Rose "Santana": features and recommendations for care

Long live breeders and amateur gardeners - enthusiasts of their business! This is how you want to exclaim, having learned the history of the origin of the climbing rose "Santana". Today the Rosen Tantau company, named after the founder Mathias Tantau, is known to many flower lovers. It was here that the Santana hybrid was bred in 1985 - a liana-like plant that beckons to touch the carpet of ruby beauties, reach for a light scent and bow to the majestic queen.



Description
Santana is not in vain recognized as the brightest representative of climbing roses. The main feature is flowering from spring to golden autumn. Intense color with a velvety shimmer in the cups of flowers reaching 8-12 cm. This variety belongs to the re-blooming, during the season the rose has time to bloom twice. Describing a flower in detail, you can give it the following characteristic:
- plant height 2.5-3 m, width 1.5-2 m;
- the size of the flower is large-flowered;
- petals, velvety to the touch, after rain become more saturated color of Cabernet Sauvignon wine;
- pink buds bloom in groups of 3-7 pieces gradually throughout the bush;
- the smell is very light;
- leaf plates are distinguished by juicy greens, waxy luster and density;



- shoots are highly branched, which makes them well suited for creating vertical compositions, and since shoots grow along the entire trunk, buds and buds are formed evenly over the entire height and width of the bush;
- the strength of the shoots is enough for stability without supports, but the plant often spreads along the walls of buildings, trellises and arches;
- if you plant several bushes next to it, then a rose scrub shrub is formed;
- "Santana" is quite resistant to cold and rain, but winter comfortably in mild climates;
- creepers have few pests, like diseases;
- for good growth, a ventilated, but draft-free, area is needed.
So, it is not for nothing that the rose is very popular among professionals and amateur flower growers. So, you can try to dilute it in your front garden. And for this it is important to understand how to properly plant a seedling and grow it.


Landing
Before buying, you need to gain knowledge of what a competent choice of a seedling is.
- Good seedling - this is the root collar, from which 2-4 shoots with green young bark and rhizome depart. Buying a seedling "from hand", most likely, the roots without soil will be clearly visible. In this case, you can carefully consider whether they are damaged, whether there is any fungal plaque. When buying a seedling with a closed root system, that is, in a pot, you can buy a "pig in a poke", but planting such a specimen is easier.
- If a plant with an open root system has been without land for some time, and the roots have dried up, then a day before planting it is recommended to lower it by the roots in water and stand for 24 hours.
- Immediately before planting, the roots are disinfected. To do this, 30 g of copper sulfate or 1 tablespoon of "Fundazol" is diluted in 10 liters of water. The seedling is almost completely bathed in solution.


- Planting in the spring is carried out when the earth has warmed up to +10 degrees. This is approximately from April 20 to May 20. In the fall, you need to have time to plant not too early, otherwise the buds will start to grow, and not too late - the root system may freeze. By time - from mid-September to mid-October.
- Santana is the flower of the sun. The southern part of the site or the wall of a house without drafts is what you need.
- While the seedling is in a bucket of water, prepare a hole for it 50x50 cm with a depth of about 30 cm. A bucket of black soil should be poured there and watered well (the amount of water depends on the composition of the soil).


- When planting in spring, the bush is planted so that the root collar remains above the surface. When planting in the fall, experts advise making a mound 20 cm high around the stem to protect the roots from frost.
- Other gardeners recommend, in any case, pour a slide., having previously tamped the soil and watering it from above. Compaction of the earth is done in order to expel air from the rhizomes, and quickly give them the opportunity to come into contact with the ground. The hill is leveled after 2 weeks, when the seedling takes root.
- There should be no leaves on the branches. From the root, you need to leave a stem 20 cm in height, cut off the rest. The purpose of the manipulation: to enable the bush to gain strength and take root faster, and not waste energy on the growth of shoots.


