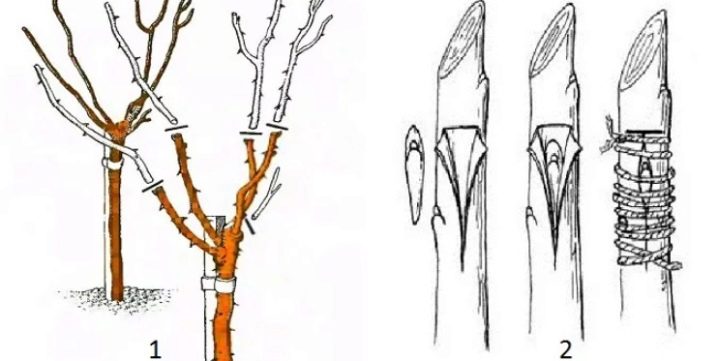
This is a rather laborious event, but the result is worth the effort, since the renewed rose looks very impressive. A stem is a tree created artificially with a straight type trunk without foliage, but with an abundant crown. An even shoot above one and a half meters is chosen, to which the grafting is carried out. It must be ensured that there are no ramifications. Standard grafting roses bloom very luxuriantly, much more spectacular than bush varieties, but the risk of diseases increases dramatically.
The soil must be kept moist, not allowing it to dry out for a long time. If the roots lack moisture, the result may be far from desired. Three inoculations are made on each trunk, and the place is chosen for each from different sides. It is quite possible to attach several varieties to one stem.
If all vaccinations are successful, the plant will turn out to be incredibly effective. The graft must be freshly cut and completely healthy. As for the height of the trunk, the following nuance must be taken into account - climbing varieties of flowers are attached to tall species, and weak-growing roses to small ones.
Rosehip
Most often, a rose is grafted onto a rosehip, this is the most common version of the procedure. The technology allows you to inoculate absolutely any variety, but it is not as simple as it seems at first glance. It takes a lot of skill and patience. It will take two years to see the result, but there is no guarantee that the first vaccination will be successful. The algorithm of actions is as follows.
- First of all, scion cuttings are prepared - shoots are cut off from a plant that is already one year old. An important point - it should already bloom. Branches with a width of more than a centimeter and with at least 3 buds are used, then the chances of success are greater.
- Cuttings, if not freshly cut, should be stored in a damp wrapper in a cool place.for the procedure to be successful.All foliage is removed from the scion, and the rootstock should be freed from the soil layer from above so that the root collar is free. The latter is wiped off the ground with a damp cloth, not a single crumb should remain, otherwise soil may get into the cut.
- After that, a kidney, a shield is cut from the prepared cutting, this is done with an eyepiece knife. The length of the scion is at least 3 centimeters.
- The bark layer from above is removed from the scutellum, an incision is formed on the rootstock. The place is chosen where the root system smoothly passes into the stem. The cut should resemble the letter "T". The zone is selected based on the position to the sun, the rays should not fall on it.
- The bark is pushed back as carefully as possible, the stalk is inserted there. Avoid cutting too large or the shield will fall out. The vaccination zone is well wrapped, for this they use scotch tape, durable polyethylene.
- The kidney does not close when wrapped, and the place itself is covered with wet soil.
After that, the process itself is considered complete, you need to wait for results that may not happen soon or not at all. Much depends on climatic features, skill and compliance with all the rules of procedure.

To another rose
A rose grafts well on other types of roses, for example, a donor bud grafted onto the neck of a rosehip root takes root well. After the attachment has grafted, the top of the bush is cut off and new shoots are allowed to develop on the roots.
It is also quite possible to plant a rose that you liked in the presented bouquet. This is done by budding. Crossing rose varieties is a common procedure, sometimes the same varieties are crossed to improve the varietal qualities of the species. As for grafting roses from cuttings, this option is possible only with domestic varieties.
Popular Dutch varieties do not take root well in domestic conditions. It is also important to hold this event during the summer. If you are not sure about the freshness of a flower from a bouquet, do not risk it. In addition, it is important that the flowers do not stand in the water for more than 4 days.



Follow-up care
Caring for roses is, in principle, very important, and for grafted plants it is vital. Unfortunately, the success of the procedure can be impaired by an excess of sunlight, improper moisture. Use the following tips for caring for roses after grafting:
- water the plant every day, but do not be too zealous, watering should not be abundant;
- weed the area near the bush in time so that there is no weed;
- loosen the soil so that air exchange is not disturbed by anything;
- it is very important to closely monitor the flower after grafting for 20 days - a good sign if the bud is greenish and the tissue is not dry;
- if the zone has turned black, you will have to carry out the event again, and this bush will no longer fit for the stock, it is too weak after the first procedure;
- before the winter period, the land is qualitatively loosened and covered with dry foliage;
- insulation for the winter must be removed in April, at the same time the bandage is removed from the vaccination zone;
- after that, the plant is cut above the grafting point;
- cuts are processed with garden varnish purchased in specialized stores;
- do not forget to feed the grafted plants once every 10 days, formulations with phosphorus, nitrogen, potassium will be required;
- the buds that appear on the grafted rose are removed, otherwise they will take most of the nutrients for themselves, while the shoots will lose them;
- do not rush to flowering, in abundant form it can destroy the grafted plant, you need to give the bush summer to become stronger and stronger;
- after that, the plant can be safely transplanted, but before the onset of frost.




































































































The comment was sent successfully.