Description of discounts and the secrets of their creation
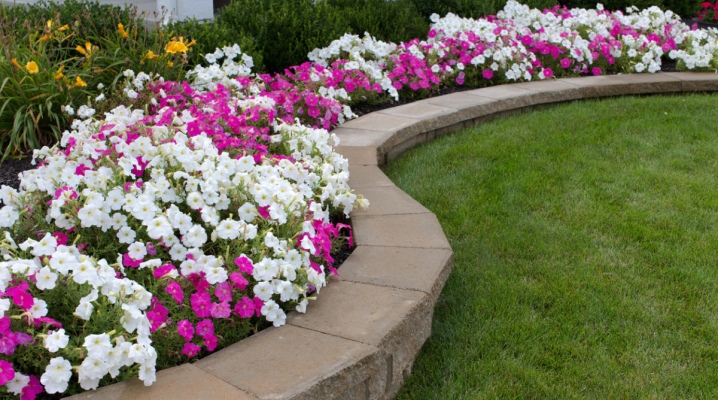

The word "rabatka" has German roots, and its literal translation is "bed". Behind many of the terms familiar to landscape designers are fairly simple definitions, but special terminology helps to separate the narrower concepts from the broader ones. So it is with the discount. It means a flower garden made in the form of a long bed. Interestingly, a few centuries ago, the rabatki was called the pharmacist's beds. Today, this is one of the great ways to structure the space in the country, enhancing the integrity of the site design.



What it is?
Rabatka is a flower bed, the same flower bed, located along the garden path or fence. This flower garden has a strict shape and parallel edges. Most often it is a rectangle or even a vegetative strip. However, the strip can turn into a wave or arc. Rabatka can be presented as an independent element of landscape design. But often this is one of the fragments of the general scheme.
Experts consider Rabatka to be a special flower garden, not agreeing that it is just a flower bed. There are strict requirements for its creation.



The discount is distinguished by:
- width maximum 3 m (less is possible, more is not);
- the length is 3 times the width, and in general it is unlimited in duration;
- the selection of plants is strict - not only color and growth are taken into account, but also the periods of flowering;
- The bed requires a clear seating plan and soil preparation.

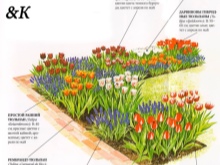

The creation of a rabat always begins with the design. The garden is a living organism, changing, dictating its own laws. Therefore, any designer, even self-taught, needs to get used to looking at plants in the context of a place. And, conversely, look at a place in the context of its capabilities: area, shade / exposure to the sun, soil features. As landscape design guru Pete Udolph says, it all starts with an idea.
It is the same with the rabatka: you need to decide where it should be, what it should be, and what type of rabatka will be most complementary to this site.


Species overview
Registration of discounts gives you a choice. The same narrow long ridge in different contexts also looks different.
Unilateral
This is the name of a flower garden that has a one-sided approach. Plants in it are planted at high altitudes: on the first lane there will be curbs, ground cover, undersized, on the second, high crops will coexist with them. In shape, such a rabatka may well be curved. On such flower beds, as a rule, there is no question of keeping symmetry.



Double-sided
Such beds have an approach from both sides, which greatly facilitates planting maintenance. This flower garden does not have to be limited in width - it will be maximum, if there is a request for that. Usually such a discount is placed along the paths. It will be an excellent zoner, framing a lawn or some kind of recreation area with a pond, hammock, etc.
Plants in this case will be planted according to the principle of a pyramid: the highest will be in the middle, the lowest will be located at the edges.


Symmetrical and asymmetrical
If the bed is classic, the planting ridge will be kept in the shape of a regular rectangle. The width of the ridge does not change along its entire length; annual plants with the longest flowering are chosen for a symmetrical bed. Symmetrical ridges are a priori double-sided.
When planting flowers, it is necessary to observe the layering, maintain the clarity of the patterns and floral ornament.


Asymmetric ridges are made in any shape, they do an excellent job of filling in not very convenient places. For example, such beds will become a beautiful edging of non-standard buildings. They can gracefully wrap around objects, emphasizing them. There are no laws in the choice of plants, everything is possible. But the proportions of width / length must, of course, be respected.


Intermittent
In this case, the flower garden will not change the width, and the length will be divided into sectors. Usually this type of bed is used in large areas. The length of the ridge is from 5 to 15 m. The ridges are planted with perennial bushes, border species, dwarf conifers. The division also involves the inclusion of mini-flower beds - either round or oval.
This is one of the most interesting species for an original group planting, for creating a lively ornamental image in the garden.



