Pine: what it looks like and how old it lives, pros and cons
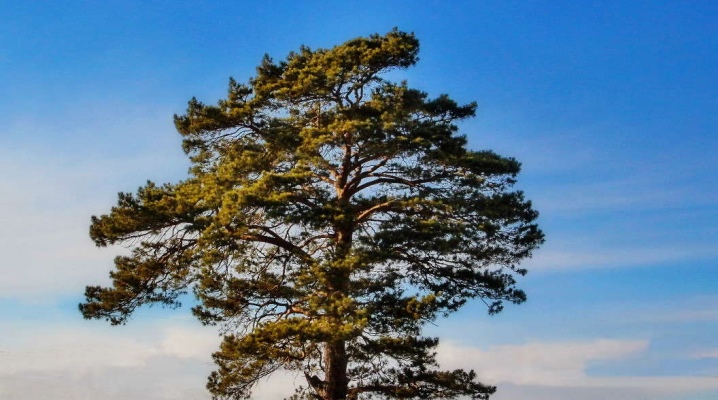

Among the most popular and recognizable conifers, pine occupies a special place, which has found its application not only in landscape design and wildlife, but also in the traditional decoration of a home on the eve of the New Year's celebration. The culture stands out for its decorative qualities, as well as features related to agricultural technology.



Description
This type of evergreen plant in many cultures acts as a symbol of immortality and vitality. Our ancestors considered this tree to be magical; in many pagan beliefs, pine branches were considered amulets. The origin of the tree's name is directly related to several Latin words - pin and pix, which literally mean "rock" or "growing on rocks", as well as "resin".
A huge number of species and varieties of pine are grown around the world; in our country, the plant is represented mostly by Scots pine, which is found not only in the north, but also in the southern regions.
Pine trees adapt well to various types of soil, therefore they can grow in hot regions with arid climates, in mountainous areas, in swampy ground, as well as in the city.
The culture belongs to light-loving plants, as evidenced by the features of its structure - the trunk of a tree is able to lengthen to a large extent, in light of which the crown very often takes the form of a mast. In flat terrain, you can find trees with spreading branches, with bizarre and curving crown shapes. The pine needles have a bluish color with a dominant green color, while the color of the bark of the tree will be reddish-brown, in some varieties the trunk is copper-colored. The needles on the branches are collected in a bunch of 2-5 pieces. Features of the color of the needles, as well as the number of needles in the bunch, help to distinguish one type of pine from another.



Wood is of particular value, for which it is in demand. It will have a yellowish color due to the presence of a large amount of resins. The flowering period of pines falls on the beginning of summer - May-June, however, the timing may shift in one direction or another, depending on the characteristics of the climate in the region of its growth. The cones dry out after flowering, releasing winged seeds, which in the future, under favorable conditions, will turn into young coniferous crops. Cones, sap, pine needles and resin are used in folk medicine.
In general, each part of the evergreen culture has found its application in production, folk medicine, cooking, etc.
Features of the root system
The pine root system stands out for its plasticity. Now there is a certain classification of ephedra roots, according to which trees are divided into 3 groups.
- Cultures with powerful roots. In conifers from this category, the main component will be the core, from which the development and branching of the lateral roots is already taking place. Typically, this type of plant is found in light and well-drained soil. Side branches are notable for their parallel arrangement in the ground relative to the surface.


- Pine trees with a poorly expressed root system. In such conifers, all the roots will have a minimum length, the branching will also be insignificant. The most suitable conditions for development with roots of this kind will be swampy areas, as well as areas with high soil moisture.


- Plants with a shallow rhizome. The root system, which outwardly resembles a root sponge or brush, is quite developmental. Crops with such a root structure usually take root in dense soil, in places where the depth of groundwater is shallow.
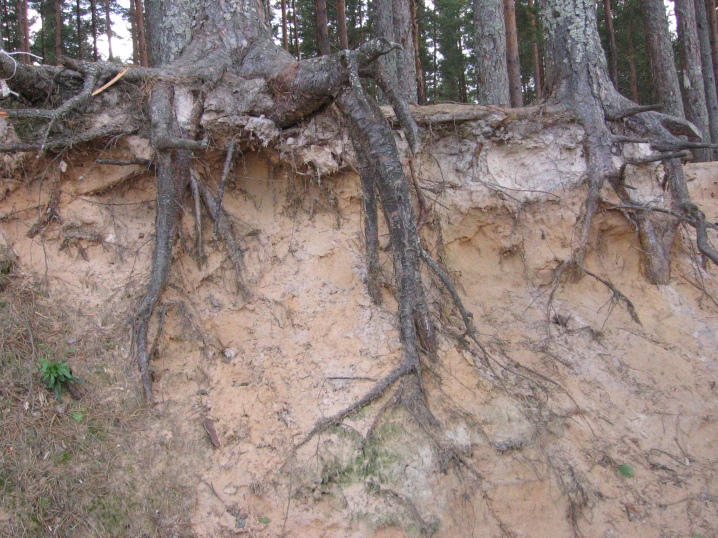

