How to feed clematis in spring?
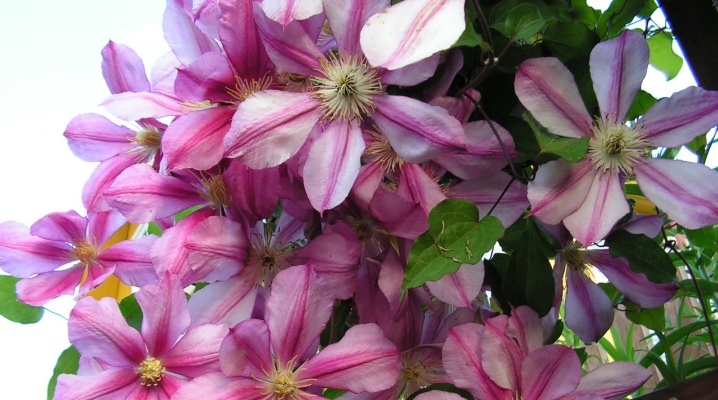

Clematis is a flowering plant belonging to the Buttercup family. These perennial vines are also called clematis or vines. They have beautiful decorative properties and are widely used in landscape design. Most common in the form of a climbing vine, but there are also shrub forms. These beautiful vines perfectly decorate the facades of buildings and hedges in summer cottages. But, in order to achieve excellent decorative landscaping with flowering perennials, it is advisable to stock up on knowledge and make enough effort.

Why feed clematis?
This decorative liana grows in the country and in the garden and does not require transplanting to another place for about 15 years. Today, there is a huge variety of species of this culture. About 300 varieties of these creeping garden vines are known in the world. The intensity and duration of flowering of clematis is influenced not only by the variety, climate and weather, but to a greater extent by full-fledged care during the entire period of growth. Fertilizing the soil and feeding in the spring for lush flowering means laying the foundation for the future abundant bloom of the vine. Fertilizing the soil in the places where the vines are planted, the gardener provides the plant with a full two-year nutrition for its vegetation. Then the soil is gradually depleted, due to which the growth and flowering of the vine slows down.


Therefore, starting from the third year of the growing season, it is advisable to begin fertilizing the soil immediately after winter so that the spring feeding of clematis helps it grow shoots and further develop fully.
Terms of feeding
Two years after planting in the ground, top dressing of clematis is carried out annually in three stages: in early spring, in summer when buds are forming, and in autumn to prepare for winter. Each dressing has a specific meaning and the most important of all is done in early spring. At this time, young shoots begin to grow and flower buds are laid. Experts advise to activate the growth of the vine with early feeding from milk of lime, which will also protect the vines from diseases and pests. In April, 3 days after the treatment of plantings with milk of lime, their foliage must be treated with succinic acid tablets dissolved in water.

After another 5 days, a liquid nitrogen-containing root dressing is added, and a week later a biostimulator based on humic acids is added. In May, dissolved urea is used. The solution is poured under the bush. Another option is to simply crumble to the soil next to the planting. In mid-May, infusions of mullein and chicken manure serve as fertilizer. In the last days of the month, liming of the soil is carried out before mulching. This achieves the acidity of the soil suitable for the vine. With the help of a solution of slaked lime, chalk or dolomite flour poured under the root, the soil is additionally enriched with potassium and calcium, which help to maintain the brightness of the flowers.

Important! Foliar dressing and irrigation of young shoots with a weak urea solution in the last days of May increase immunity and activate the formation of buds.
Later, when forming buds, you cannot use spring nutrient mixtures, you need to use summer ones: superphosphate and potassium nitrate. A formulation with a low nitrogen content and a high potassium content is suitable. The first two summer months - June and July - are the period of active growth of buds and prolonged flowering of the vine.In these months, it is better to significantly reduce, or even completely stop fertilizing the vines, the abundance of flowering will noticeably increase.