Where to locate?
The main way of the rabat device is according to the curb principle. That is, it will border garden paths, a fence, other significant places, zones, buildings on the site. Rabatki are not uncommon as bordering city roads, pedestrian sidewalks and park paths. Their main principle is the plot repetition system, which sets the rhythm of the landscape element.
For zoning a site, not very wide flower stripes are really convenient. Usually summer residents make ridges along the paths, but then they decide to use this simple and cute technique for visual division of the site. For example, for an open landscape with a reservoir, ridges are practically irreplaceable.


Selection of plants
The composition needs to be planned, there are a lot of conditions and nuances. For ease of choice, you can use the following overview of plants, which differ in height and growing season.
Here's what you can plant.
- Tall plants. In this group, phloxes and peonies, chrysanthemums and ferns can be considered the most unpretentious perennials. There are plants that require control from increased growth: you will have to constantly monitor lupins, asters, echinacea, bells and delphinium, buzulnik and rudbeckia.
If the bed is one-sided, the most preferable flowers are clematis and roses, hydrangea will do, as well as lemongrass and lianas.


- Medium and short perennial flowers. If you control the growth, irises, daylilies, hosts and daisies will look great on the bed. If the bed is wider than 1 m, you can plant both astilbe bushes and mini-roses there. Of the perennials, the most unpretentious are carnation, chamomile, gravilat, brunner, and fescue.
If the region is warm, you can decorate the rabatka with lavender, evening primrose and maned barley.


- Medium-sized and low-growing annual plants. This group cannot be imagined without zinnia, viola, ornamental cabbage, cochia, lobelia, coleus, alissum. Rabatka will bloom longer if you decorate it with marigolds, petunia, calendula, nasturtium and pelargonium. Asters and dahlias do not promise continuous flowering, but they will delight the eye from mid-summer until the end of the season in the country.


- Bulbous. These are primroses, which begin to "embroider" the flower ornament of the rabatka earlier than others. The earliest will be daffodils, crocuses, and also snowdrops and tulips. They will be followed by hazel grouses, freesias and hyacinths. In June, flowering will also touch lilies, ornamental garlic, hippeastrum. And the celebration of the flowering of gladioli is crowned.


- Shrubs and conifers. The most popular shrub for the ridge in this sense can be considered a spirea. It is diverse: you can choose a species suitable for the height, color of the foliage. The most successful acquisitions will be Japanese maple, boxwood and weigela. Of the conifers, preference is given to undersized species of pine and dwarf Christmas trees. Junipers should not be ignored either, especially their ground cover and creeping species.If you look closely to the thujas, then to the spherical.


Obviously, the choice is great, and compositions can be made as simple, modest, and impressive with a progressive rhythm and active interaction with other elements of the site.
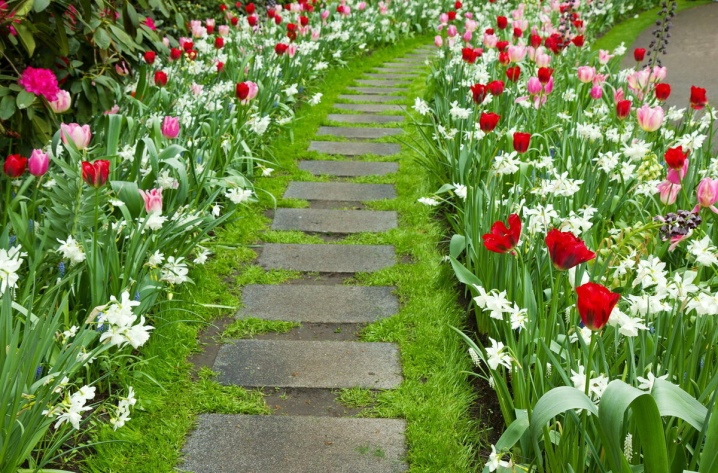