The diversity of the structure of the root system in pine trees makes it possible to highlight the peculiarity of such a culture to adapt its underground part to the individual characteristics of the type of soil where they took root.
Thanks to this nuance, pine trees can be ranked among the universal coniferous crops with high survival rate and the ability to quickly adapt to any features of the planting site.
Also, among the remarkable qualities of the root system, it is worth noting its development only under the condition that the air temperature is at least + 3C. Usually, in a healthy pine, the rod can go 2-3 meters into the ground, while the lateral shoots can increase in size up to 8-10 meters.
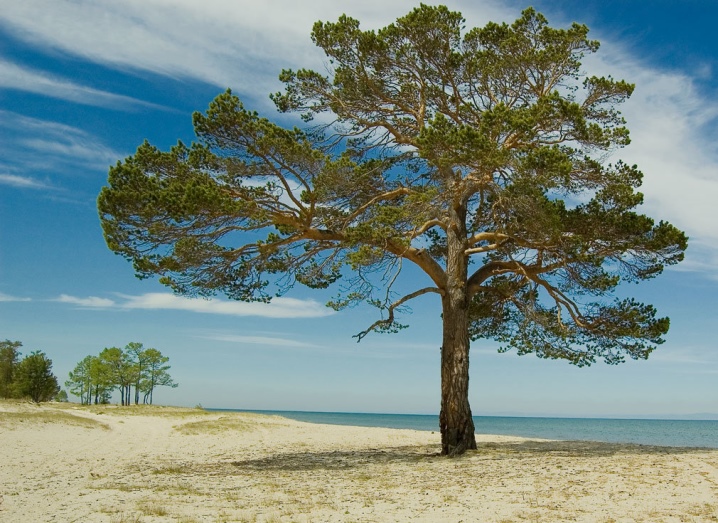

Height
Since there are about a hundred varieties of pines in nature, most of which develop well in domestic latitudes, the size gradation of conifers will be quite significant. However, among the most common species and varieties, it is worth highlighting the most demanded:
- Scots pine - the height of the tree can be up to 40 meters;
- Korean pine - 40-50 meters;
- Crimean pine - on average, the culture grows up to 30 meters;
- Weymouth pine - its size can reach 40-50 meters.




Large growers are popular in terms of urban greening, as well as for rooting in forest plantations, nurseries, however, breeders have bred many dwarf or slow-growing species of pine trees. The maximum height of such low crops sometimes does not reach half a meter, in addition, small plants are notable for the minimum average growth per season.


How many years has it been growing?
In some cases, when buying a pine seedling, it can be quite difficult to determine the age of the plant, so it is important to know the approximate life cycle of the ephedra, as well as the average annual growth rate in ornamental and wild-growing varieties. It has been established that in 1 year the planted culture adds no more than 6 centimeters in height, however, additional stimulation from the gardener will help to double these indicators. This can be achieved by satisfying the needs of the pine for light, as well as ensuring the free development of culture on the site without the unwanted neighborhood of weeds or shading shrubs.
In the first 2 years after rooting, the root system of ephedra seedlings will also grow at a rather slow pace.



Scotch pine and other types of tall pines after five years of age and until they reach 10 years of age are able to increase in growth by 20-60 centimeters every month. Dwarf decorative varieties do not show such an increase in subsequent years, as a rule, they can increase by 2-10 centimeters in a year. Some crops on the lawn over 10 years old are capable of growing 1 meter per year. By the age of 30-50, the growth rates and developmental stages slow down, but only in terms of size in height.
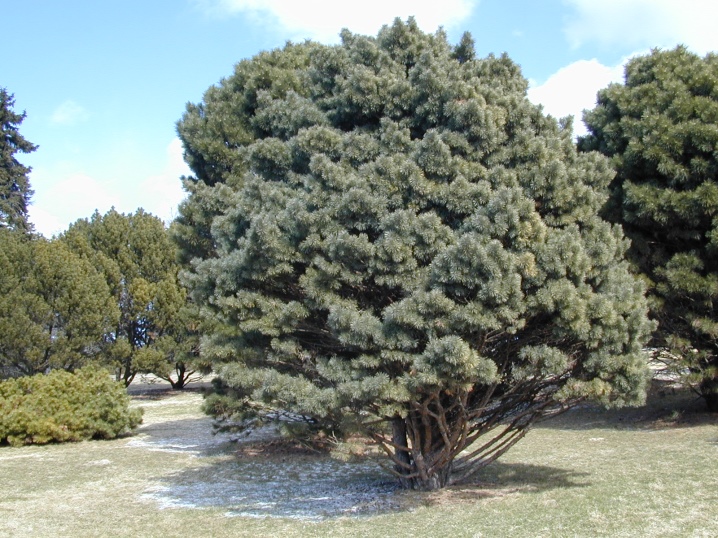

Further, the culture begins to develop in width, increasing the crown in diameter, as well as increasing the thickness of the trunk. It is these features that should be taken into account when planning pine planting on your site. Since the wrong choice of a species or variety in the future will result in the presence of a giant plant in the garden, the entire decorative appeal of which, concerning the needles, will be concentrated at the very top.
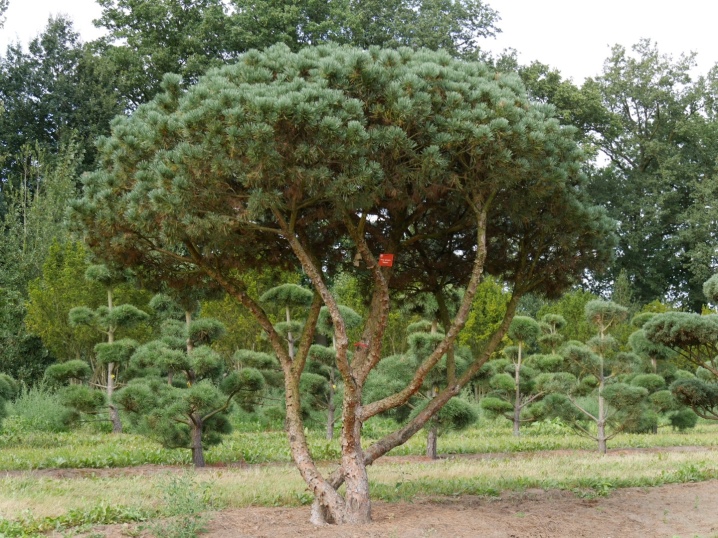

How many lives and how to determine age?
On average, with proper care, a pine tree can grow in one place from 100 to 300 years, however, among evergreen crops there are also centenarians that can grow on a site for about 1000 years. It is noted that the rapid pace of development of the ephedra determines its long lifespan.



