Daisy: description and varieties, planting and care
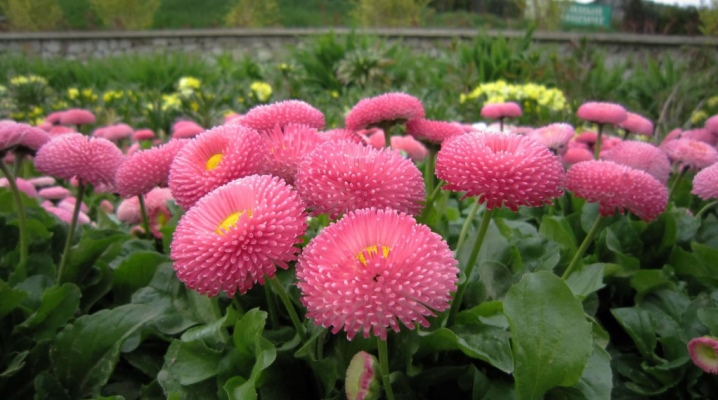

Delicate daisy flowers can be seen in almost every summer cottage. These flowers look like small bright suns, scattered over the flower bed and decorating the garden with their color variety. This culture gained its popularity in the circles of flower growers not only for its attractive appearance, but also for its unpretentious care.

Peculiarities
This representative of the flora is considered one of the first wildflowers to settle in the garden. Already in the 16th century, terry varieties were known - not only snow-white, but also red.
The plant belonging to the Aster family is distinguished by good frost resistance. Its height ranges from 2-30 cm. The leaf plates have a spatulate shape and are located closer to the roots, so the stem itself turns out to be without leaves, and one simple inflorescence in the form of a basket appears at its top. The middle is always yellow. The diameter of the flower is 1.5-6 cm, and the fruit of the presented culture is characterized by a flattened shape.
The appearance attracts gardeners with rich greenery and the ability to bloom several times per season. The first bloom most often occurs in early spring, and the second wave is usually observed closer to autumn after the heat has subsided.


Types and varieties
Usually the culture is kept as a biennial plant, but according to the general description, daisies can be classified into annual (bellis annua) and perennial (bellis perennis) species... The first type is a pattern with double white flowers and a yellow center. Flowering starts in August and continues until the onset of cold weather. Perennial varieties reach a size of 15 cm and have spatulate toothed leaves covered with pile. This flower blooms in May-June and blooms until November.
Another classification refers to Compositae boles., which can be plain, semi-double, or terry. Among them, the early and late varieties stand out.
Plants also differ in size - they can be divided into small, medium and large species. At the same time, keep in mind that the large-flowered variety will bloom much later, but its flowering period is also longer.


If you classify varieties by color, then the most common are:
- white;


- pink;


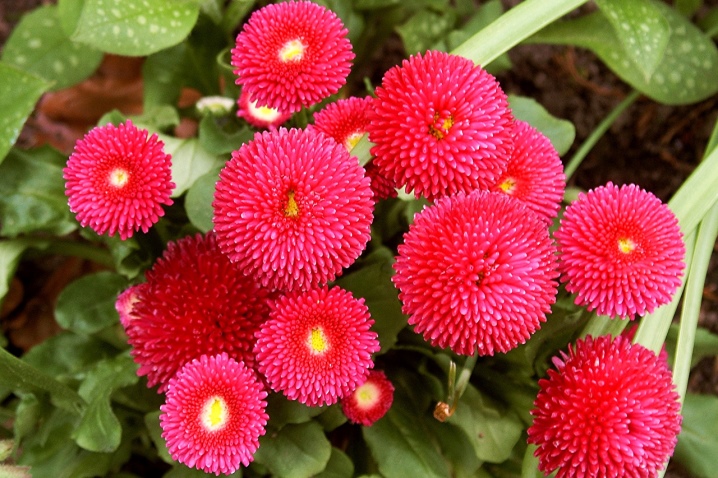
- red;

- light orange.