Basic rules for creation
To make a really beautiful rabatka with your own hands, you need to think over its scheme in detail. 5 basic principles help in this.
- Keep width. If the strip for the bed is 50-70 cm high, it is better to fill it with medium-sized crops and only in 2 rows. If the ridge is from a meter to one and a half meters, you can resort to a three-row planting. You can combine it with the planting of conifers and shrubs.
- Know the size of an adult plant. A typical mistake of beginners: they do not predict the growth of a plant, they look at its initial size. At the same time, the density of vegetation must also be observed, it is desirable that the land in the rabatka does not show through at all.
- The best is the enemy of the good, that is, we must get rid of the diversity. Plant varieties need to be combined according to color compatibility. If there are more than 3-4 contrasting tones, the design becomes chaotic or simply "cutting" the look.
- The composition should be liked. This is not difficult to achieve, including tricking the rhythm of flat islands, for example.
- Planting density is sacred. Simple calculation: 9 small, 4 tall and 5 medium-sized types of crops need to be planted per 1 square meter. More than 18 plants per square are taboo.
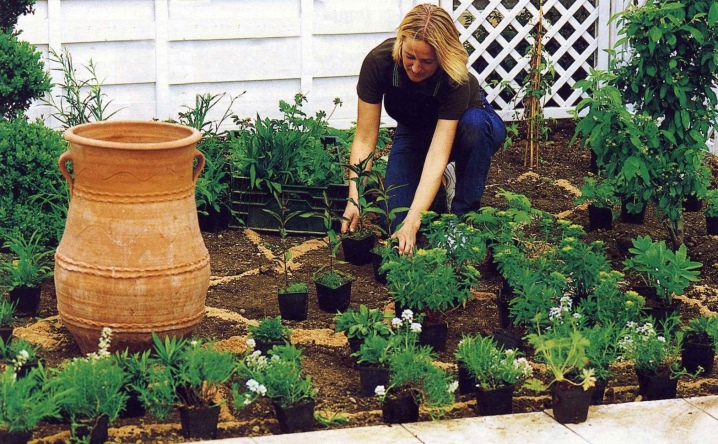

And these are just the basic rules. What else you need to remember the florist: the varietal characteristics of those crops that will be on the bed, you need to clearly know. If a shade-tolerant species is planted in the sun, and a thermophilic species in the shade, nothing good will come of it.
You will also have to take into account wind load, soil moisture and lighting.


Brief instructions for beginner landscape designers to create a rabatka:
- the design scheme initially needs to be drawn on paper (you can simply draw with geometric figures - stripes, circles, squares);
- when everything is drawn, the plants are selected and there are no questions, it's time to take up the tools - this is a shovel, a rake and a watering can;
- now you need to draw directly on the ground - you will have to mark the boundaries with stakes and a rope;
- with a shovel, you need to remove the top layer of soil, the approximate value of the immersion is 15 cm;
- the edges of the groove must be laid out with a border material;
- the prepared site must be covered with fertile soil, and it is not worth making the surface perfectly flat, otherwise water may stagnate in the center of the rabat after rains;
- it's time to plant flowers, focusing on the drawing - you don't need to do it too tightly, it is important to take into account the subsequent growth of crops;
- after planting, the sprouts must be watered and left alone for a week.

It is better not to approach the rabatka for a week: the plants rest from the stress of transplanting, they adapt.
Care features
Everything is simple here: the flower garden needs to be watered on time and weeded regularly. In this sense, a rabatka does not differ from an ordinary flower bed. Top dressing according to the schedule, as required by the plants. When autumn comes, annuals should be removed and perennials should be pruned. The root system is protected by tightly wrapping the roots for the winter. Each flower that remains overwintering must be viewed: diseased plants must be removed, and healthy ones must be left.
There are no secrets, the whole point of care is the regularity of watering and weeding, calculating diseased plants and eliminating the causes of the disease.
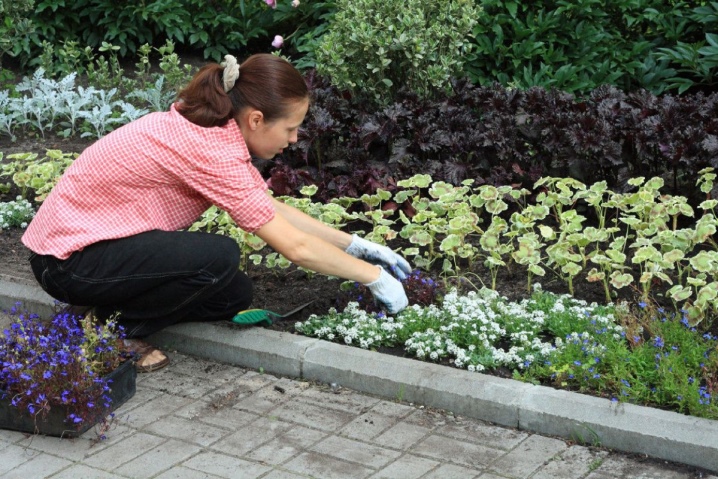
For those who are just trying themselves in floriculture and landscape design, it makes sense to fix the process of transforming the site. You can even keep a diary on your phone: take pictures of the newly created rabatka, take pictures as the flowers grow, mark good moments.