At the end of August, the application of phosphorus-potassium compounds is continued. Not often on warm days and always at sunset, the leaves should be sprayed with a weak solution of boric acid with potassium permanganate. It is useful for stimulating growth and increasing chlorophyll content. Spraying this way will reduce the negative effects of heat and increase the number of flowers.
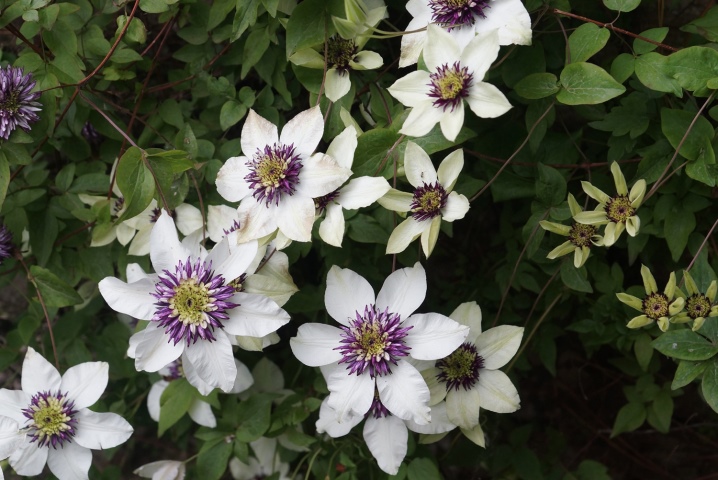
In September, the liana ends its flowering, in the future it will have a rest period. Nitrogen is completely excluded from the nutrient mixtures, since young shoots are no longer needed. Now the autumn phosphate-potash fertilizers should prepare clematis for the cold days. At the end of September, the most important autumn procedure is carried out - mulching. Again, at the roots of the perennial, a layer of wood ash is poured. The potassium contained in the ash enhances the winter hardiness of all ornamental plants. This ends the autumn fertilization.

Fertilizer selection
The basic principle of feeding clematis is based on the following rules:
- if feeding is necessary for the formation of young shoots and the laying of flower buds, nitrogen fertilizers are used in the spring;
- when top dressing is necessary for the formation of buds, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are applied in the summer;
- for better transfer of cold weather in autumn, phosphorus-potassium fertilizers are also used.

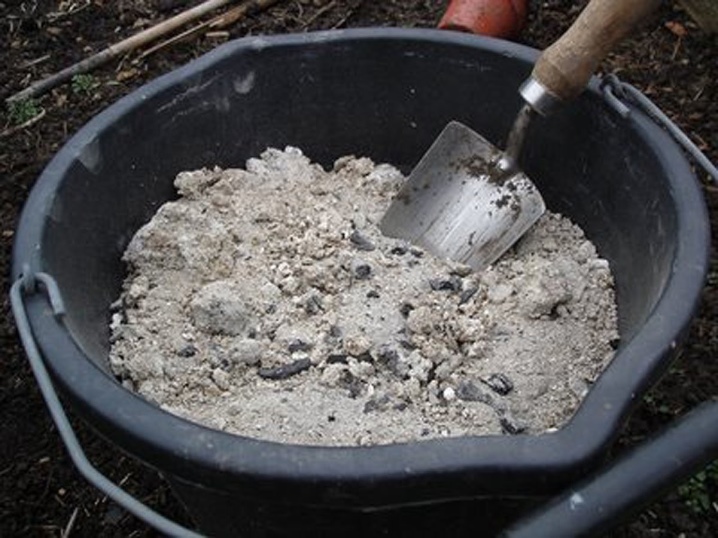
For development, the plant needs 16 micro and macro elements, which it receives both from the air and from the soil fertilized by gardeners. Organic matter must be alternated with mineral fertilizers to ensure the normal growth of seedlings. The vine finds the building material that forms the cell in nitrogenous supplements, as well as activating the processes of cell division and preventing their aging. Therefore, in the spring, the vines are fed with nitrogenous fertilizers of organic composition, using humus, humus, rotted manure. Mineral fertilizers can replace organic matter - solutions of urea or ammonium nitrate. A pale pink solution of potassium permanganate will increase the content of manganese, potassium and will stimulate the production of chlorophyll. The assimilation of organic matter occurs better in the form of an infused aqueous solution.
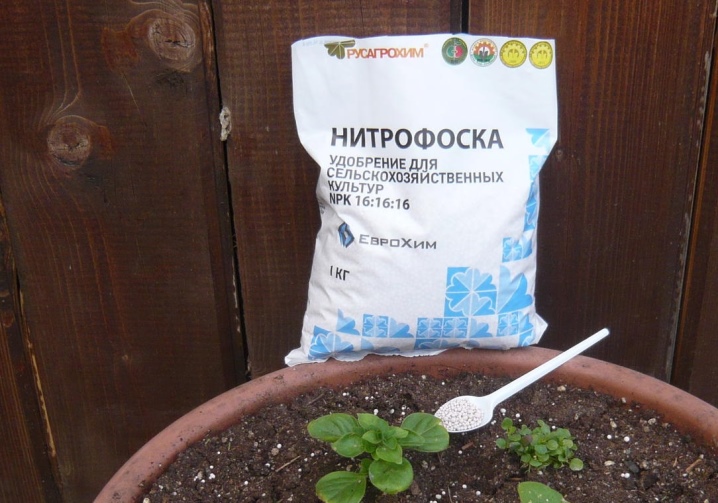
Then all the necessary microorganisms will penetrate deep into the soil and are easily absorbed by the vines. The most often used infusions from weed grass or fermented manure, which are diluted with nitrophosphate.