Very often the question arises regarding the determination of the age of the pine. It will be quite difficult to solve such a problem, especially if there is no information regarding the planting of a forest beauty.
If the life span will directly depend on the variety and type of crop, then it will be possible to determine the age of the pine by the width of the trunk, however, this method has a serious error in the end result.
There is a more effective and accurate way to determine age, it concerns counting whorls or rows of branches on a tree. Thus, the presence of errors will be unlikely, since it is in conifers that the branches form regular and symmetrical rows. You can also find out how old the pine is by counting the number of growth rings on the trunk of the plant. The disadvantage of this method is the need for a preliminary cut of the pine.

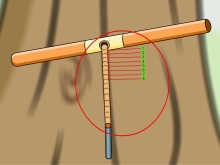

An alternative to this option would be to count the rings without destroying the ephedra. This is accomplished by taking a wood sample with an incremental drill.
Pros and cons of growing
Despite the fact that the evergreen crop is presented in a large species and varietal variety, there are certain general advantages and disadvantages of growing pine in the country, in a backyard, in public places. So, the advantages of having an evergreen culture in the open field include the following.
- The main advantage of the ephedra is its high decorative appeal. Based on the type and variety, the crown of a pine can take various forms, from openwork and ovoid to hooked, creeping, fluffy umbrella-shaped. In addition, the color variety of pines will speak in favor of decorative attractiveness, therefore, a well-planned landscape design will turn a plot with a pine tree into a source of aesthetic pleasure.
- The range of species will allow you to create in the open ground not only classic single compositions of several pines, but also intricate variations of group plantings with bizarre shapes.
- Conifers are notable for their undemanding nature of the soil on the site, therefore, thorough preparations before planting a seedling or pine seedling are not required.
- It is also worth noting the undemandingness of pine in terms of care, which allows you to grow a tree even with minimal labor on the part of the gardener.
- Pine trees are frost-resistant crops, so they are suitable for rooting in regions with a harsh climate. Crops withstand temperature fluctuations, frequent frosts and snowfalls, which will be especially relevant for Russian winters.
- Evergreen crops have the ability to purify the air thanks to special substances - phytoncides, which they release into the atmosphere. In addition, the aroma of resins and needles has a beneficial effect on the respiratory tract and the human nervous system.




However, with all the advantages, pines are not without disadvantages. The disadvantages of cultivating coniferous crops include such moments.
- Pine trees are very sensitive to the air quality in the area where they grow. Therefore, an excessively polluted atmosphere will have an extremely negative effect on the appearance of the tree, as well as its lifespan, even if the plant is considered young. When rooting near large highways, the needles begin to turn yellow and wither.
- Large crops take up more and more space as they grow, and also form a rather dense shade that prevents the growth of crops that are not shade-tolerant plants.



Types and varieties
Today, a huge number of varieties and types of pine are known, and also actively grown, among them the following are especially in demand.
Scots pine
In the wild, it is most often found in Europe and Asia. Real giants among the representatives of this species can be found on the shores of the Baltic coast.

The height of the trees varies between 20-40 meters with a trunk diameter of about 1-1.5 meters. The tree has an upright trunk, the bark is gray-brown, and has deep cracks.
The upper part of the trunk and branches are colored red-brown. Scots pine looks attractive even at a young age, when the shape of its crown resembles the outline of a cone. Subsequently, the branches take a horizontal position, and the crown becomes wider. Scots pine wood is a valuable species. The species is represented by the following varieties:
- Alba Picta;
- Albyns;
- Aurea;
- Bonna, etc.




The culture grows up to the 40-meter mark, however, most of them are plants of average height - 20-25 meters. The tree stands out for its thick branches and lush crown with many tops. The trunk of the tree will be straight with a gray bark. The needles of the plant are represented by long and soft needles, painted in a deep green color. The culture matures closer to 60 years, at this age egg-shaped cones begin to form on the tree.
Swamp pine
A large tree that can grow up to 45-50 meters, the diameter of the crop trunk also stands out for its size, sometimes reaching 2 meters.


A distinctive characteristic of pine is its yellow-green needles, the needles of which can grow up to 45 centimeters in length.
Long-coniferous pine is notable for its fire resistance, it is most common in the south of North America, in Texas.
Pine of Montezuma
The culture grows up to 30 meters, while the needles can be 30 centimeters long. The color of the needles is gray-green, the needles are collected in a bunch. It is also called white pine. Most often, this tree is found in Guatemala and America. However, such a culture is quite possible to grow on lawns and plots as an ornamental one. In addition to its visual appeal, white pine is valued due to the ability to collect fruits from it - edible nuts.


Dwarf pine
The plant belongs to the low varieties of the evergreen bush type conifer, the plant is notable for its spreading branches and a similar arrangement of needles.
Pine can have a tree-like, bowl-shaped or creeping crown, on average, the size of the tree is about 4-8 meters.
The color of the needles is gray-green, the cones ripen small, have an ovoid shape. Among the popular varieties of needles, it is worth noting Glauca, Chlorocarpa, Dwarf, etc.


Crimean pine
A tall evergreen plant with a pyramidal crown, which in old age takes on the appearance of an umbrella. The culture's needles reach a length of 12 centimeters, while the cones are brown in color and the size is not inferior to the length of the needles. This species is listed in the Red Book. A wild tree can be found in the Caucasus and Crimea. Also, a hedge is created from a valuable ephedra, pine is used for landscaping and arranging a protective forest belt.


Mountain pine
A tree-like shrub with a multi-stemmed crown. The needles are notable for their twisted shape, painted in a deep green color. In length reaches average values - 4-5 centimeters. The wood has a red-brown color and is of particular value for joinery production. Some parts of the young ephedra are in demand in cosmetology. In the wild, the plant can be found in Central Europe, in addition, the species is actively used in landscape design, seedlings are grown in nurseries and at home. Among the popular varieties of needles, it is worth highlighting "Gnome", "Winter Gold", "Pumilio" and others.


