Everything you need to know about the marigold
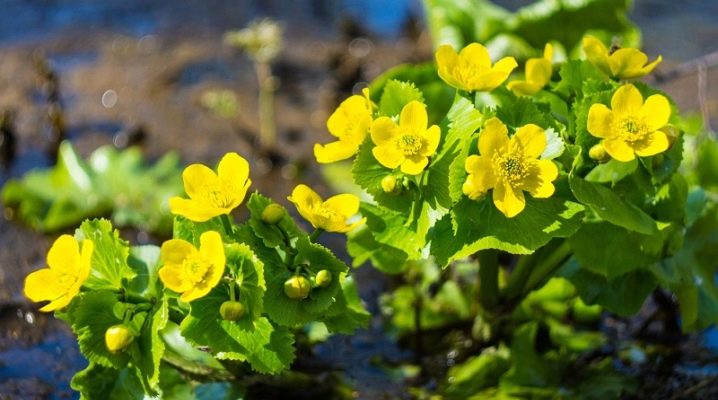

Blooming marigold can become a true decoration of a country flower garden. It is unpretentious, but loves moisture; it is found naturally in many regions of Russia. The study of the description of the plant, the features of its planting and caring for flowers in the open field will help to choose the appropriate option.


general description
The flower called marigold belongs to the genus of the same name of perennial plants. It belongs to the buttercup family and has a characteristic egg-yellow tint of the petals. Kaluzhnitsa as a genus numbers, according to various estimates, up to 40 species, all of which are poisonous. It is a relative of the buttercup, it grows mainly in places with wet or swampy soil.
This flower received its Latin botanical name for the shape of a corolla that looks like a bowl.


In Russia, the marigold was also called a water snake and a paddling pool. The plant has a number of typical traits for it:
- rhizomes are simple, short;
- the stem is strong, thickened, branched;
- height - 15-80 cm;
- leaves are smooth, rounded;
- flowers are large, male and female;
- petals are white or yellow;
- fruits with many leaflets.
Kaluzhnitsa grows in cold and temperate climates. Its swamp variety is found in the Scandinavian countries and the Russian Arctic. You can meet the plant in damp flooded meadows, in swamps, in water bodies and coastal zones. Most of the marigold species bloom in April-May, with rare re-budding in early autumn.



Popular species and varieties
Traditionally, the common marigold is represented by the forest form, but its garden variety with white, yellow petals, including the double type, is also grown on the plots. Such plants are more decorative, they are eye-catching, they are used to decorate the landscape. The main classification includes the following types of marigold.
Swamp
The most common garden plant species, often found in nature. The culture is perennial, with a stem height of up to 0.8 m, bright yellow flowers with 5 petals on long stems. Her corollas are the largest, and the budding period begins earlier than in other subspecies.
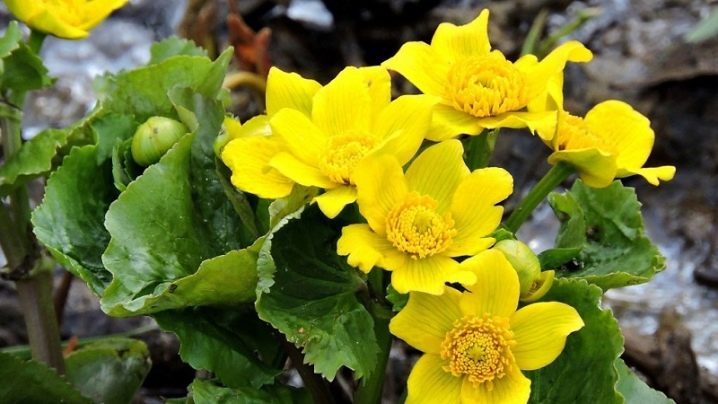

