Climbing roses: varieties, tips for choosing and care

Climbing roses are considered an unusual decoration of landscape design. The plant perfectly complements the decorative design of the site, harmoniously fitting into any of its styles. Caring for such roses is simple, so even a novice gardener can grow them.



Peculiarities
Climbing roses are a beautiful garden plant that looks like a tall bush, its stems curl and can reach several meters in length. Typically, this type of rose has a height of 5 to 15 meters. Due to this quality, flowers are widely used in landscape design; they are often used to hide outbuildings, which, with their architectural forms, spoil the general appearance of the site.
Climbing roses cannot be matched by any other climbing plant as they are characterized by their incredible beauty, delicate scent and long flowering time. The only thing is that the long length of the plant requires careful maintenance, but the excellent decorative qualities are worth such attention.



All climbing roses are subdivided into large-flowered and small-flowered. They differ from each other not only in appearance, but also in flowering periods. Small-flowered plants have too long and flexible shoots, thanks to which you can decorate huge areas (build arches, fences or pergolas). The main feature of such roses is that they need support and proper pruning, since flowers appear on both new and last year's shoots. The stems of small-flowered roses are creeping and arched, they reach a length of more than 5 m, are characterized by a bright green tint and a surface covered with thorns. The leaves, placed on the shoots, are small in size and have a slight glossy sheen.
The diameter of the inflorescences usually does not exceed 2.5 cm, flowers, depending on growing conditions and varietal characteristics, can be simple, semi-double and double... Small-flowered roses have a faint sweetish aroma, their flowers form into inflorescences and cover the entire length of the shoots. One of the advantages of this type of roses is that they have a long and profuse flowering that exceeds 4 weeks. Flowering begins, as a rule, at the end of June, after which it can be repeated. Most varieties of small-flowered roses are frost-resistant and perfectly tolerate wintering even under light shelter.



As for large-flowered roses, in comparison with small-flowered roses, they have stronger and thicker stems.that do not exceed a height of 3 meters. In addition, their flowers are large (up to 4 cm in diameter) and their flowering period is continuous. These plants bloom only on the stems of the current season, so they are easy to care for and they are pruned according to the general rules, as for other roses. Climbing large-flowered species were bred by crossing tea, remontant and hybrid varieties. Therefore, their flowers outwardly resemble tea roses.


Climbing large-flowered plants, which are called branding, are also very popular among gardeners. They are mutating rose bushes with huge flowers (11 cm in diameter) and vigorous growth.The inflorescence of such species can be either single or consist of several small flowers. Claims are characterized by repeated flowering and fruiting, which is usually observed in late autumn.
It is recommended to grow these roses in the southern regions of the country, where the climatic conditions in winter are mild and warm.


The best varieties and their characteristics
Today, there are many varieties of climbing roses, which differ in size, growing conditions and colors. Despite the fact that all types of these roses perform a decorative function and are a chic decoration of the site, only a few are the most popular of them.
- Bobby James. It is a vigorous plant, reaching a height of 8 m and having a bushes width of 3 m. Since the bushes are covered with many cream-white flowers, their bright green leaves remain invisible. The flowers of roses are characterized by a small size, their diameter is 5 cm. During flowering, the decorative culture pleases with a light nutmeg aroma.
Before choosing this variety for planting, you need to pick up a large area on the site, since flowers love a lot of space and light. The climbing plant is resistant to frost, not whimsical to care for, but requires reliable support.


- Ramblyn Rector. This is a small-flowered rose, with the help of which you can get an original green arch or hedge in landscape design, strewn with small creamy flowers. The height of the bushes, as a rule, does not exceed 5 meters, the clusters of inflorescences are formed from 40 miniature semi-double flowers. They fade in the sun and acquire a snow-white color. The culture is easy to care for and adapted to any climatic conditions.


- "Super Excels". This variety represents the most beautiful re-blooming roses, their distinctive feature is the raspberry color and small two-meter bushes without thorns. The flowers are collected in racemose inflorescences and delight with their gorgeous appearance until the end of summer, while if the bushes are planted in an open area, the bright crimson shade of the inflorescences can burn out. The culture is resistant to powdery mildew and overwinters well.