Let's consider in detail the popular varieties.
- Bellissima. A pompom variety, the width of the flowers is 5 cm. The basket is located at the level of 12 cm, the stem is characterized by density and elasticity. Most often, growers choose red, pink, white or two-color varieties for growing. Initial flowering can be observed already in the year of sowing. The variety is highly dependent on additional nutrition.


- Tasso Red. This variety is characterized by tubular, dense, strongly doubled petals. The flowers do not rise high above the rosette - by 6-8 cm. The Tasso variety has many colors, but it is Red, the red type, that is especially popular. The leaves are green, resilient, formed into a dense rosette close to the ground.


- Habanera. This variety belongs to the large-flowered varieties. The diameter of the pom-poms is usually up to 6 cm, although the basket itself is not particularly dense, due to which the flower takes on an openwork appearance.Peduncle "Habanera" grows up to 15 cm, and the colors are white, pink, red, white with red edges.


- "Pink ball". The variety is grown as a biennial, the height is no more than 15 cm. It forms many leafless, fleecy peduncles. The inflorescences are terry, the diameter is 3-5 cm. As the name suggests, the petals are pink in color, they are thick, the yellow center barely shines through them.


How to grow at home?
Some growers grow this representative of the flora in indoor conditions. To make him feel comfortable at home, place the flower in a pot in a well-lit place. To witness lush bloom, you can create a light partial shade or arrange diffused lighting. If you put the pot in a heavily shaded area, the culture will stop growing.
To keep a flower at home, choose a substrate that is well permeable and retains moisture. For example, a mixture of loamy soil with humus is suitable. Give preference to wide and shallow containers - in these pots the plant will feel more comfortable.
Indoor culture needs regular and abundant moisture. With a moisture deficit, the gardener will notice that the specimen grows poorly, has small and non-fluffy flowers.


It is systematically required to feed the plant, usually additional nutrition is applied every 2-3 weeks. Florists recommend using complex mixtures or alternating mineral and organic compounds. Particular attention should be paid to fertilization at the beginning of spring - at this time the plant starts growing.
Winter is not a problem for a flower that is grown on a windowsill. The growth of such a plant slows down, and development resumes in the spring. After 2 years, the specimens become old, and for rejuvenation they need to be seated.

Growing seedlings
The seedling method of breeding this culture is quite popular, let's analyze it in more detail.
Sowing
As a rule, sowing is done in February-March. It is recommended to sow the seeds in separate containers. So, paper, plastic or peat pots can be used as containers. If 1-2 samples hatch in one container, then they are allowed not to dive. When planting in a large container, seedlings should be dived.
Sowing is carried out on top of a moistened substrate over a long distance, the seeds are slightly sprinkled on top with soil or sand. At the same time, drainage holes must be made at the bottom of the container.
After sowing, the container is covered with a film or glass lid, creating greenhouse conditions for future seedlings. Every day the pot is ventilated, and with the appearance of the first shoots, the shelter is completely removed.


Seedling content
As soon as the first shoots hatch, you should continue to moisten the soil and maintain good lighting. When forming two true leaves, the seedlings are seated in separate containers.
Make sure that the soil does not dry out, and also maintain a 14-hour daylight hours. 2 weeks after germination, the room temperature should be lowered to +15 degrees Celsius, and in mid or late May, that is, a week before transplanting into the garden, it is recommended to harden the plant.
To do this, expose the seedlings to fresh air for a while, gradually increasing the time the sprouts are outdoors up to a full day.


How to plant in open ground?
You need to plant a plant on the site, following certain rules.
Optimal timing
It is customary to plant seedlings in April-May, after the gardener is fully confident that night frosts are no longer expected.
When sowing seeds on the site, other dates should be observed. For example, if the greenhouse is heated, then planting is carried out from the second decade of January to March inclusive; sowing in a greenhouse is recommended to be carried out from March to April.If planting with seeds is carried out directly into open ground, then you should wait until May, starting sowing after the soil has warmed up.