White pine
The culture is notable for its smooth and light bark, it can grow with a straight or winding trunk up to 20-25 meters.
In young conifers, the crown has a conical shape; in the process of growing up, it becomes round.


The needles grow in length from 3 to 7 centimeters. Pine bears fruit with edible seeds, which are actively eaten by animals in the forest.
Himalayan pine
A large culture that is used in landscaping around the world. On average, the tree grows up to 30-50 meters. In the wild, it can be found in Afghanistan and China. Among the most popular varieties will be the following crops:
- Densa Hill;
- Nana;
- Zebrina.
- italian.




An attractive tree, growing up to 20-30 meters, has a small crown with dark green needles. The needles grow up to 15 centimeters, the cones take a rounded shape, the seeds are actively used in cooking. The culture is grown outdoors and has also found its way into the art of bonsai. Today pine is cultivated all over the world.




Pine black
The plant can be found in the Mediterranean, as well as in Algeria or Morocco. The tree develops up to 20-55 meters.
In young cultures, the crown will have a pyramidal shape, changing to an umbrella-shaped one with age.
The length of the needles is average - from 9 to 14 centimeters, can have a varied surface - matte or glossy. The species is actively used in landscaping. Among the popular varieties it is worth noting "Pyramidalis", "Bambino", "Austria".



Weymouth Pine
Found in North America, in some provinces of Canada. The tree develops with an upright trunk, the diameter of which can reach 120 centimeters. Coniferous culture can grow in size up to 67 meters, the crown initially has the shape of a cone, over time it becomes round. In the shade of the color of the bark, there is a purple color, the length of the needles is 6-10 centimeters. Pine wood has found its application in construction. Popular varieties of the crop are Aurea, Blu Shag, Densa.



Angarsk
In the wild, the culture is most often found in Siberia, in addition, natural forest coniferous stands are found in the Krasnoyarsk Territory and in the Irkutsk Region.
The tree grows in size up to 50 meters, with a trunk girth of 200 centimeters.
The crown is pyramidal with a pointed crown; the color of the needles, which has an ash-silver tint, is considered remarkable.

Seat selection
In light of the fact that today a huge number of species and varieties of pines are grown, the selection of a place will be carried out based on the characteristics of each crop, in particular, this concerns the size of a young and adult tree. For giant pines, it is worthwhile to select in advance large areas where the coniferous beauty will grow independently or with plants that develop well in the shade.
The general requirement for a place for all pine trees is a sunny area. However, in the first few seasons after the rooting of the ephedra in the garden, the crop owner should be able to shade the young seedling. You can resort to the option due to which young crops are naturally shaded in the wild - due to the proximity to other taller plants.

How to plant?
The optimal age for seedlings that can be rooted in open ground will be from 3 to 5 years old, while most gardeners agree that it is most correct to acquire young crops for planting with a closed root system, since even a minimal finding of the rhizome in the open air will lead to the loss of vitality. The culture you like should be purchased exclusively in specialized nurseries.
Immediately before rooting, the pine must be kept in water for some time without removing the tree from the container or pot.

Spring is the right time for an evergreen culture to take root.Pines are usually planted in late April or the first weeks of May. Autumn planting of crops is also common, in which case planting work falls on the end of August - beginning of September.
To root a pine, you will need to dig a hole, the depth of which will be at least a meter. If the culture takes root in heavy soil, then a drainage layer of at least 20 centimeters should first be laid on the bottom. Broken brick or expanded clay will be a suitable material for this, the selected material must be combined with sand. To fill the well, you should also prepare a nutrient substrate in advance. The optimal soil mixture for planting pine will be a composition based on:
- clay;
- sand;
- turf land.
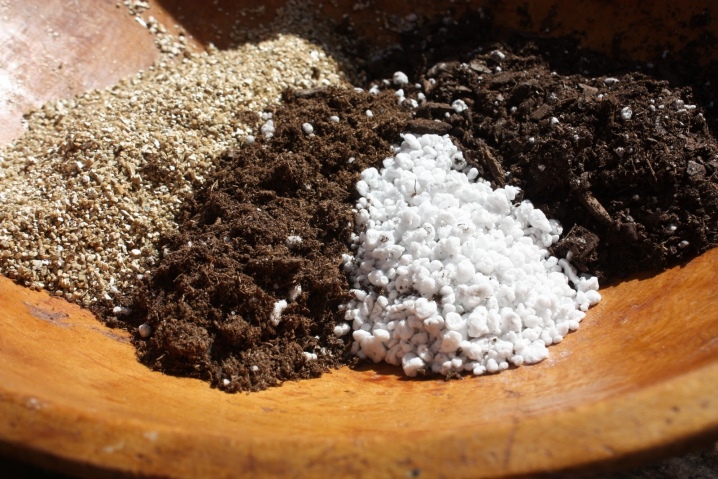

An additional component to the soil mixture for pine will be "Kemir-universal" or "Nitrofoska", which will require 100 or 50 grams. Slaked lime is added to the soil with high acidity to bring its performance back to normal. The pine planting algorithm is as follows.
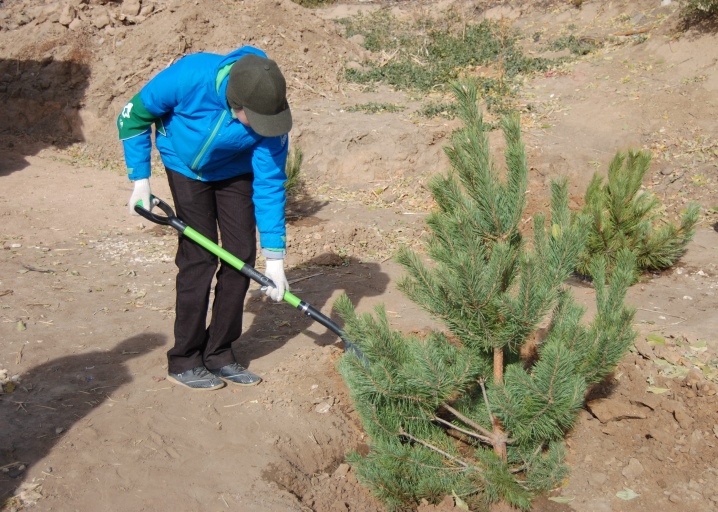
- Part of the prepared soil mixture must be poured onto the drainage layer from above. Place a seedling in the center of the hole without a container for temporary storage, but together with an earthen lump around the rhizome.
- Then fill the formed voids with the remaining earth layer by layer, compacting the soil in the process.
- When the plant is planted and all the land is in the hole, you will need to water the crop. To do this, at least 20 liters of water are poured into the near-trunk circle. After all the liquid has been absorbed into the ground, you need to check the location of the root collar of the ephedra above ground level.
If several crops are planted on the same site, the distance between the pines should be at least 4 meters. For dwarf species, the distance can be on the order of 150 centimeters.