- "Elf". A medium-sized climbing rose of this variety has received many positive reviews due to its diminutiveness and delicate colors. A vigorous, erect shrub, as a rule, is 1.5 m wide and 2.5 m high. The diameter of the flowers may vary, but often it does not exceed 14 cm. The flowers are distinguished by a delicate white color with a slight greenish tinge and smell like fruit. The ornamental culture blooms until the first frost and is not susceptible to disease.


- Santana. If the original design of the site is planned, then the climbing rose "Santana" will be an ideal choice for this. Its four-meter stems are decorated with bright green carved leaves and large velvety flowers 10 cm in diameter. The rose is blue, red and yellow. The plant blooms several times per season, is frost-resistant and rarely gets sick.


- "Polka". The height of these shrubs does not exceed 2 meters. The rose is characterized by dark green glossy leaves and beautiful apricot flowers. Since the plant can bloom up to three times per season, it can be used to decorate gazebos and garden arches.
Despite the fact that the variety is resistant to disease and frost, the bushes need to be well covered for the winter.


- "Indigoletta". It is a three-meter, vigorous bush that grows in diameter up to 1.5 m. The foliage of the rose is dense, painted in a dark green shade. Fragrant flowers gather in inflorescences and delight with their lilac colors several times per season. This variety is successfully grown both in the southern and central regions of the country, as it is resistant to frost and fungal diseases.


- Golden Gate. It is characterized by many shoots and a height of 3.5 m. The inflorescences are formed from large yellowish flowers, the diameter of which is 10 cm.The rose blooms several times and smells strongly of fruit. An ornamental plant quickly takes root, is unpretentious in care and is not afraid of cold weather.


- Camelot. It is one of the varieties of ramblers, which differ in one-time flowering. The rose has an unusual pink color on the petals. The flowers have a citrus aroma, up to 10 of them are placed on the stem. Under favorable growing conditions, the bushes grow up to 2 meters long.
The main advantage of the variety is that it does not need constant pruning, complex shelters for the winter and is resistant to diseases.


- Spenish Flag. It is an amazingly stylish and beautiful rose that, when woven, creates a composition reminiscent of the Spanish flag. This species was bred by British breeders from two varieties - "Golden Showers" and "Flammentanz". The main difference of the plant is the unusual combination of shades, consisting of bright yellow and red flowers. Both varieties get along well with each other and, as they grow, intertwine, forming a bright rich bouquet.


- Westerland. It is a winter-hardy and fast-growing variety, the flowers of which can have pink, golden, orange and apricot hues. The bushes grow small, up to 1.7 m, but they grow too much, therefore they require a lot of space. In addition, the stems of these roses are too prickly. The culture begins to bloom early and its flowering can be repeated until late autumn.


- Rosanna. This variety will serve as a decoration for any suburban area. The flowers of the plant resemble in appearance a hybrid tea rose, at the beginning of flowering they acquire a delicate pink color, which later becomes coral. The bushes grow up to 3 meters high and are resistant to drought and frost.


How to choose?
In order to originally decorate a suburban area with weaving of roses, it is necessary to correctly select their varieties, taking into account the peculiarities of growth in a certain climatic zone. For example, harsh Siberian conditions can adversely affect the development and growth of climbing roses. But this does not mean that gardeners in these areas should completely abandon the cultivation of garden "beauties". For Siberia, it is recommended to use special winter-hardy varieties that are able to survive in frosts and delight with their flowering in summer. It is best to purchase planting material grown directly in Siberian nurseries for breeding varieties. Such plants are grafted and highly resistant to low temperatures. These include varieties:
- Rosarium Uetersen;
- Westerland;
- New Dawn;
- William Shakespeare;
- Golden Celebration.



