Diseases and pests of phlox: what are they and how to treat?

Diseases and pests of phlox with descriptions, indicating methods of their treatment deserve the most close attention. Many summer residents and amateur flower growers want to have flowering plants in their garden. But phloxes are quite vulnerable to the effects of fungal infections, attacks of insects, slugs and other inhabitants of the sites. How to identify the disease in time, what rules will help to respond quickly and save the plant from death? What to do if the lower leaves turn yellow, can this be prevented?
Experienced flower growers remind that preventive measures are still the only effective means of combating pests and plant diseases. If, upon regular inspection, the leaves look strange, the flowers have stopped forming, the stems show signs of dwarfism, you should think about how to study the symptoms of the problem in more detail.


Causes of occurrence
Why do phlox diseases occur? This question is asked by every summer resident who has already faced the death of a lush, flowering plant. Usually, the basis of all problems is the wrong agricultural technology - a violation of the requirements for growing a plant. For example, all types of fungal microorganisms require a humid microclimate. If the soil around the root is too saturated with water, a favorable environment is created for their appearance.
Viral infections are most often carried by pests, for example, aphids, mites, roundworms, cicadas and other insects... All of them, in contact with healthy phloxes, increase the risk of developing a dangerous disease. Plants get sick quite badly upon contact with the virus. It is often easier to destroy an entire bush than to try to save individual shoots. Garden equipment can also be a source of danger: it is recommended to thoroughly disinfect tools and containers from time to time.
At the slightest suspicion of a virus, the diseased plant should be quarantined, covered with linen bags to avoid spreading the danger through pollen. It is important to consider that diseased plants are often marketed as exotic or new species.


An alarming factor should be the recommendation for reproduction by dividing the bush - if vegetative processes are disturbed, cuttings are also difficult. Among the reasons for the spread of infectious diseases or insect pests, reluctance to comply with elementary plant quarantine standards is often mentioned. For example, for phloxes, the recommended insulation period is 2 years... This is especially important if a whole collection of species and varieties grows on the site.
Wrong agricultural technique - the main source of all troubles. Phlox problems are mainly related to the fact that the wrong place for planting was chosen - too shaded or, conversely, a lit area, too dense soil, lack of sufficient watering, fertilizers.
All this leads to the fact that the immune system begins to malfunction. The problem can be partially solved by mulching the soil with sawdust or shavings that absorb excess moisture well.


Description of diseases
The manifestations of phlox diseases are quite diverse and, with an attentive attitude to the plants, are well distinguishable. An attentive gardener will easily notice a discoloration of the leaf plate, its deformation, and the appearance of other symptoms. Let us consider in more detail what diseases affect phlox most often.
Verticillary wilting
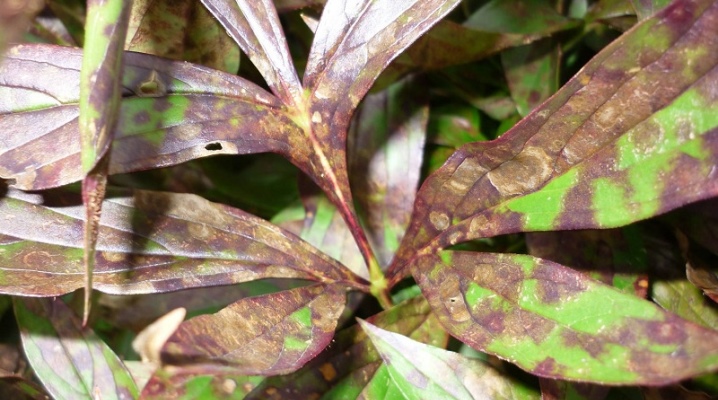
A fairly common infectious disease of phlox. It manifests itself during the period of active bud formation and during flowering. The main focus of the lesion is the root system of the plant. The fungus affects the area of the root collar, interferes with the normal flow of nutrients. Initially healthy flower stems hardly change at an early stage of the disease, but the leaves on them turn yellow, curl, dry out and lose all attractiveness.
Over time, the stems themselves change color to brown, dry up and die. If you do not take action, the plant will die during the season. It is recommended to dig out especially valuable bushes from the ground, rinse the rhizome, removing possible spores, process it by soaking in biofungicide (solution at a concentration of 0.2%) and plant in a hole with the addition of Trichodermin.
If the plant has already died, it must be destroyed, the soil in this place is spilled with fungicidal compositions, not used in the future for some time.