How to care?
Growing pine trees in the open field will require a gardener to perform a number of mandatory activities.
Watering
The culture is drought-resistant, so the tree will be enough for the life of natural precipitation. But young pines at the age of 1-3 years need abundant autumn watering after the end of the leaf fall. Stagnation of water in the ground should be avoided. As a rule, one tree will require about 1-2 buckets of water.
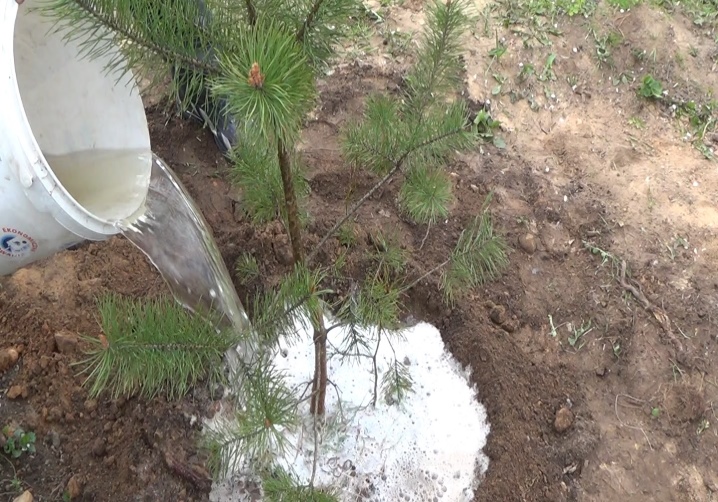

Top dressing
The first 2-3 years are quite important for an evergreen culture, therefore, during this period, it is recommended to additionally fertilize the needles by introducing universal fertilizing. Usually, such work is performed once a year, using complex mineral compositions introduced into the near-trunk circle.
The optimal dosage to feed the needles is 40 grams per 1 square meter of area.
In subsequent years, thanks to the coniferous litter, there will be no more need to feed the pine, since organic matter naturally accumulates in the soil, which will be enough for the normal development of the culture. That is why there will be no need to remove the needles in the trunk circle.

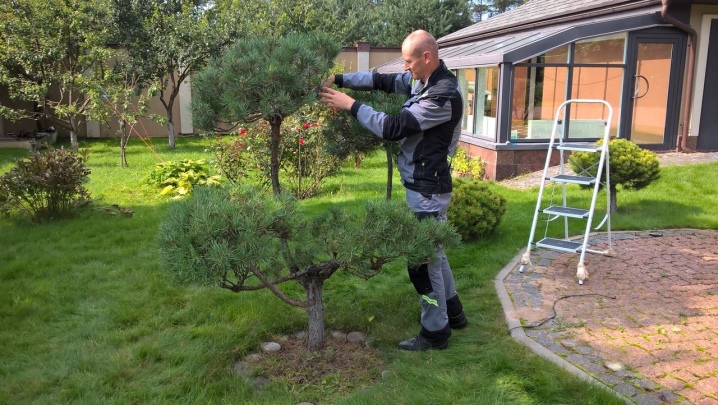
Pruning
Pines do not need pruning, so such manipulations with the crown are extremely rare. However, some gardeners, in order to make the crown lush, and its growth is not so rapid, resort to the option of breaking off young shoots, removing a third of their size.

Preparing for winter
Frost resistance is a distinctive feature of all types of pine trees. With the onset of cold weather, all the main processes of life in a culture slow down, but do not stop completely, in light of which the plants must be properly prepared for winter. To do this, gardeners will need to perform water-charging irrigation, usually this work is performed in mid-November.
Before the introduction of moisture around the trunk circle, a dump is made from the soil in order to exclude spreading of liquid throughout the entire area.
A little earlier, in September, the gardener will need to introduce phosphorus-potassium fertilizers for young crops, which will stimulate the lignification of green shoots, they can die from frost without bark. Also young trees will require laying a layer of mulch in the trunk circle... For these purposes, you can use sawdust.


Reproduction
Get a new coniferous culture today will succeed in several ways:
- vaccination;
- cuttings;
- by the seed method.
The first two options are considered the most productive, planting seeds, as a rule, will take more time for a new plant to develop.
Reproduction by grafting
This method is suitable for gardeners with extensive experience in growing crops. The main advantage of grafting is considered to preserve all the maternal characteristics inherent in the species or variety in the new pine. It is recommended to use a plant that is at least 4 years old as a suitable rootstock for propagation; pyramidal needles on a trunk are suitable. The scion is cut with growth, the age of which will be at least a year.
Before grafting, it is necessary to remove all the needles from the selected planting material, leaving only the buds on the cuttings, which will be concentrated on the upper part of the branch.
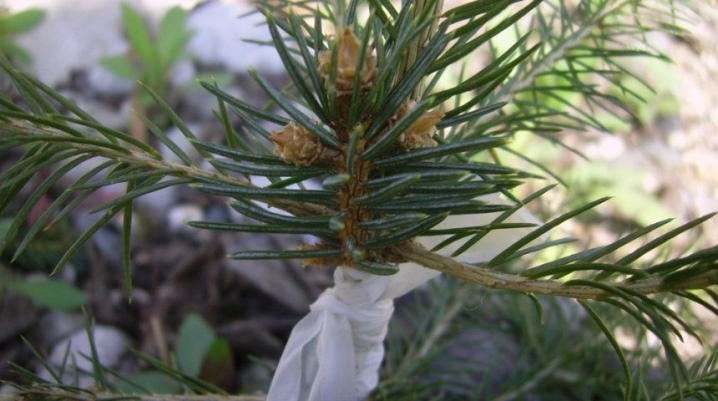