Fundamental rules
Before starting a transplant, you should choose a suitable site. As mentioned, this is a light-loving crop, so choose a brightly lit flower bed. The flower will feel good in partial shade or in the tree trunk circle.
Favorable soil type - light permeable soil, for example, loam with medium acidity. If the ridge contains a sandy type of soil, then you can dilute it with manure, humus, ash, peat.
Landing is done one month after the dive. Seedlings on a garden plot should be planted using the transshipment method. If the seedlings were grown in peat pots, then the transplant is carried out with them. The recommended distance between two specimens is 15-20 cm. Immediately after this procedure, water the planting site abundantly.

How to care?
Despite the fact that the daisy is unpretentious, some care will not hurt her.
Watering
Along with watering, loosening is an important procedure for the culture. So, in order to access the roots of fresh air, the soil is loosened in the spring after melting snow or precipitation. On dry days, the plants are well watered, but so as to prevent moisture stagnation. Bogging will avoid the mulching procedure. In the cool summer time, the earth is moistened 2-3 times a week.


Top dressing
The first time after transplanting, the sprouts do not need additional nutrition. The first fertilizer is usually applied after 1-1.5 months; during this period, liquid mineral dressings are suitable. Further, the land is fertilized once every 2 weeks, and it is better at this time to give preference to water-soluble mixtures, which contain nitrogen. The recommended volume is 10 liters of water per 20 g of the substance.
In the second year of life, the flowers begin to feed from early spring, adding nutrients every 2-3 weeks. They especially need abundant nutrition during the flowering period. Experienced summer residents advise feeding the plant with organic matter several times per season, for example, infusion of bird droppings or mullein. The ratio of substance and water is 1: 10, no more, since there is a chance of harming and burning young bushes.

Wintering
These flowers do not need to be dug up for the winter or hidden from the snow - the plant withstands cold weather well in the ground. Almost all varieties are quite acceptable for planting in the middle lane.
If the cultivation takes place in the northern regions, then it is worth preparing the plant for winter. To do this, the culture is spud and sprinkled with dry foliage, you can cover the flowers with spruce branches. Some gardeners prefer warming with dry sawdust or film, agrofibre is also suitable. If the bush is planted on the balcony, then it is better to remove it for the winter in a dark room with an air temperature of + 3 ... 8 degrees Celsius.


Transfer
This culture reacts very well to transplantation - this procedure serves to rejuvenate the specimen, it stimulates growth and development even at the stage of flowering and bud formation. Usually, it is customary to transplant in the second year. Do not forget to observe the gap between two adjacent plantings of 15-20 cm.

Reproduction methods
It is possible to breed the presented culture by the following methods:
- seeds;

- cuttings;
- dividing the bush.

Cuttings begin in late May - early June. First, a shoot with buds is separated from an adult plant, the leaves are cut by ½ and placed in the soil treated with Kornevin at a level of 1 cm. The planting site is constantly supplied with water and controlled so that the earth does not dry out. At the end of September, the seedling is transplanted to the finished site and insulated for the winter. Blooming is possible only next year.