Powdery mildew
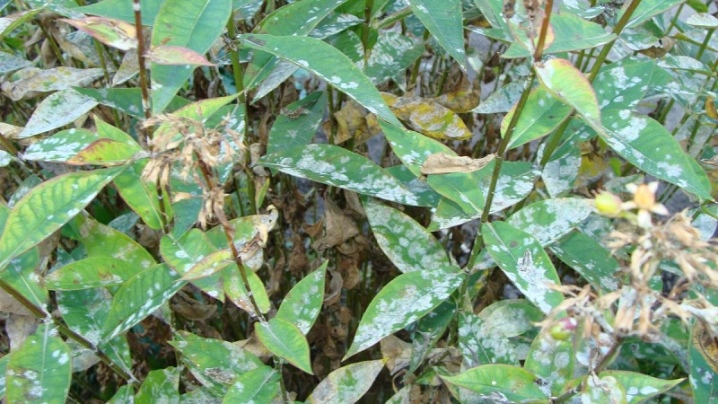
This fungal disease affects not only phlox. Allocate true powdery mildew, caused by fungi of the family of erysipheans, and false, provoked by the appearance of peronosporous. With powdery mildew, the characteristic white spots cover the phlox leaves like a thick spider web. First, the top of the leaf plate is affected, then its lower part. Further, the plaque gradually becomes gray, dark spots of the mycelium are clearly visible on it. With the uncontrolled development of the disease, the plant inevitably dies.
The false form of the infection looks like a yellow-spotted lesion of the leaf tissue. It spreads rather quickly, leading to the wilting of the shoots, their drying out and death. Fragmented myceliums are separated from shriveled leaves. As with other fungal diseases, false and true forms of powdery mildew can be eliminated by spraying plants with products containing copper.

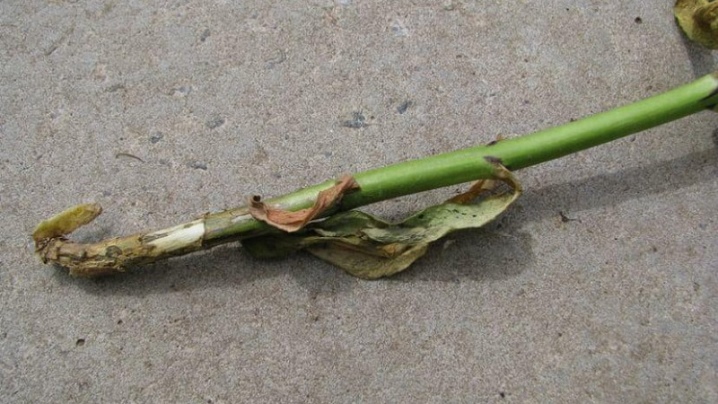
Fomoz
One of the most common diseases of perennial phlox. With it, the lower leaves turn yellow, they are covered with dark spots of straw-brown shades, the shoots at the base turn brown. In just a week, the leaf plate begins to die. The edges curl, the plant dries up, the underside of the leaf is covered with black spots of mycelium.
With deep phomoses, the stems lose their elasticity and cracking. The plant wilts, breaks, dies. In most cases, treatment does not work, phloxes are easier to exterminate. You can try to save the most valuable, rare specimens through rooting by cutting off the tops of healthy shoots and keeping them for at least 12 hours in a fungicide solution. For the first 2 years, rescued phloxes need to be grown in isolation, in a separate quarantine section of the garden.
If phomoses are detected at an early stage, you can try to save them by carrying out treatment. For this, copper-containing preparations are used - "Hom", Bordeaux liquid in a 1% concentration, which will prevent the spread of fungal infection.

Phlox rust
The cause of this disease is the fungus Uredinae. Infected leaves begin to cover small, and then more and more extensive brownish-red spots. As the affected areas grow, the plant begins to wither, the leaves dry, lose their natural color, the plant dries up. With the timely initiation of treatment with preparations containing copper, rust is quite successfully eliminated. It is necessary to spray medicinal solutions both directly onto the soil and onto the plant itself.
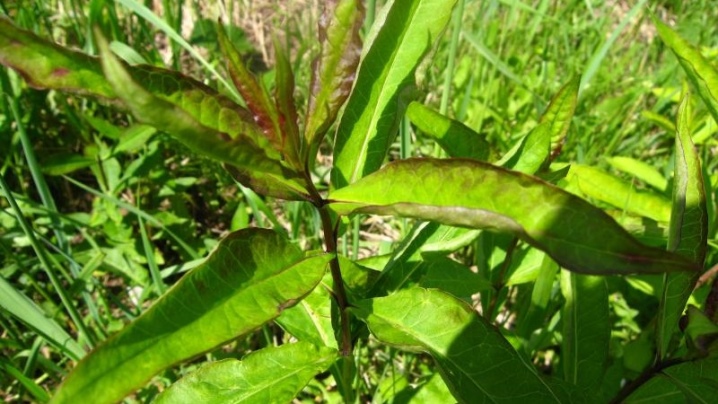