Usually, the grafting is done in early spring, at a time when the sap flow of crops is just beginning. You can also use this breeding method in the middle of summer. Depending on the season, a suitable shoot is chosen for grafting - in the spring the pine is grafted onto the ripe part of the crop last season, and in the summer - onto the shoots of the current year.
Propagation by cuttings
It is worth planting pine branches in the autumn. The essence of the method is to separate the lignified planting material from the culture, the size of which must be at least 8 centimeters. The maximum length of the cuttings will be 12 centimeters. The cuttings should be separated together with a part of the wood from the branch on which the cutting had previously grown.
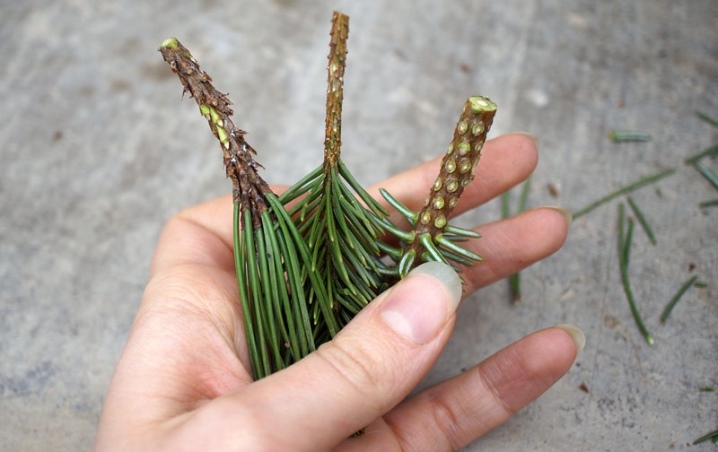

It is recommended to carry out work on the collection of material for breeding in cloudy weather. It is most correct to collect cuttings from the lateral apical branches from the northern part of the crown. The separation of the material is carried out with a sharp disinfected instrument, the movements must be fast, the material must be separated in the direction of the branch.
Before rooting the collected cuttings, they must be prepared for planting. For these purposes, they are cleaned from needles and burrs. After such work, the collected pine parts are immersed in water with the addition of "Fundazol" or potassium manganese. Cuttings should stand in liquid for at least 4 hours.

So that the twig does not dry out and begins to form the root system faster, it is best to immerse the stalk with one side into a growth stimulator just before rooting. For these purposes, you can use any store composition - "Epin", "Kornevin" or "Heteroauxin".
The algorithm for rooting cuttings will be as follows.
- The first priority will be to prepare a suitable soil mixture for planting the material. The optimal soil for young crops will be earth, combined with sand in equal proportions.
- Planting cuttings is carried out on a slope. After that, the container with cuttings must be covered with a glass jar or transparent film. This is due to the pine's attitude to light, as well as the need to create greenhouse conditions for young crops, which will become an impetus for their further development.
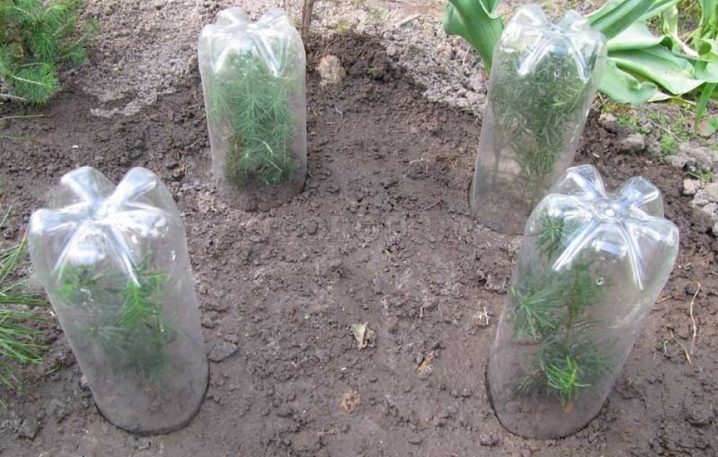

Subsequent care of the planted material is reduced to regular ventilation of the container, removal of condensate from the walls.
For the winter, containers with seedlings are usually transferred from the dwelling to the basement; in the spring, the planted material is gradually accustomed to the fresh air. For this, containers with cuttings are taken out into the street. If all the conditions described above are fulfilled, the cuttings will root in 1.5-3.5 months.
Together with the growth and development of the underground part, young shoots will form on them. A year later, in April-May, young crops need to be watered with the addition of any growth stimulant to the liquid. For the next season, the crops will already be ready for rooting in the open field.

Seed propagation
For this method to bring results, it is necessary to use only fresh and ripe seeds, crops in the open field may not bear fruit every time, so the collection of cones should be planned and carried out in advance. Usually, the preparation of planting material is carried out in October or November. As practice shows, it is during this period that the seeds will already be completely ready for sowing. Cones are collected exclusively from a tree; on earth, the material for the development of new crops will be unsuitable.

The collected cones are dried indoors, which greatly facilitates the extraction of seeds from them. After that, the collected material is placed in transparent glass jars with a lid, sending them cool for 2-3 months. Over time, seeds suitable for sowing are selected from it, for this they are immersed in water, all floating specimens must be disposed of. Further, the remaining seeds are sent for stratification, keeping for half an hour in manganese potassium, after which they are soaked in a clean liquid for a day.
The next step will be mixing the seeds with sand, then all this is placed in a nylon stocking and sent to the refrigerator for 1 month.