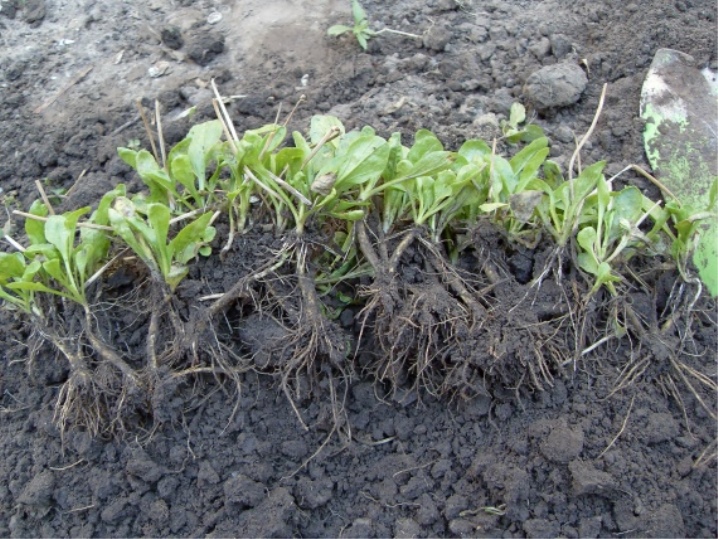
For reproduction by divisions, 3-year-old specimens are suitable. This procedure is performed in early spring or after flowering.First, the bush should be dug out, divided into 5 fragments, the roots should be shortened and planted in the prepared areas. Typically, each sample produces up to 12 new copies. Flowers and buds on such plants are cut.
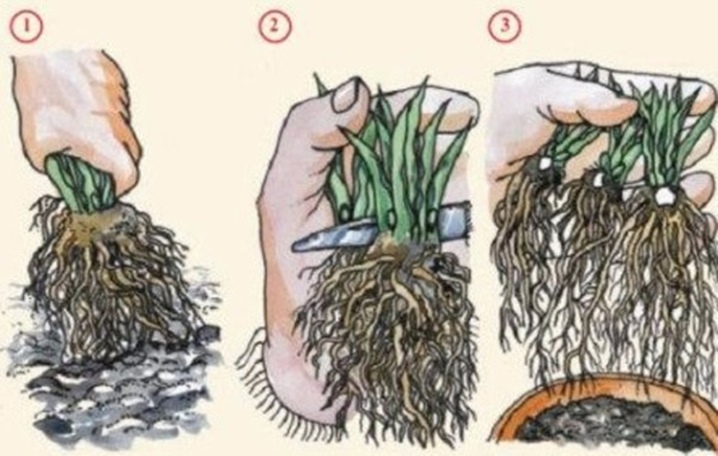
The process of propagation by seeds was described above, but the process of collecting seed should be described in more detail. It is harvested from non-hybrid mother plants, picking off only faded inflorescences. Then they are laid out on a paper sheet and left in the sun to dry. It is much easier to get seeds from dry inflorescences. The resulting grains must be wrapped in a paper bag, marked accordingly and stored. The seeds can be stored for about 3 years.
Diseases and pests
Diseases and dangerous insects often become a problem when growing this miniature shrub. It is important to notice the signs of the disease in time in order to start the fight in a timely manner and save the plant. First of all, as a preventive measure, it is important to observe all the rules of agricultural technology, and then common diseases will bypass this delicate flower. Thrips and caterpillars most often affect the culture.
- Thrips. These creatures prefer to hide on the underside of the sheet. The attack of thrips is indicated by the uneven yellowish-brown color of the foliage. Insecticides will help protect the plant. In this case, it is important to process not only the damaged specimen, but also all neighboring healthy plantings.
A week after treatment, re-treatment should be carried out.
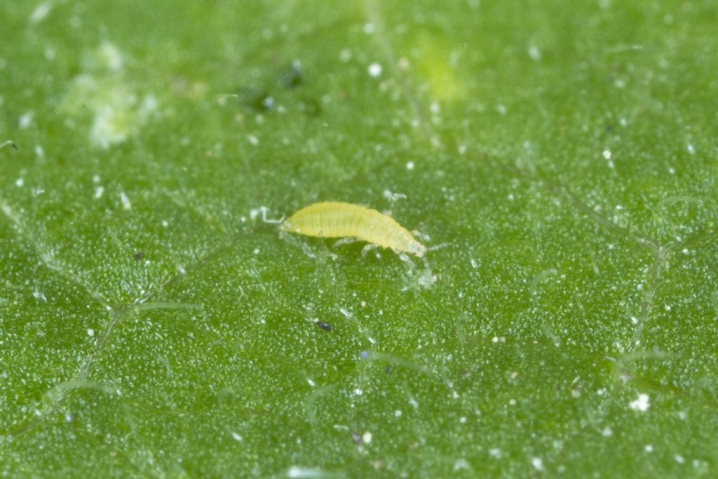

- Caterpillars. This is a fairly frequent unwanted guest of the presented flower. You can get rid of the tracks mechanically by manually collecting them in the evening. And also with these creatures you can fight with insecticides.