The aforementioned varieties can be considered real "Spartans"; with a reliable winter shelter, they successfully survive even at a temperature of -40. The only thing is that in Siberia, land plots are deprived of sunlight, so rose bushes should be placed on the south side.
For the middle zone of Russia, it is necessary to select climbing roses that are resistant to winds, instability of climatic conditions and are undemanding to the type of soil. Baltimore Belle, Bobby James, Golden Wings, Dortmund and Mermaid are good choices. Such roses bloom several times a season, and in the southern zones of the country they can delight with their beauty even in winter. Plants are frost-resistant (withstand temperatures up to -35 degrees), easy to care for and only require insulation for the winter. In other climatic zones of Russia, you can plant all varieties, choosing roses for your personal taste.



Landing rules
All types of roses are characterized by simple cultivation, but despite this, they have a "capricious" character. Climbing varieties are no exception. This species is picky about planting and care, so before growing these flowers, you should take into account the recommendations of experienced gardeners and adhere to certain rules. The location of the rose garden plays a huge role. The site should be adequately illuminated by the sun and protected from gusts of wind.You can not plant bushes in open areas, since at lunchtime they will not be shaded and may die from burns.
It is undesirable to decorate with roses and the corners of the building, as they will be exposed to the harmful effects of drafts. The most optimal place for planting crops is considered to be garden plots located on the southern side of the buildings.
The choice of soil is also considered important in planting roses. In addition, it is necessary to take into account the characteristics of each variety, since some roses are planted in the spring, and others in the fall.



Before planting roses, regardless of the type of soil (with the exception of sandy), the pit is drained, for this it is covered with expanded clay or sand. When planting seedlings in the spring, in order to speed up their adaptation, the root system is trimmed by 30 cm and the shoulder straps are shortened by 20 cm. Such roses should be placed in areas protected from the wind, creating greenhouse conditions for them - the ground is covered with a film from above.
In addition, during spring planting, you need to additionally pour a small layer of mulch into the holes, it will retain moisture well and save young plantations from night frosts.



Selection and storage of seedlings
Planting climbing roses should begin with the acquisition of high-quality seedlings, since the growing process and the health of the future ornamental plant will depend on them. When buying planting material, experts advise paying attention to any little things. First of all, this applies to the root system. If it is open, then you should give preference to samples with healthy and well-developed roots that do not show signs of damage. In the event that a seedling with a closed rhizome is bought, the shoots are carefully examined. It is advisable to choose plants up to 70 cm in height, which have two strong stiff stems.
In addition, you need to purchase planting samples that are at rest. (without buds and green shoots). They will take root better and get stronger for the winter. Seedlings with pale or light colored shoots are not suitable for planting, as they are grown in poor conditions with insufficient lighting. Purchased seedlings with open roots should be placed in a container with water before planting, this will allow them to be well saturated with moisture. Roses with a closed root system are placed in a cool place, having previously treated the roots with a growth stimulant.


Disembarkation time and place
Climbing roses, like any other varieties, should be planted according to general rules. Autumn is considered the best time for planting. Plants planted on the site in the fall are distinguished by good health, good growth and begin to bloom earlier. Depending on the climatic conditions of the area where the site is located, planting can be carried out from late September to early October. Thus, the rose, before the onset of the first frost, manages to root perfectly and in the spring continues to grow actively without adaptation.
If, for some reason, planting work is planned for the spring, then you should be prepared for the fact that such seedlings will lag slightly in growth and flowering time, since they will need more time to root.
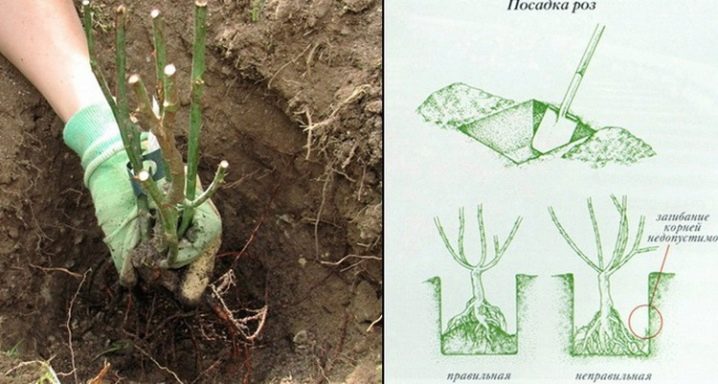
The choice of a place for planting roses also plays a huge role. To do this, it is worth considering the characteristics of the variety, the length of the shoulder straps and the spreading of the bush, since the plant is perennial and will grow on the site for more than a dozen years. In order for the culture to quickly adapt, it is not recommended to choose areas where the soil has high alkalinity and acidity. It is also worth avoiding areas with difficult terrain and close location of groundwater. In addition, the flowers should receive good lighting, for this they need to be planted in places where the sun's rays will fall most of the day, excluding the north side.
The rose garden should also be located at a distance of 60 cm from the walls of residential buildings and fences, while a step of 100 cm or more is made between the bushes. The selected area is covered in advance and the condition of the soil is assessed. If it is too clayey and heavy, then peat with sand is poured into it, and compost or manure is additionally added. For areas with a high acidity level, it is imperative to make an adjustment by adding lime or ash to the ground. Sawdust is suitable for alkaline soil.