On a personal plot, where, along with ornamental plants, vegetables and fruits are grown, it is better to use folk remedies, and not to use chemicals. Herbal or yeast infusions will completely replace the missing chicken droppings or manure. And if there is no organic matter at hand, then mineral feeding in the form of an aqueous solution or granules will be a substitute. The granules are scattered around the trunk and watered thoroughly. Aqueous solutions of urea and ammonia will bring the plant out of hibernation, enhance growth and help form buds.
For the formation of buds and the duration of the subsequent flowering, clematis needs phosphorus and potassium. Phosphorus contains superphosphate, double superphosphate, phosphorite and bone meal, which is even more effective than phosphate rock. Superphosphate is used both in liquid and dry form. In double superphosphate, the amount of phosphoric acid is doubled, therefore, it must be used in a lower concentration.

A solution of boric acid and potassium permanganate, which is sprayed with decorative perennials in the middle of summer, will not only enrich the soil with the necessary trace elements, but also become a good antiseptic and raise the immunity of the vine. Ammophoska or nitrophoska is used as nutrient formulations with a high potassium content. Landowners recommend using one more top dressing - milk of lime.He is very fond of clematis, but should only be used on acidic soils.

Recommendations
It may be difficult for beginners to grow this decorative culture. But if you know the peculiarities of caring for this magnificently blooming vine, then they can be successfully bred on your site. If you apply the following simple tricks, you can make these vines bloom profusely and for a long time:
- it is necessary to start feeding the vines in April, when the air temperature rises to + 10 ° C with an interval of 2 weeks and before bud break;
- before feeding, the trunk circle is cleaned of weeds;
- for each adult liana, at least 5 liters of fertilizers are consumed, diluted strictly according to the instructions;
- for each individual plant when planting, 20 kg of humus useful for a vine should be used;
- do not spare ash for clematis - it promotes flowering, prevents decay and scares off creeping pests; wood ash during mulching is scattered at the rate of about 0.5 kg per 1 bush;
- in the mineral complex there should be no harmful clematis chlorine, which weakens its immunity;
- it is important to strictly adhere to the order of application of each type of fertilizer;
- when using nutritional mixtures, it is necessary to strictly observe the technology of their preparation and adhere to the recommended concentration of substances; failure to comply with these requirements causes irreparable harm to plantings;
- clematis for development needs spraying with biostimulants, which will enhance the growth of lateral shoots for greater splendor of the bushes; with their help, clematis will better tolerate low soil temperatures.
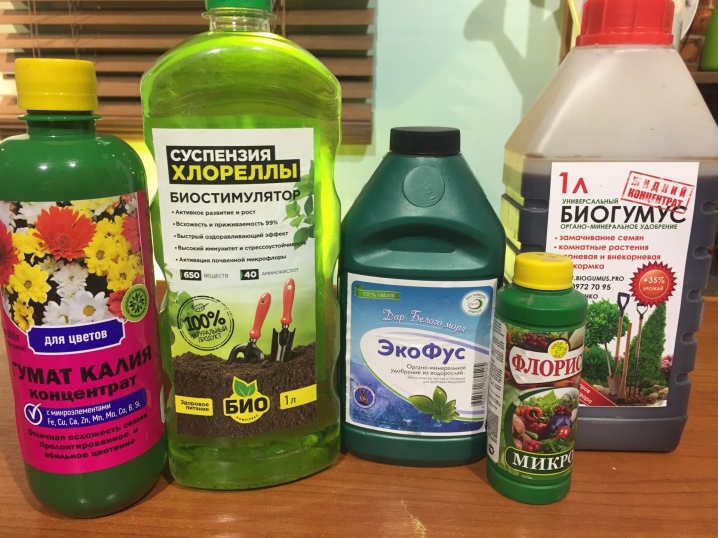

There are many ready-made compositions for climbing vines.
This is a liquid complex fertilizer for vines "Good power", complex organo-mineral fertilizer "Garden recipes", universal fertilizer "Kemira wagon", drugs "Avkarin" and many others. If you apply these recommendations in caring for clematis, then these beautifully blooming vines, which can decorate any area, will turn it into a garden of Eden.
How to feed clematis in spring, see below.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.