Septoria or spotting
When infected with septoria, the shoots of the plant dry out at the bottom. During the period of bud formation, the disease can be detected by detecting gray spots on the leaves. Gradually, they grow, hitting the shoots from the bottom up.... If the lower leaves turn yellow, traces of a reddish border appear on them, septoria has passed into a severe stage, the probability of plant death is high.
The main therapy here is always associated exclusively with the treatment with drugs containing copper, starting treatment on time can save phlox.
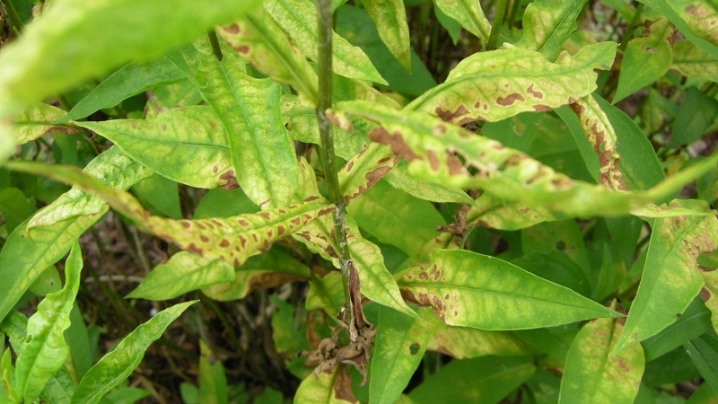

Chlorosis
This is most likely a complex of symptoms in which the shoots change their color, turn white or yellow, and the leaves acquire a faded border. Chlorosis is associated with a lack of a valuable biological substance - chlorophyll, which is necessary for the proper course of photosynthesis processes. The most common cause of chlorosis is micronutrient imbalance.
As a rule, the problem can be solved by applying top dressing - a mineral complex with iron, magnesium, sulfur, lime, zinc. And also the causes of chlorosis can be deterioration of conditions for the growth and development of the plant, caused by stagnant water at the roots, too acidic soil and infections.

Viral diseases
Among the viruses dangerous for phlox, especially a few.
- Curliness. The virus causes deformation of the leaves - yellow-green or black spots appear on them, uneven in shape and color, the veins of the leaf turn brown. With severe neglect of the disease, the leaf plates twist spirally around their axis. The bush looks stunted, when compared with its fellows, its flowering stops. Methods for the treatment of vein necrosis virus or cucumber mosaic on phloxes include treatment with fungicidal preparations and complete removal of affected leaves.
- Ring spot. The appearance of ring-shaped spots, which is one of the symptoms of black ringed tomatoes, becomes a sign of the disease. Further, the leaves are deformed, curled. The affected plant is destroyed along with the root, the soil is cultivated from nematodes - carriers of a viral infection.
- Variegatedness. It is not typical for phlox, but it is found in some varieties - Darwin's Joyce, Phlox paniculata Drakon. Their petals are covered with symmetrical strokes in contrasting shades. Pathology manifests itself in a slightly different way - in the form of radial stripes, sectors covering the flower. If a variegation virus is detected, the plant must be destroyed. Its pollen, seeds and juice are contagious.


Pest overview
Among the pests that threaten phlox in the garden are microscopic nematode worms that infect the leaves and roots of plants, as well as a variety of caterpillars. In the absence of a timely response to the appearance of parasites, the bushes simply die, their vegetative processes are disrupted. If the plants wither, do not bloom, grow poorly, dry out, it is worth starting the diagnosis by looking for a source of danger in the ground or on leaves and stems.
Nematode
Most often, phloxes are affected by the stem or leaf variety of these roundworms. Root or gallic is quite rare. They have a filamentary, almost colorless body and are poorly visible without special equipment. Nematodes feed on plant juices and spread rather quickly in the soil, especially if the composition of crops rarely changes.
Signs of plant damage are the following characteristics:
- swollen neoplasms on the stems;
- fragility of shoots;
- dwarf bushes;
- waviness, deformation of the sheet plate;
- chopping flowers.
You can confirm the presence of nematodes using a simple experiment: the stem is cut off from the plant, its lower part is split into separate pieces, and placed in a container with water. If you look at the environment with a microscope or a magnifying glass after a few hours, you can see the worms. After that, all phloxes affected by the nematode are dug up and destroyed. The remaining soil is treated with bleach, not used in cultivation until 3-5 years.