How to reproduce?
Today, there are many ways to propagate a branch rose. These include reproduction by seeds, grafting, layering and cuttings. If you plan to grow a plant from seeds, then you need to purchase seed in a specialized store, since samples collected at home cannot retain varietal characteristics and a flower that is completely unlike a rose can grow from them. Before planting the purchased seeds, they are soaked in a mixture of hydrogen peroxide for 30 minutes. This will improve germination and protect the crop from mold growth. After that, the seeds are spread on damp cotton pads and placed in a cool room until sprouts appear, then they are planted in small peat pots, sprinkled with mulch.
The planted seeds should receive the required amount of light and moisture. Providing normal conditions for growth, the first buds will appear on the plants in two months, and after 6 weeks they will begin to bloom. Additionally, you can feed roses with mineral fertilizers. In spring, the grown seedlings are moved into open soil and properly cared for.



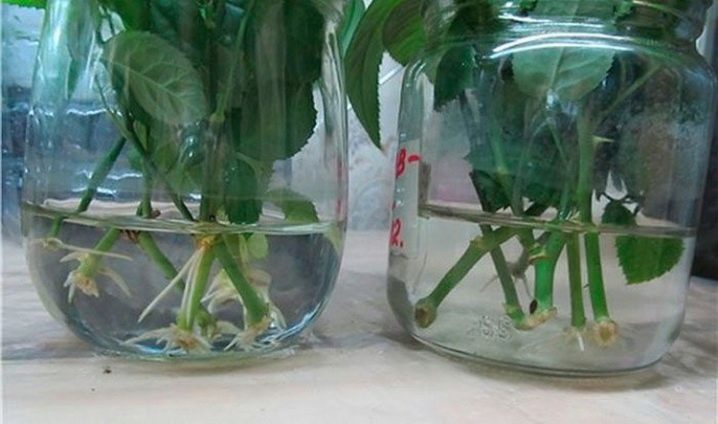
It is much easier to propagate roses by cuttings, as this method gives excellent results. As cuttings, you can use both already faded stems and flowering ones. They are cut at the end of June. The lower cut should be done under the kidney, observing an angle of inclination of 45 degrees, while the upper cut should be straight and placed at a distance above the kidney. At least two internodes are left on the prepared cuttings.
In addition, when grafting, you need to cut off all the lower leaves and shorten the stem from above by 1/2 part. The cuttings must be planted in a soil mixture consisting of sand and earth, to a depth of no more than 1 cm. After that, the cuttings are covered with a vessel with an open neck on top and make sure that they receive moisture and lighting. Watering the cuttings is necessary without cleaning the protective shelter.
To speed up the rooting process, the lower part of the cuttings can be treated with a growth stimulant.