Sowing is carried out in December, using containers with light and nutritious soil mixed with river sand, a layer of sawdust is placed on top, evenly distributing the seeds, slightly deepening into the ground. After that, the crops must be moistened, covered with a film. The first shoots should appear in the spring. Planting material care consists in airing and moisturizing.
Diseases and pests
Pine often suffers from fungal ailments that arise from mistakes in agricultural technology. Among the diseases dangerous to needles, it is worth highlighting the following.
- Rust. Signs of the disease are neoplasms on the lower part of the crown, while sometimes the lower branches die off, needles fall out. The fight against the disease consists in treating the culture with copper-containing preparations; for prophylaxis, gooseberries or currants can be planted near a pine tree.
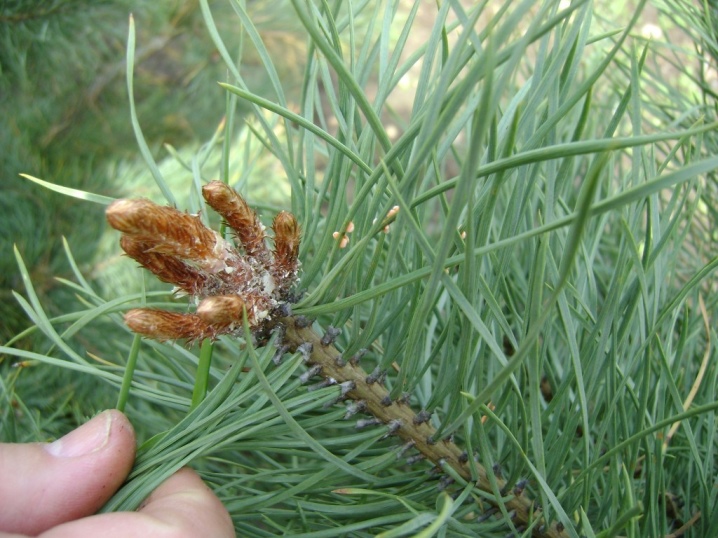

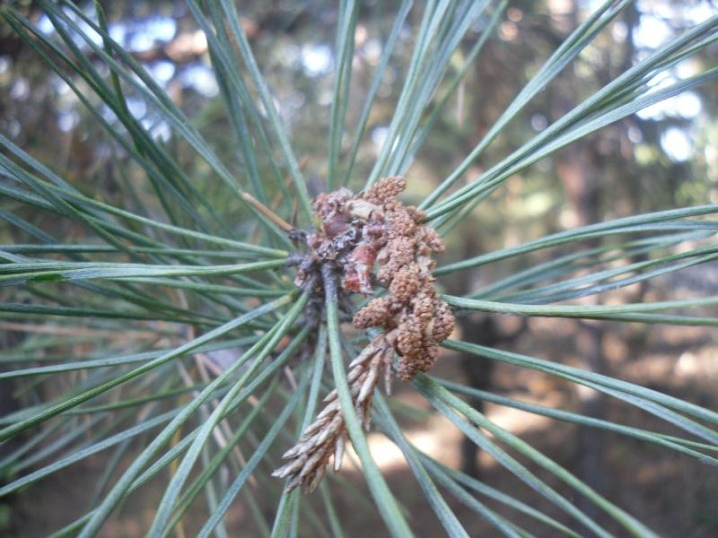
- Pine fiddler. The disease is manifested by the appearance of swelling on the branches, painted in golden shades. The further development of the disease leads to the curvature of the shoots, the formation of wounds and resins on the surface. The fight against the disease is carried out with store-bought fungicides; complex fertilizers are used to maintain the culture's immunity. The affected parts of the pine must be removed.

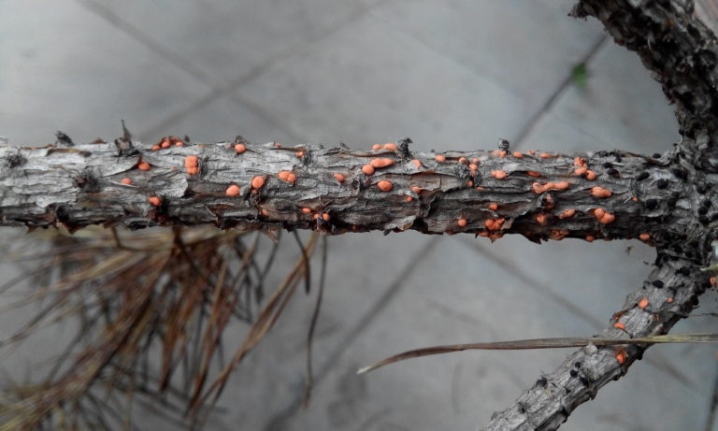
- Resin cancer. The most dangerous disease for pine, which is manifested by cracks on the trunk of the culture, the formation of bubbles. Treatment is carried out by stripping the affected areas, as well as polluting the wounds with a solution of copper sulfate. Also, good results are obtained using garden varnish mixed with fungicides. Affected shoots must be removed from the crop and burned to prevent the spread of the disease.

- Cortex necrosis. A symptom of the disease is a change in the color of the bark to yellow, followed by death, including branches. Most often, this ailment affects weakened pines after severe frosts. Treatment is carried out by treatment with fungicides, removal of damaged areas and neoplasms.

Among the insect pests that can cause serious harm to the pine tree, it is worth highlighting:
- aphids;
- conifers;
- spider mites;
- pine sawflies;
- silkworms;
- pine moth;
- miner mole;
- pine cone fires and smolens;
- bark beetles;
- barbel.