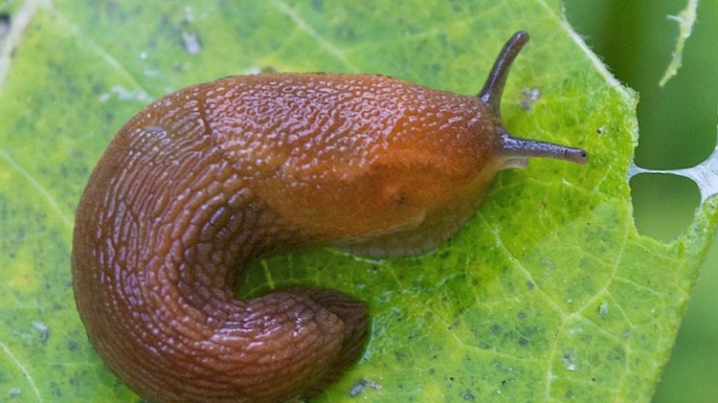
Slugs
Phlox is hunted by several species of these gastropods at once.They appear especially often in the garden in rainy, damp summers, attacking leaves and flowers at night. Slugs are extremely dangerous for young plants. To destroy them completely, it is recommended to take preventive measures - regularly weed out weeds, collect pests by hand, arrange traps with bait.
It is recommended to sprinkle paths and borders with ash, fluff lime.

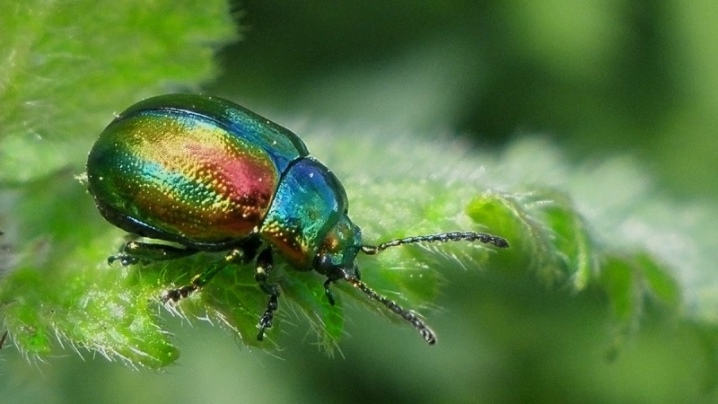
Bronzovki
This winged insect hunts for the sweet nectar of phlox, but its large size leads to the fact that the flower petals are torn and look unaesthetic. You will have to catch pests manually, otherwise they can greatly spoil the plantings.

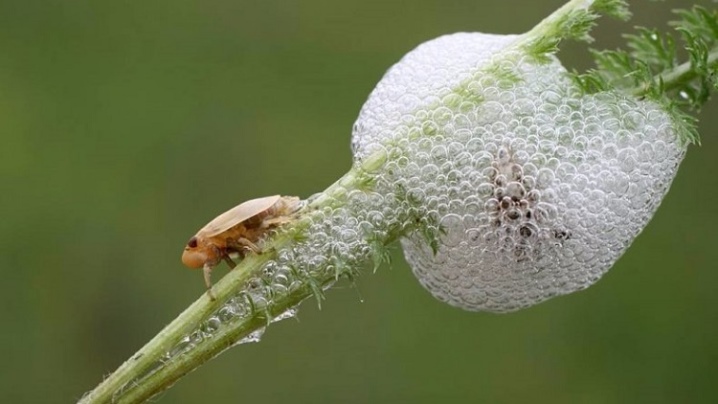
Slobbering penny
This pest belongs to bedbugs. It feeds on phlox leaf juice. The affected plant is not only damaged, it is also covered with secretions from the secretory glands of the pest. The slobbering penny breeds actively in dry weather.
Inside the foamy traces of its presence lurks the main danger - the larvae, which continue to destroy the plant.