Care
Professional gardeners say that the rose requires special care in the first year, then it will be easier. Whether this is so, you can check only on your own experience. Taking care of the flower consists in watering, mulching, feeding, loosening, preparing for wintering, and pruning.
Watering
How often to water depends on the stage of growth, weather conditions, and the quality of the land. In the spring, when Santana wakes up, the buds are gaining strength, leaves and new shoots appear - more and more watering is required. But with daily watering, little by little, moisture evaporates quickly from the soil surface, leaving the root system without water. For an adult bush in a dry warm season, watering 15-20 liters a week is required twice.
If the soil is rocky, marl, then more watering will be required. Roses should not be watered with cold, especially running, water using a hose. Plants are not watered in the heat: you can burn the leaves, moisture quickly evaporates from the surface, leaving cracked soil, similar to asphalt. But even wet leaves that do not have time to dry before a cool night can become a breeding ground for fungal diseases.
Since September, roses stop watering so as not to provoke growth. But in dry autumn, the bushes moisten about 10 liters of water once a week.

Loosening
Loosening is called dry irrigation. It supplies the rhizome with oxygen, simplifies the access of water to the roots, and protects it from weeds. Many plants do not like slides of earth at the roots, but holes. Roses are no exception. The sides of the holes will retain moisture and will not flood the paths.
They loosen the earth from spring to August. Late loosening is impractical, because the rose is preparing for wintering.
Loosening is carried out with a ripper, a small hoe or a hoe to a depth of 10-15 cm. Large tools can damage the roots.

Mulching
Mulch or bedding is a way to protect the flower from weeds, overheating of the earth, rapid drying of moisture, crust formation on the soil surface, weathering and freezing of roots. Mulch can be organic or inorganic. Organic matter in the form of mowed grass, sawdust, straw, humus, needles is more familiar - it is laid out with the onset of spring before the buds awaken. But this mulching attracts insects that harm the roses.
Therefore, some people use inorganic mulching: non-woven fabric, cut rubber, geotextile. But perhaps the best option is gravel, pebbles or large stones. In dry summers, the warm morning air creates dew by contacting the cold stone. Dew drops run down the stones, providing additional watering for the plant.


Top dressing
The quantity and quality of nutrition will affect the abundance of flowering and color saturation of leaves and flowers. During the season, the bush needs to be fertilized 5 times with minerals and organics (2-3 times in the first year).
In May and early August, the flower is fed with nitrogen fertilizers: 1 tablespoon of urea, sodium humate or liquid organic matter will help the rose grow.Pruning is stressful for the rose, and this is where nitrogen will help.
The formation of strong shoots is achieved by adding superphosphate. Phosphorus applied from June to August will also provide abundant and long-lasting flowering.
Potassium is needed for ovary and flowering. He will also ensure the preparation of the bush for winter. Top dressing is carried out all summer and early autumn.


If the soil on the site is acidic, then it is neutralized with dolomite flour, wood ash, slaked lime, crushed chalk. During the entire growing season, the flower is fed with manganese, iron, boron, magnesium. These micronutrients are sold as mixtures. The last mixture is applied in early November in the form of organic mulching. This will help the flower wake up easier in spring and strengthen the root system.
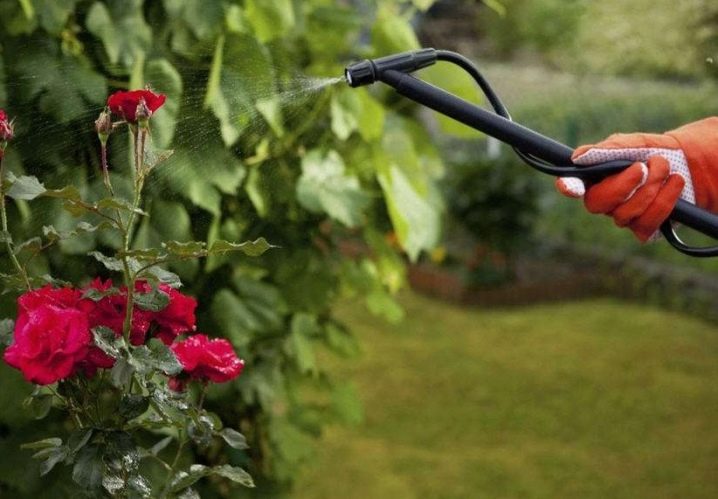
Foliar dressing, that is, spraying, can be carried out every 10 days. This will help saturate the leaves and buds faster. It is important to make the solution correctly and use it according to the instructions. The leaves should be sprayed on both sides.
Both root and foliar feeding is carried out in the morning or evening. The goal is to protect leaves and stems from burns. When spraying, it is important that the solution has time to be absorbed before it rains. All instructions indicate the time to use the drug before rain.