To reduce the risk of pest attacks on pine, it is recommended to observe all the nuances related to agricultural technology, especially for young coniferous crops.
To kill insects, the culture is sprayed with acaricides and insecticides.
Possible problems
The decorative attractiveness of a coniferous culture largely depends on the receipt by it of all the necessary trace elements from the soil. Therefore, some gardeners may face the following problems:
- yellowing of needles can be triggered by a lack of iron;
- a reddish-purple shade of the needles will indicate a phosphorus deficiency;
- the lack of nitrogen will translate into slower crop growth rates.
Timely introduction of top dressing in any form will help eliminate problems of this kind.
Choosing the wrong place for rooting pine can also negatively affect the appearance and health of the crop.
This is especially true of the inadequate state of the air if the tree grows near large highways, industrial facilities. In this case, the pine will need a transplant.

Advice
To have a beautiful ephedra on your site, it is worth adhering to the following recommendations:
- seedlings of Chinese white pine, "Spielberg" and other varieties must be purchased exclusively in specialized nurseries;
- planting material should be sold only with a closed root system, otherwise the pine will not take root on the site;
- you should not choose young trees in a nursery that are too large, since the risk that such a culture will not be able to adapt to new conditions is quite high.

What to plant under a pine tree?
An evergreen crop will look good and thrive with beautiful flowers, grasses, shrubs and grains. Among them it is worth noting:
- reed grass;
- maned barley;
- rye;
- flowering crops from the Liliev family;
- lilies of the valley;
- bells;
- phlox;
- lingonberries;
- strawberries;
- juniper;
- rhododendron;
- Eric.


Examples in landscape design
Due to the high decorative appeal of pine, even miniature varieties planted in pots will harmoniously complement the evergreen composition being created in the open field.
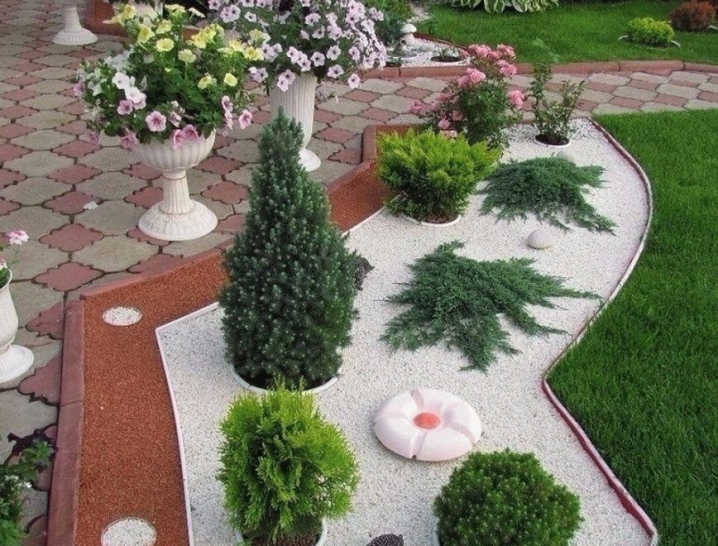

Pine trees are perfectly combined not only with evergreen crops, but also with flowers, which together create an attractive and juicy contrast of shades on the backyard.
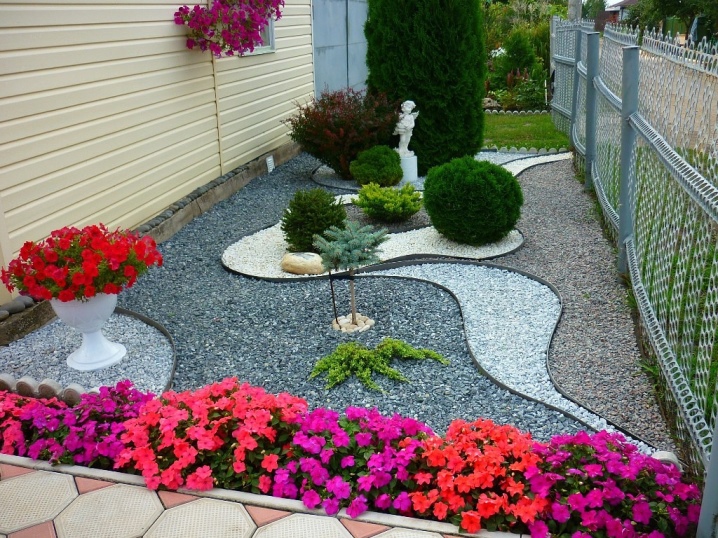

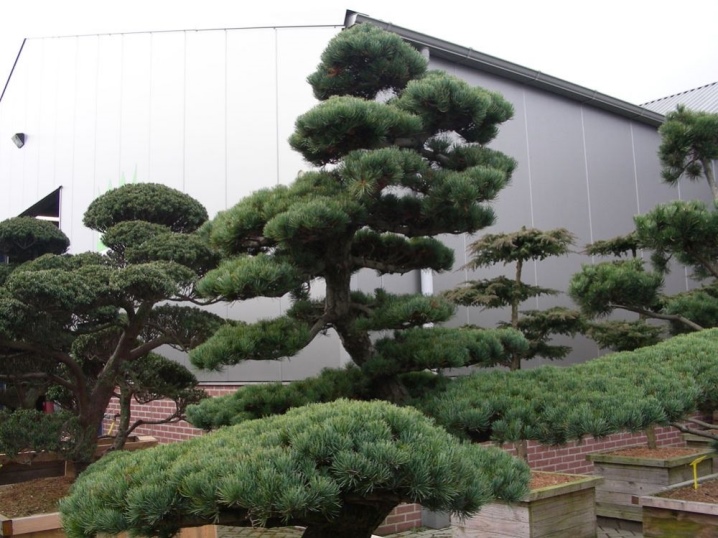
Large pines with bent trunks in a bizarre shape will become a real pride and adornment of any landscape design when planted together or alone.

For planting and caring for a pine tree, see below.



































































The comment was sent successfully.