Pay attention to the most common diseases that can affect a member of the Aster family.
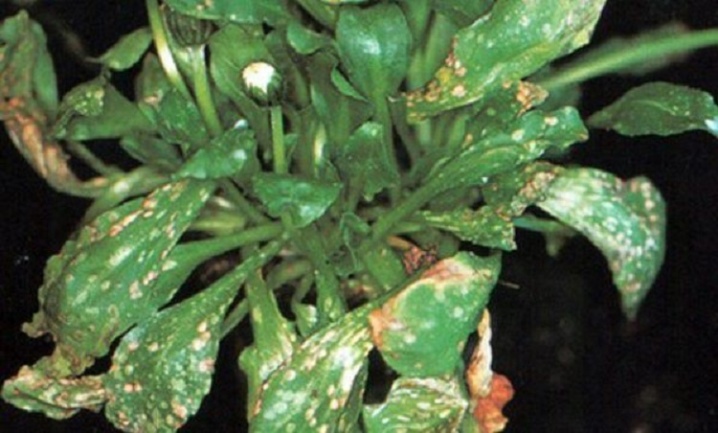
- Powdery mildew. A whitish bloom indicates the presence of the disease. Fungicides will help to cope with the disease. At the same time, it is important to carry out several treatments at intervals of 1-1.5 weeks.
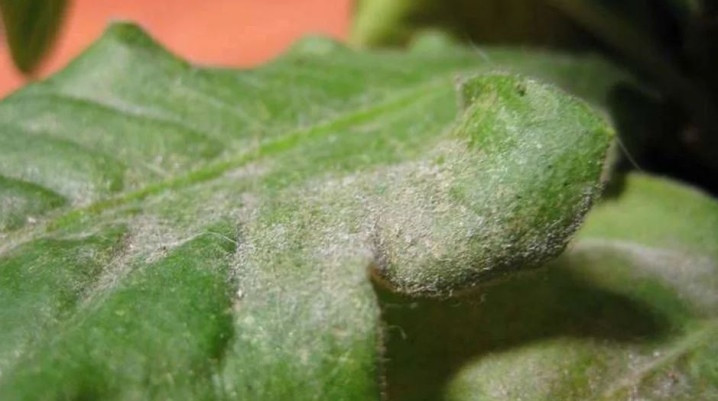

- Brown spotting. You can recognize the disease by the parchment-like spots on the leaf plates. Usually the cause is high humidity in the soil and air. It is recommended to dig up the affected specimen, dry it thoroughly and plant it in looser soil in a ventilated area.

- Gray rot. It is more often formed in autumn and spring. To prevent the disease, summer residents are advised to completely remove old foliage before winter. If the plant shows signs of rot, then the problem can be eliminated by treating the infected fragments with Fundazol.
Use in landscape design
The presented culture is distinguished by a variety of flower forms and a wide range of colors, therefore it can be present in a wide variety of garden compositions. It is always easy to find an aesthetic neighbor for her, but in a single planting these flowers look boring.


It is recommended to use them as a companion for taller crops such as tulips or daffodils. A picturesque landscape can be created by planting asters next to primroses, lilies of the valley, hyacinths, and other blue or orange flowers.


Garden ponds and streams, framed with pompom flowers, look very beautiful. And they are also planted as a ground cover crop on urban, Mauritanian and meadow lawns. In a collective planting, the gardener can turn to his creative abilities and plant flowers that vary greatly in variety and color, or, conversely, place similar buds next to each other. If this is a small-flowered variety, then it is customary to use it to decorate borders and alpine slides.

There are also tall varieties, for example, Cape varieties. They can be planted as a background for ferns, host, brunner, badans. Miniature shrubs look more harmonious in ceramic flowerpots, pots and containers.


Growing and caring for a daisy in the video below.







































































































The comment was sent successfully.