Some gardeners also prefer to propagate climbing roses by layering. To do this, in the spring, a small incision is made above the shoot buds, it is placed in a previously made groove no more than 15 cm deep. A small layer of humus is poured onto its bottom in advance, the shoot put into it is covered with earth from above. The shoot is fixed in several places and it is checked that its upper part remains on the surface. The cuttings need to be watered regularly, and with the arrival of the next spring, they are cut off from the mother bush and planted in open soil in a permanent place.
Budding (grafting) is considered an equally popular method for propagating roses. It is usually held at the end of July. Before this procedure, a rosehip bush is selected, it is well watered with water. Then the bark of the wood is pushed on the root collar and a neat "T" cut is made. After that, a rose stalk is taken, it is placed in the prepared incision and tightly fixed with a special film. With the arrival of spring, it is removed.
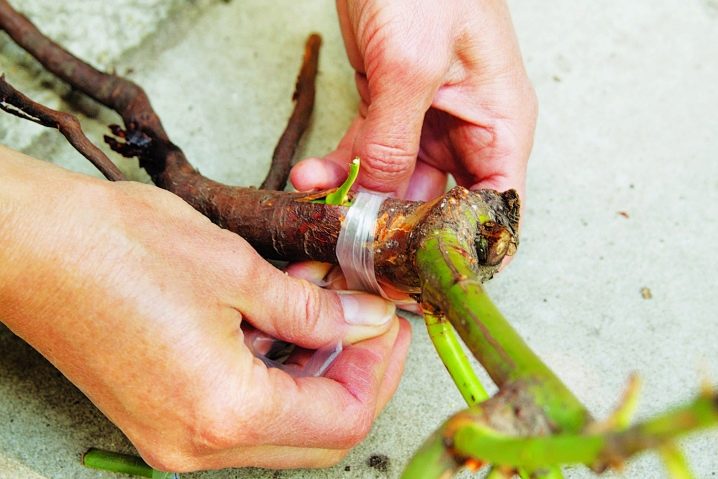

How to care?
Growing climbing roses is considered a simple process, but it requires proper plant care, which includes timely watering, pruning, treatment from pests, diseases and fertilizing. Care after flowering is also considered important, when the culture needs to be insulated for the winter. In the event that the rose bushes are large and tall, they must also be tied to a support.



Sometimes, mature shrubs may need a transplant. This is usually done if the site is not suitable for plant growth. The transplant is performed in late autumn or spring before the buds appear. The bush is removed from the support structure, the stems that are more than two years old are cut off, and a circular digging is made with a shovel. Since the roots of the rose are located quite deep in the soil, it is important not to harm the tips when digging them.
This process is complex and only experienced gardeners can handle it. To avoid replanting bushes, you should find a suitable site in advance for growing an ornamental plant.

Top dressing
The most important thing in caring for roses is their systematic feeding, which is recommended in the fall. In the spring and summer, it is not necessary to add minerals, since they are in the soil in sufficient quantities after planting the seedlings. With the onset of autumn, roses must be fed with potassium preparations, as they contribute to a good preparation of the roots for winter. They can be fertilized both with ready-made preparations and with an infusion of wood ash.
For the next season, organic and mineral substances should be introduced into the ground, which alternate. In the third year of growth, the bushes need to be fed only with organic components, which are perfect for wood ash or manure, with special attention should be paid to the growth period when roses require five feeding times. When in bloom, roses cannot be fertilized.


Watering
Despite the fact that branchy roses tolerate dry summers well, they still need watering. Water procedures are usually carried out once a week or ten days at the rate of 20 liters of water per bush. It is worth remembering the rule that it is better to water a little, but more often. To keep moisture well in the soil, you need to build a small earthen rampart around the holes. After each watering, on the third day, the soil requires loosening of the surface to a depth of 6 cm, which improves the penetration of air to the roots.
If it is not possible to carry out frequent watering and loosening, then you can cover the surface of the hole with mulch.


