Boxwood: description, types, planting and care
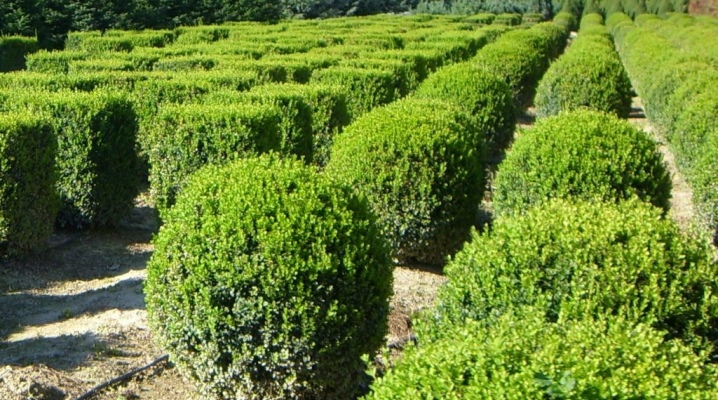

Boxwood is an evergreen shrub, and although it is native to the western regions of India and southeast Asia, the plant is found on almost all continents.


Peculiarities
Boxwood belongs to one of the oldest plants grown as an ornamental crop. The shrub is also known under other names: buks or buksus, green tree, gevan, and bukshan. Scientists suggest that the boxwood is about 30 million years old, but at the same time it retained its original shape and properties almost without modification. Under natural conditions, buxus is a low tree, reaching a maximum of 10–12 m in height. The shrub belongs to the category of long-livers of the plant world, some of its representatives have reached 500 years of age.

Boxwood has leathery elliptical leaf plates growing oppositely. Young leaves are characterized by a greenish-olive color, but as they mature they turn brown and become tough. The plant, which has reached 15–20 years old, begins to bloom, the flowers are tiny, unisexual, gather in small inflorescences. Buxus emits a rather strong odor during flowering.


The fruit of this shrub looks like a tiny rounded box with three branches, where shiny black seeds are placed. After ripening, the capsule opens, throwing out the seeds.


Bux is classified as a honey plant, but its honey cannot be eaten, since the shrub is considered poisonous, its leaves are especially toxic.
For growth and well-being, the boxwood is quite enough one hundredth of the necessary light. It can be called one of the most shade-tolerant trees. In ancient times, boxwood was highly valued for the similarity of its wood to amber.


Bux is also called an iron tree, because its trunks are extremely heavy and can sink in water. The wood of the green tree has a special strength; a variety of household items are made from it, characterized by significant strength and durability:
- canes;
- weaving devices;
- pieces for chess;
- various chests and travel bags;
- musical instruments;
- church bracelets.



The description of the axle as a plant with valuable wood can be found in Homer's "Iliad", as well as in ancient Roman myths and folk works of Georgia. Parts of the plant, in particular, the bark and leaves, are used in folk medicine, and the beech juice contains many useful substances.

Varieties
Boxwood is distinguished by a significant variety of species, on average there are about 30 of them, but most of them do not belong to ornamental crops. The most famous and common among gardeners are the following types:
- evergreen;
- Colchian;
- small-leaved;
- Balearic.

Buxus evergreen or Caucasian palm is the most commonly cultivated species as a garden plant. In nature, it is found in the Caucasus and the Mediterranean regions, where it grows as a small tree, reaching 12-15 m in height, and as a shrub. This variety of boxwood grows mainly in deciduous undergrowth. Directly this type is most often used in landscape design. In the garden, evergreen boxwood can grow up to 3 m.


This culture is considered melliferous, but the honey collected from it is inedible, since this type of buxus is extremely poisonous. The leaves are elongated (1.5-3 cm in length), with a shiny surface, not pubescent. They grow oppositely, petioles, in fact, are absent. Blooms in small greenish inflorescences. The most common varieties of this type are:
- "Sufrutikoza" is used in the design of fences and curbs;
- "Blauer Heinz" - a new variety, ideal as a carpet;
- Elegance is distinguished by good drought resistance.



Colchis boxwood is in Russia under state protection and is a plant in the Red Data Book. This type of bux grows in the highlands of the Caucasus and Asia Minor. It is characterized by very slow growth, of all varieties, it has the smallest leaves, they have a lanceolate shape and a length of 1-3 cm. Colchis beech is a fairly frost-resistant species and, in addition, its representatives have the longest life cycle. The height of the plant can reach 20 m, and the diameter of its trunk is on average 25 cm.

The small-leaved buxus belongs to the dwarf species; it rarely grows in height above 1.5 m. The leaf plates are also small, their length is about 1.5-2.5 cm. The characteristics of this species include frost resistance, the bushes are able to grow even at -30º, but they are afraid of the scorching spring sun, for this reason in late winter - early spring they need in the shelter. The characteristic features of small-leaved axle box include compactness and decorative appearance of the crown. It is considered the Japanese or Korean version of the buxus.