Fisty
The species is typical for the climatic zones of northern Japan, Sakhalin. Plants are distinguished by a powerful constitution, the stems are thickened, hollow inside, capable of stretching up to 120 cm in height. Flowering occurs at the end of May, the corolla of the pine marigold are large, up to 7 cm in diameter, painted in a rich yellow color.
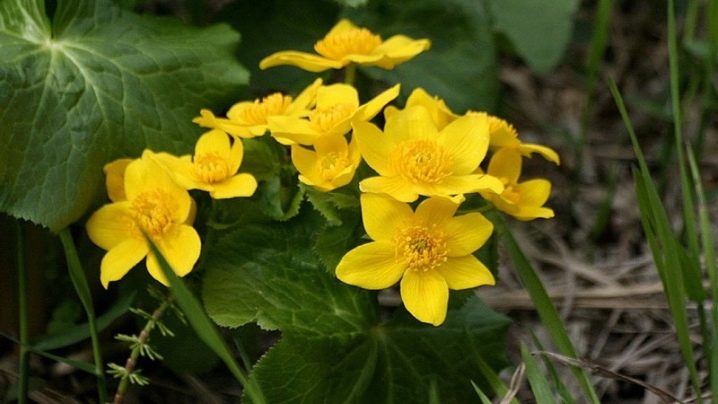

Multi-lobed
This species is found in alpine and subalpine climatic zones, in Asia and the Caucasus. Bushes are compact, no more than 30 cm high. Flowering occurs from May to June, with the formation of very large corollas up to 80 mm in diameter.
These varieties of marigold can be most often found on the plots of Russian summer residents, as well as in nature in a wild form. But plants are much more diverse. It is enough to study all subspecies included in this genus.
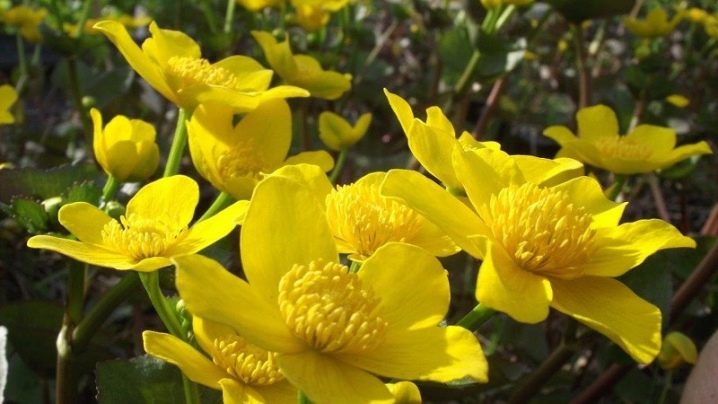

Other
Some marigolds are found only in certain regions of the world. Their petals can be colored during flowering not only in the traditional white, yellow tone, but also have a pink tint. Among the noteworthy varieties are the following.
- Bartier. A rare subtype with lush red-brown petals in the corolla.
- Rooting. A herbaceous plant, not very decorative in terms of decorative value, is found in the north.
- Japanese. A low-growing form of marigold with unusual leaves. Their plates are reniform, with pronounced jagged edges.
- White-flowered. Quite an exquisite plant. During the flowering period, snow-white buds bloom on it.
- Araneosa. Perennial shrub form, characterized by increased shoot formation. Araneose marigold blooms profusely and magnificently.
- Himalayan. This subspecies has unusual flowers with a yellow center and white petals. A very decorative form, found mainly in the Himalayas.
- Purple. This rare form impresses with its unusual color of petals during flowering. They are red and pink.
- Terry. Spectacular golden balls of flowers of this plant look incredibly beautiful. Terry marigold is most often a subspecies of the marsh form, which has undergone careful selection. Plants have a more compact and dense bush, look good in multi-stage landscape compositions.
- Floating. They are found exclusively in water bodies, due to the large leaves hanging on the surface of the water, they can be mistaken for a water lily. The color of the plates is red-brown, the flowers are small, white, with a yellow core.
- New Zealand. A miniature perennial variety with thick shoots and powerful roots. The shade of the flower petals varies from cream to light yellow, their shape is narrow, elongated.
- Fine petals. These marigolds are found in Alaska and in other parts of North America. Herbaceous perennial reaches a height of up to 20 cm, flowers are snow-white or pale yellow. There is also a cultivated variety with very large flowers.
- Arrow-shaped. A thermophilic variety, such plants are found in South America. In this subspecies, elongated creeping rhizomes, lancet spear-shaped leaves are formed. Bushes are small, up to 15 cm, cream or yellow flowers.
- Stem. A close relative of the marsh subspecies, this marigold is found in Nepal, India, China. The plant is miniature, with bright yellow flowers.
At present, it is not possible to establish the exact number of marigold varieties. The classification includes, according to various estimates, from 12 to 40 types of this plant.
Difficulties with the classification are mainly associated with the fact that the marigold is prone to variability. Mutations can be mistaken for new forms.