Disease and pest control
Most species of climbing roses are resistant to fungal diseases and pests, but sometimes spider mites and aphids can settle on the bushes. With a small number of pests, it is recommended to use folk remedies and remove insects by hand. If pests have massively occupied the plant, then it will not work to collect them manually. In this case, the bushes are treated with soapy water or chemicals. It is advisable to do this on a sunny, windless day.
In addition, in a dry summer, thrips, cicadas, leaf rollers, and fire sawflies can also appear on the leaves of roses. Such insects also settle on the bushes and if the rules in caring for the rose are not followed.
To protect an ornamental crop from pests, it is necessary to carry out timely treatment with chemicals and plant marigolds near the bushes, which are able to scare off most types of insects. In spring and late autumn, seedlings should be sprayed with Bordeaux liquid.


As for diseases, climbing roses are most often exposed to powdery mildew, black spot, gray rot, coniothyrium and bacterial cancer. Each of these diseases manifests itself in different ways.
- Coniotirium. Lumpy growths appear on the surface of the stems. After some time, they become dark, hard and lead to drying out of the bushes, after which they die. Such a disease is incurable, therefore, when buying planting samples, they should be carefully examined. In addition, before planting seedlings, it is recommended to disinfect the roots.To do this, they are immersed in a solution of three percent copper sulfate for several minutes. If, nevertheless, the bush is sick, then the affected areas must be immediately cut off by treating the sections with a solution of copper sulfate (3%).
- Bacterial cancer. This disease is fungal and leads to bark burns. As a rule, the first signs of the disease can be seen in the spring, after cleaning the protective shelter. Red-brown pimples appear on the surface of the stems, later they turn black and, in the form of rings, affect all parts of the trunk. If this is detected, you must immediately cut off the diseased stems, while capturing healthy areas, the cut shoulder straps must be burned. For the prevention of bacterial cancer, it is necessary to timely apply nitrogen and potash fertilizers in the fall, as well as ventilate the bushes, raising the shelter.


- Powdery mildew. Sometimes, in some areas of roses, a white bloom may appear, which later acquires a brownish tint. This is powdery mildew, which usually falls on crops with a sharp change in temperature, high humidity and excessive use of nitrogen fertilizers. The affected parts of the bushes should be cut and destroyed, after which the plants are sprayed with iron or copper sulfate.
- Black spot. If the roses are not properly fed, red-brownish spots with a bright yellow rim can form on the bushes. If they are not noticed, then they merge into a large circle and lead to the death of foliage. In order to prevent this, it is necessary to introduce potash and phosphorus substances under the root in the fall, as well as carry out a three-stage cultivation of the land and bush with Bordeaux mixture or iron vitriol. It is recommended to take a week break between treatments.
- Gray rot. This disease is considered dangerous, as it can affect all parts of the plant, from shoots to leaves and buds. After that, the rose loses its beauty, does not bloom and turns into nondescript plants. When most of the bush is affected, it must be dug up and burned. With a slight spread of the disease, the plant can be treated with Bordeaux liquid diluted in water (50 g of the drug per 5 l of water). For a complete cure of a rose, as a rule, at least four treatments are required, between which there is a break of 7 days.



Many gardeners can face the problem of a rose not blooming despite taking proper care of it. The reason for this is not a disease of the plant, but the planting of a low-quality seedling. The rose can also stop flowering when planted in an unsuitable place for its growth, where the soil is too heavy and there is little lighting. In addition, the lack of color is observed when stems are damaged after wintering.
Pruning
Since climbing roses are a large and branched plant, pruning is required for the beautiful formation of their crown, which also helps to improve the decorative qualities of the culture and increase flowering. If pruning is done correctly, then the rose will delight with its gorgeous appearance throughout the season. When forming a bush, special attention should be paid to vegetative stems, since flowers usually appear on last year's shoulder straps. Pruning can be done both in the spring and in the fall. To do this, at the beginning of the season, all dead branches are removed, as well as frostbitten parts, and in the fall the tips are cut off to the level of a strong bud.
The frequency of pruning branching roses depends on the characteristics of the variety and how many times the culture blooms per season. In the event that a plant blooms only once, then its flowers are formed on last year's shoots. Faded (basal) stems completely replace the restored shoots and they can be grown on a bush up to 10 pieces. Since such stems will give color the next year, they must be removed in the fall by cutting them at the root.
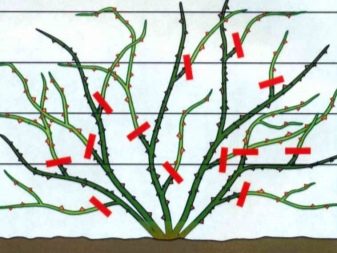