Treatment methods
What to do if a disease is identified or the problem is not diagnosed accurately enough? For example, yellowing of the lower leaves may not necessarily be the result of an infection. Normally, it manifests itself in the fall, with the onset of leaf fall. In addition, overflow or lack of moisture, excessive shading, prolonged contact with the sun's rays also cause similar symptoms.
If the sources of problems still turn out to be an infection, a virus, damage to roots, stems, leaves by insects, you should pay attention to the methods that can be used to treat the diseases that have arisen. Usually, it is proposed to fight in several ways.
- With a viral lesion - mosaic or variegated - it will not be possible to bring the plant back to life. The fight is rather for the immunity of other landings. The affected phlox is dug up and burned.
- For powdery mildew, rust and other fungal diseases the main thing is to treat the plants in time with preparations containing copper. It is usually done prophylactically, but emergency treatment can also be used. First, all damaged plant parts are completely sprayed with a solution. Then they are eliminated - the shoots are cut off and burned.
- When affected by a nematode, the bush is destroyed along with the root. Especially valuable plants are saved by early spring separation of the most healthy shoots up to 4 cm in height, together with a part of the rhizome. The seedlings obtained in this way must be rinsed with running water, then sent to the ground under a shelter. The mother plant is dug up and burned.
- With verticillary wilting, the bush can be cured. It is recommended to rinse the roots with soaking in the “Maxim” preparation. Then the plant is transplanted by placing it in the well with the "Trichodermin" agent. A measure of disease prevention will be soil deoxidation with ash or lime.
- With phoma, it is quite difficult to get rid of the disease. The fungus affects the bushes for 2-3 years of life. If they do not represent a breeding value, it is better to immediately decide on burning. You can save individual parts of the plant by choosing healthy cuttings and keeping them in the Fundazole solution before planting.
In most cases, only timely started treatment gives results. If the disease has passed into an advanced stage, the easiest way is to destroy the plant.


Prevention measures
As a preventive measure for phlox diseases, experienced florists recommend using careful and timely care. The intensity of irrigation, the frequency of weeding, and the density of planting will all matter. The processing of plantings, which is carried out in the spring, is also mandatory. To prevent the reproduction of insect pests, a thorough autumn garden cleaning is required. Garbage is collected, burned, dead trees are uprooted - rotten stumps become a favorable breeding ground for various parasites.
It is not recommended to make surface watering, sprinkling of phlox. They are advised to apply water under the root, especially plentiful during the period of bud formation and flowering of the plant. Before planting, transplanting and rejuvenating, a thorough check of the material for the presence of root rot and parasites is mandatory. For effective prevention of phlox diseases, it is recommended to create a special treatment plan in the spring and carefully adhere to the selected schedule in the process of caring for plants. This also applies to treatment with insecticidal or antifungal chemicals, the use of which requires adherence to certain intervals between procedures.
Among the means used for prophylactic purposes are the following:
- contact;
- systemic;
- combined.


For example, when planting phlox seeds, it is recommended to use a contact action fungicide - copper oxychloride, which does not penetrate into parts of the plant, but protects it superficially. Before sprouts appear, it will fight dangerous fungi and mold. The duration of such protection is 2 weeks, you need to repeat the treatment 3 times in a row. Means based on strobilirubins protect longer, up to 42 days, but when spraying, beneficial mushrooms are also destroyed. For prevention purposes, such compositions are used no more than 2 times during the season, spraying them only on the leaves.
Systemic fungicides are distinguished by the fact that they protect plants by penetrating into their tissues and suppressing pathogenic microflora. Unfortunately, phlox infections quickly adapt to the composition of such drugs, develop immunity to them. The frequency of application of systemic drugs during the season is no more than 2 times. Preventive treatment provides protection for 30 days.
Many systemic products are recommended for preventive spraying at the stage when the sprouts are just emerging. This is how penconazole-based formulations work, coping with powdery mildew and other types of mycoses. The recommended concentration of the substance is 10 ml per 10 liters of water, the protective effect lasts up to 5 weeks.
Relevant among modern lovers of phlox and a preventive measure, which consists in the cultivation of useful mushrooms. Biological protection methods involve the use of natural enemies of dangerous bacteria or mold. The preventive use of such funds is carried out 3-4 times during the season. You can use "Fitosporin", "Baktofit", "Trichocin" - they all provide protection against powdery mildew for 3-4 weeks.


An approximate calendar for preventive treatment of phlox will be as follows:
- disinfection of seeds - the compositions "Glyokladin", "Gamair" are used;
- preliminary pre-planting soil cultivation - here "Trichocin", as well as preparations similar to it, has proved to be the best;
- vegetative treatment in 3-4 stages with an interval of 25-30 days - treatments with "Trichocin" and a complex of "Gamair" and "Alirin" are used.
It is important to understand that in the case of phlox, compliance with agrotechnical recommendations is of great importance in maintaining their health. If they are kept, then the own immunity of annuals and perennials will be strong enough to withstand a variety of sources of danger.
See below for more details.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.