Beautiful examples in landscape design
And in addition - clear evidence that the rabatka structures the space well, helping to maintain compositional principles.
Several beautiful beds in the garden.
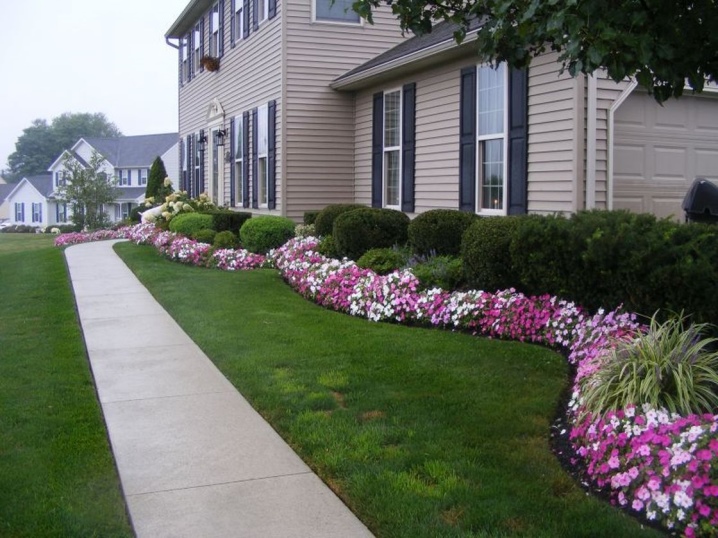
- The curved romantic pink rabatka perfectly complements the shrub layer.

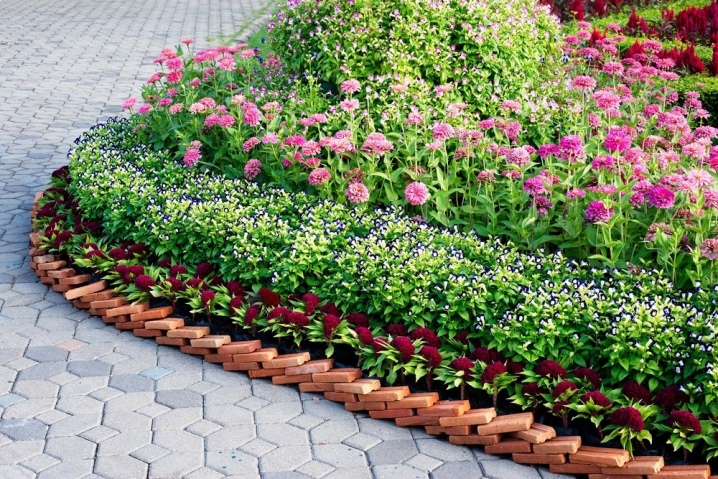
- Very clear, almost beaded ornament. The bordering with bricks also looks organic.

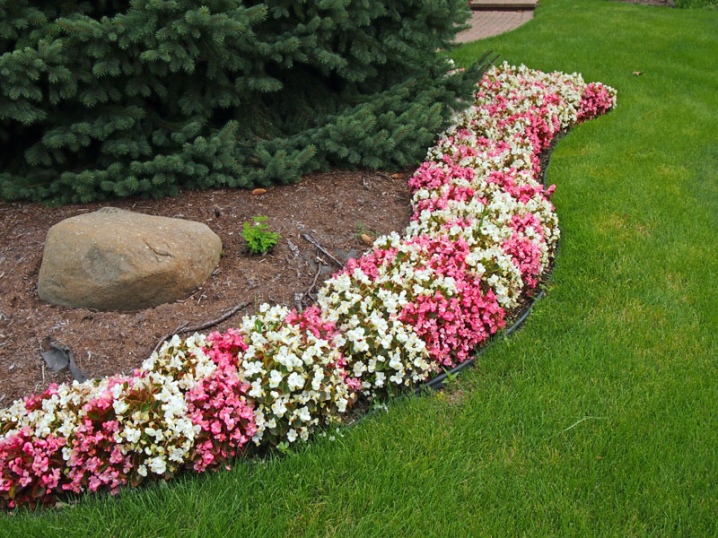
- Well-sustained floral rhythm, the softness of the color matching is also successful.