In garden culture, the most beautiful and rare decorative forms of marigold are increasingly used. Among the most popular varieties are the following.
- Grandiflora. Fine-petalled marigold variety with increased corolla dimensions.
- Auenwald. Large-flowered variety with yellow flowers.
- Monstrosa. Beautifully flowering terry form of marsh marigold. Lush and large corollas strongly bend peduncles to the ground.
- Double Gold. An unusual variety with refined petals and fringes around the edges.
- Richard Maatsch. Dwarf marigold with delicate lemon flowers and a simple flower shape.
- Goldschale. Large-flowered form with golden petals and purple-colored peduncles. A very decorative variety.
- Semiplena. An unusual variant with a decorative eight-petal corolla.
- Yellow Gigant. A variety with very large flowers of a rich yellow hue.
Despite the fact that marigold is a rather rare guest in Russian gardens, in European countries it is widely used to create spectacular landscape compositions.



Landing
Kaluzhnitsa takes root well in summer cottages and backyards with open spaces and moist soil. Plants need sunlight, especially during the flowering period. But they can be planted in partial shade, under deciduous trees. The soil is preferable moist, fertile, rich in humus.
Planting is carried out in early spring or autumn, in September. The distance between plants is maintained in the range of 30 cm.For the rooting period, it is imperative to ensure that the marigold is shaded on the south side so that young shoots do not die under the hot sun.


Care
When grown outdoors, marigold can easily endure the harshest winters. There is no need to shelter her for this period. The main care from spring to autumn is regular and abundant watering. The ground must always remain moist. The space between the bushes periodically needs to be loosened, weeded, ridding it of weeds.
During the season, fertilizing with complex fertilizers helps to maintain the health of the plant. Repeat it 2-3 times during the growing season. It is recommended to replant plants every 4-5 years. At the same time, the division of the roots is performed so that they do not grow too much. All work is carried out with gloves to exclude skin contact with the poisonous parts of the plant.



Reproduction
You can get planting material from marigold by vegetative and generative methods. Most often, it reproduces by dividing the bush. For this, the plant is dug up along with the roots. Then it is divided into several parts by hand. Each plant obtained in this way is placed in a separate hole or groove with a distance of about 30-35 cm, watered.
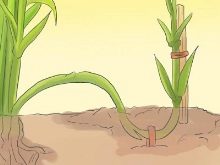
It is also quite easy to propagate marigold by layering. The procedure will be as follows.
- Selection of stems. They should be strong, rather long.
- Laying on the ground. The selected stems are fixed longitudinally on the ground surface.
- Digging in. Only the top of the layer remains on the surface.
- Care. It is no different from what the main plant needs.
- Formation of outlets. It takes place until next spring. The finished plant must have its own roots.
- Branch and transfer. The socket is cut off from the mother bush. Then you can act in a similar way to layering.
Seeds (generative method) rarely propagate marigold. This is due to the fact that they remain viable for only a short period of time. The collection of material takes place in June. Plants are sown immediately, then by the end of summer the seedlings will be strong enough to survive the cold.
The marigolds obtained from seeds begin to bloom in 2-3 years.


Diseases and pests
Kaluzhnitsa practically does not suffer from damage by typical plant diseases. When grown in a summer cottage, it does not often have to be treated with chemicals. For insects and other pests, the plant is also not very attractive.









































































































The comment was sent successfully.