Roses that delight with flowering several times a year are pruned differently. During three years of growth, 2 to 5 branches of different sizes appear on the main stems. If they are not cut off, then in the fifth year of the rose's life, these branches will grow and the color will become scarce. To prevent this, the main shoots are removed in the spring (in the fourth year), pruning to the very base. The bushes should have no more than three annual regenerative stems and 7 flowering stems, which are the main ones.
It is also important to remember that in plants that bloom several times per season, flowers can appear on successfully overwintered shoulder straps, so in early March they need to be pruned, leaving the upper part with productive buds. Frequent pruning is mainly required by young bushes that were planted this year or grafted.
Before completing the process of forming the root system, the plant should be cleaned of rose hips. After two years, they will disappear on their own and roses will already appear on the bush.


How to prepare for winter?
Climbing roses tolerate wintering well, but to protect them from severe frosts, insulation should be done in the fall. It is recommended to cover the bushes when the temperature drops to -5 degrees. If the rose is insulated earlier, then it can rot under cover without air penetration. Preparation for wintering is carried out in calm and dry weather. To do this, the branches are cleaned of leaves, the damaged stems are removed and the strapping is made with a rope. Then they are carefully laid on a soft bedding made of spruce branches or leaves. Roses should not be placed on bare ground.
The bushes prepared in this way are gently pressed and fixed to the surface, sprinkled with dry grass or spruce branches. The base of the bush is additionally sprinkled with sand or soft soil, after which it is covered with lutrisil, roofing felt or durable material that does not get wet. It is important that a small layer of air remains between the shelter and the plant.
If the winter is not cold or with frequent thaws, it is recommended to raise the shelter for a while, providing the roses with fresh air. In this case, spruce branches and dry leaves should remain. In the spring, the protective cover is removed. If this is done at the wrong time, then the bushes can get sick.


Use in landscape design
When decorating summer cottages with climbing roses, most often they create compositions such as tapeworm, hedge, shrub group, row planting and vertical gardening. Such roses in the garden, planted in the form of an arch, also look beautiful. They not only delight all summer with their gorgeous appearance, but also with a delicate aroma. Each of the above compositions has its own characteristics.
- Tapeworm. It is a single piece of decor, which is placed in an open place. Large-flowered roses are required for this design. The tapeworm looks interesting near the entrance to the courtyard, near the windows and next to the recreation area. The tapeworm is often placed near the arches as well. In order for the plant to evenly braid the pillars, its shoots must be placed in a spiral.


- Shrub-woody group. Most varieties of climbing roses are perfectly combined with other types of ornamental plants, which allows you to create an unusual landscape design. For this, trees serve as the main background, and small rose bushes are placed at their foot.


- Ordinary landing. It is most often used to decorate garden paths and the perimeter of the site.
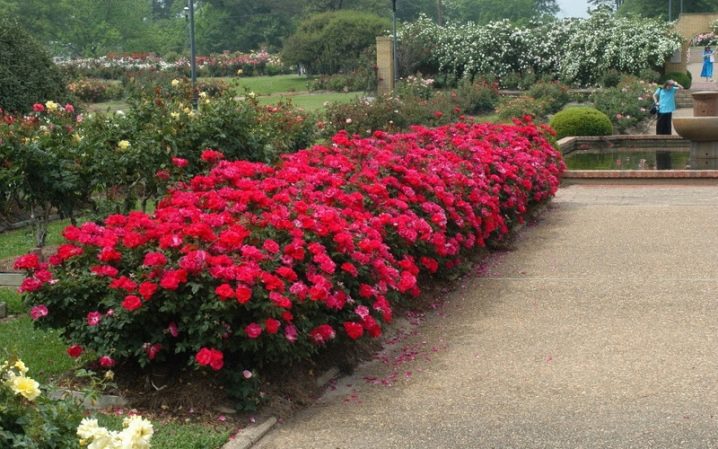