Preparing for winter
In the southern regions, the climbing Santana hibernates without insulation, but in the middle lane there is a possibility of freezing. Before the onset of frost, the bush is cut and covered. The height of the covering material should be at least 20 cm. It can be coniferous branches, potato or tomato tops, tires covered with boards on top. Often the bush is covered with garden film in several layers.
Before covering, the branches are tied in a lash and laid not just on the ground, but on some kind of insulation: foliage, rags, conifers. To prevent the branches from rising, they must be pressed down to the ground in a gentle way.
Thorough covering is carried out only when the temperature has dropped to -5 degrees. Do not strive to cover the plant early: it will wear out under the "fur coat" and will hurt.


Pruning
Not only the density of the bush will depend on how correctly the pruning is done, but also whether it wakes up in the spring. Therefore, they use a knife disinfected in a steep potassium permanganate. This will prevent mushrooms from getting into the slices. Slices on lignified branches are treated with garden pitch.
Cropping can be of several types.
- Preventive - in the spring, at the time of swelling of the buds, frozen and diseased branches are removed. All others are cut to the very top swollen.
- Thinning - cut off the shoots growing inside the bush, weak, thickening, old, crooked. The goal is to tidy up the bush, add beauty to the plant.
- Rejuvenating - every fourth year old woody branches are removed from liana-like roses, leaving 30 cm from the root.
- The enlarging flower is an innovative technique in which all old branches are first cut out, and all the remaining ones are cut in half.
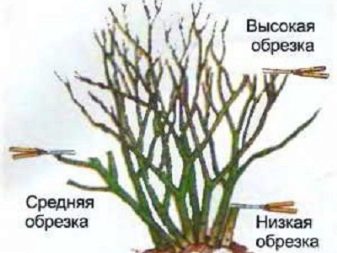

Pruning gives shape, decorativeness, eliminating thickening. It must be remembered that flowers will only be on lignified 1-3-year-old shoots. The ever-growing young growth must be cut very carefully. The first pruning is carried out immediately after planting the seedling in the hole, as we wrote above.
In the spring "Santana" is cut off immediately after removing the shelter. Weak, sick, broken branches are removed. In summer, the plant is cleaned of faded buds and overgrown young shoots. In late autumn, pre-winter pruning is carried out.
With a sharp knife, so as not to crush the twigs, remove the longest shoots. With this pruning, the bush will give its strength to the formation of buds, and not greenery.


Diseases and pests
You can determine that a plant is sick by its appearance. And this means that the disease is progressing with might and main. To avoid this, you need to regularly inspect the rose bushes. Otherwise, the disease can spread from one rose to another. Most often, you can see the following signs of damage:
- swollen cones on the root system - bacterial cancer, not treated, but removed from the plant; healthy roots are treated with copper sulfate;
- white bloom, similar to spilled flour - powdery mildew; in order to save other plants, and not only roses, the bush is uprooted and burned far outside the garden and vegetable garden;
- black spots on the leaves - marsonina or black spot; the affected leaves are removed and burned in a remote place, the bush is treated with preparations with copper and systemic fungicides.



The rose has a lot of pests: spider mite, green rosy aphid, rosy leafworm, rosy scale insect, drooling penny and others. They fight them with chemicals - insecticides. But you can also use folk remedies. For example: 300 g of onion or garlic, 400 g of green tomato leaves chop in a blender; Insist for 5-6 hours with 3 liters of water; strain; add 7 liters of water and 40 g of soap. A well-mixed solution is sprayed on the plants.
For tips on caring for climbing roses, see the video below.

































































































The comment was sent successfully.