- There is a beautiful rabatka right next to the house with a clear geometry and respect for the neighborhood of cultures.


- This is a bunk bed - it will take a lot of effort to create and maintain it, but it's worth it.
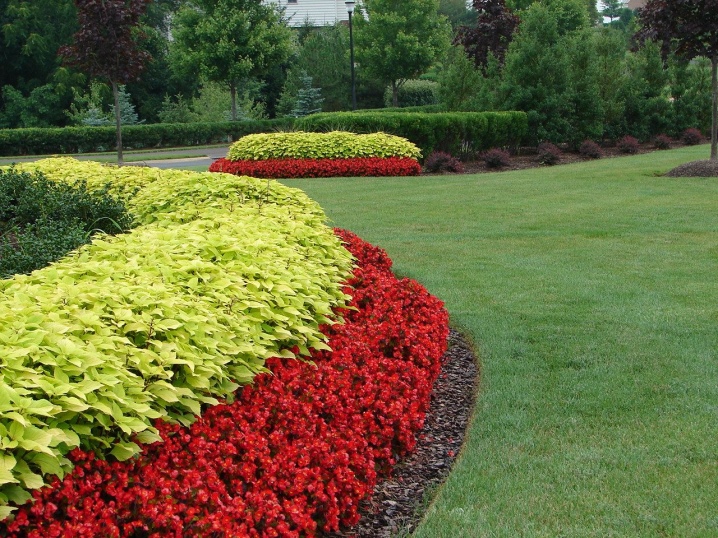

- Very wide, curved, bright - but these are only good for large gardens.
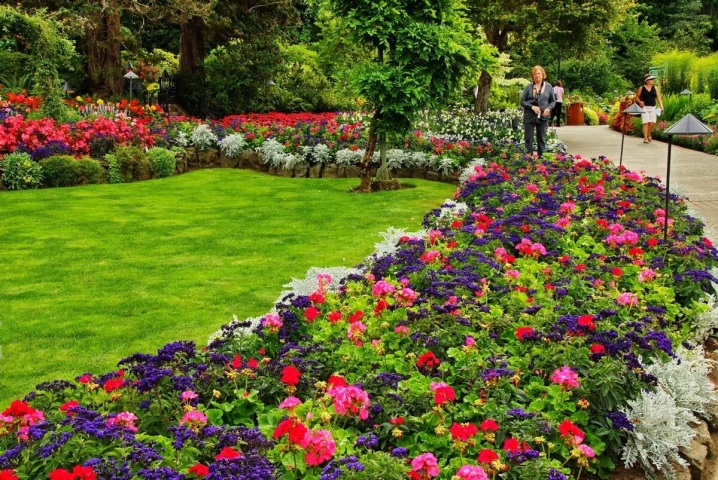

- Clearly separates the path from the lawn.


- An example of how to create complex pattern of simple plants.


- Wide discount - like a flower cake at home.


- Very gentle, very picturesque flower bed.
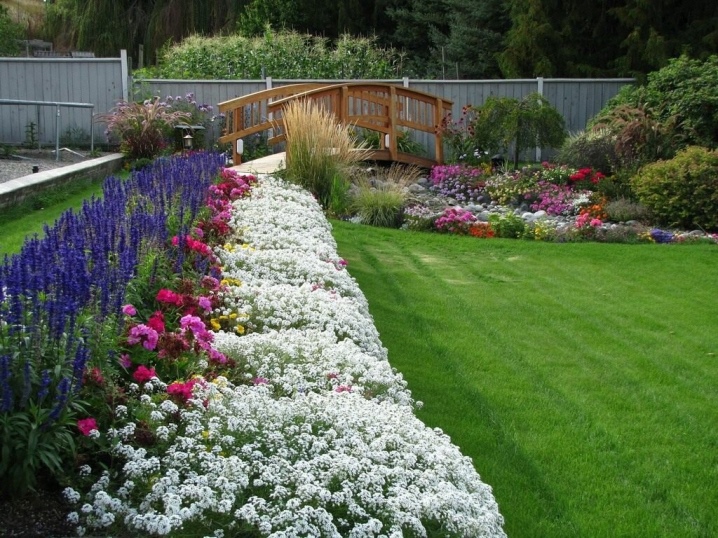

For information on how to create a discount, see the next video.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.