- Hedge. To give the summer cottage an interesting look, it is necessary to plant curly roses tightly in a closed row. Such a fence can be of any height and length. It is best to decorate it with a lattice fence or a special frame.
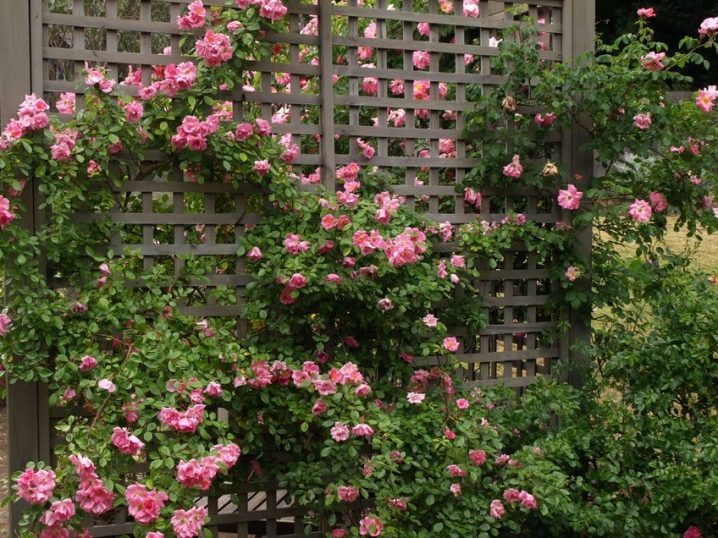

- Vertical gardening. In this design, the climbing plant looks stylish and unusual. Long shoots of roses are fixed on gazebos, pillars and other structures. Flowers can be planted next to the roses to create a carpet.


Recently, many designers have also used climbing roses to decorate pergolas. To do this, a simple structure of vertical columns is installed on the site, an ornamental plant is planted near them, which, after weaving, creates a full-fledged recreation area. If the fences are small and painted white, then roses with delicate pink or beige colors can be planted near them. This design will also serve as an original fence between the garden and the work area.
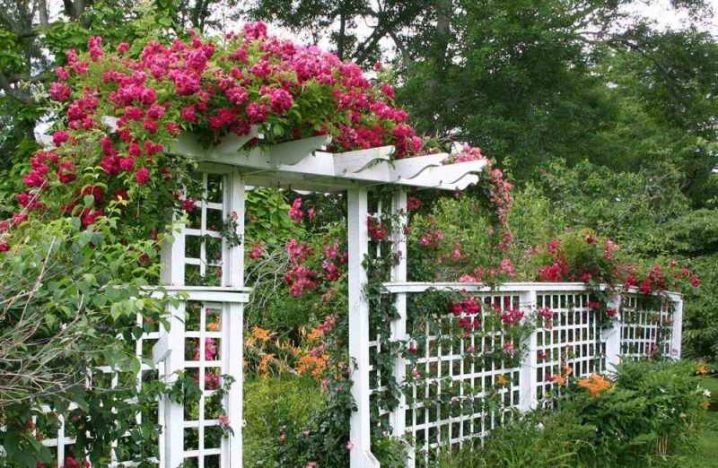

Looks great in gardens and baskets woven from roses. They can be used to drape gratings, trees and walls of residential buildings. At the same time, it is important to note that it is important to think over the design of the landscape to the smallest detail and use not only roses, but also other plants in it. The plant decor looks especially beautiful against the background of architectural structures.


In the event that the territory of the summer cottage is large and its landscape design provides for the presence of columns, then climbing roses will elegantly decorate them, creating a floral oasis. To dilute the color scheme of the composition, roses are recommended to be supplemented with vines.
At the same time, when creating a garden design, it is important to take into account the color palette of colors. White rose goes well with any shades, pink is in harmony with blue, purple and lilac, yellow with white, and red should always be the dominant color.


For the peculiarities of caring for climbing roses, see the following video.

































































































The comment was sent successfully.