Distribution area - Taiwan. Popular varieties include:
- Winter Jam is quite fast growing;
- Faulkner stands out for its beautiful balloon crown.



Bolear Bux is the largest species of the family. The boxwood got its name from the namesake of the islands located in Spain. The main place of its growth is the Mediterranean. Representatives of this species differ in rather large leaves (length 3-4 cm, width 2-2.5 cm) and rapid growth, but absolutely unstable to frost. The plant needs a constantly moist soil, it normally tolerates direct sunlight, even for several hours in a row.


We take into account the climate
Previously, it was believed that boxwood can only be grown in the south and, for example, the middle zone of Russia is absolutely not suitable for it. But with proper agricultural technology and a well-chosen variety, even a southern plant can easily overwinter in such a climate. Evergreen and bolear box trees do not tolerate frost, therefore such varieties are suitable only for the south, but small-leaved ones are frost-resistant species. For the middle lane, such varieties as "Faulkner" and "Winter jam" are suitable. Feel good in cold climates and varieties of Colchis boxwood.



How to choose a seat?
Bux belongs to a rather unpretentious shrub, this applies to both planting and conditions of detention. It can grow under the sun, with insufficient moisture and even a lack of nutrients in the soil.
But still, the optimal environment for the normal growth of the buxus is clay soil with good water permeability and containing a sufficient amount of lime.
Moist soil stimulates the rapid rooting of the plant, but heavy and too salty soils are not suitable for planting boxwood, it will simply disappear on them. Ideal soil acidity for normal plant formation 5.5-6 units, therefore, a slightly acidic or neutral soil is suitable for the development of the root system and its growth.

The axle box does not like swampy soil and areas with stagnant water. You can try mixing boxwood soil yourself. For him they take:
- 2 pieces of deciduous land;
- 1 part coniferous;
- 1 part sand;
- some birch coal.



At what distance from each other to plant?
Boxwood is planted for different compositions and, accordingly, the distance between plantings depends on their type. With a single-row hedge, the bushes of the buxus are placed in 4-5 pieces every 25-30 cm. Low curbs or planting in the form of carpet are formed from 10-12 bushes, which are placed at right angles, but in a checkerboard pattern. The distance in such a planting is provided by about 15–20 cm between seedlings. Designers recommend using axle boxes for planting above 10-15 cm from the estimated height of the composition, this solution makes it possible to form the desired shape of the crown already on the site.
Thus, at the same time regulate the uniform level and density of planting, and also stimulate its vitality.

How to plant?
Boxwood is planted mainly in autumn, preferably in September - early October. A bush planted at such a time will be able to take root well before the start of frost. For planting, it is worth choosing a shaded area, without direct sunlight. The day before planting, it is worth preparing the tree:
- it is good to moisten the plant, this procedure makes it easier to extract the seedling along with an earthen clod, or soak the bush with its roots in water for a day;
- dig a depression, the size of which will be three times the size of an earthen coma;
- place a drainage layer 3-4 cm at the bottom of the pit;
- carefully place the bush in the hole vertically, straighten the roots well;
- fill the depression with a mixture of soil and perlite in equal parts;
- compact and moisten the soil around the plant.



Some gardeners recommend sprinkling a small layer of perlite around the stem of the planted plant. Re-watering the bush is necessary only after a week, provided that there was no rain.
In order to prevent the water from spreading during watering, but to be absorbed into the soil, a small earthen shaft is made around the plant. Its radius should be approximately 25–35 cm.

How to take care of it properly?
Boxwood is characterized by a relatively slow growth, the bush grows on average by 5-7 cm per year, and the diameter of the trunk adds about 1 mm. However, the decorative properties of the axle box significantly compensate for this slowness. Caring for a shrub is notable for its simplicity, so even a beginner will be able to grow it in the garden or in the country.
Watering
Boxwood does not need abundant moisture, a meter-long bush is quite enough 5-7 liters of water for one watering. It is necessary to water the plant in the morning or in the evening; in hotter weather or in regions with an arid climate, the axles are moistened somewhat more abundantly (once a week). From time to time it is worth washing the bushes to wash off the dust from the leaves.


Top dressing
For the first time, you can feed the bushes when they turn a month after planting, but if ash or compost was added before planting, then fertilizer should be applied only after six months. In spring and summer, boxwood has an active growth period, then it should be fertilized with complex mineral mixtures and nitrogen fertilizers. In autumn, potassium chloride and superphosphates are introduced under the shrubs. Organic fertilizers should be fed to the buxes every 3 years.
Also verified that a trace element such as magnesium has a beneficial effect on the condition of boxwood bushes, especially on its leaf plates... With its deficiency, yellowish spots form on the leaves.

Mulching and loosening
It is necessary to mulch the bushes in the last spring month and before wintering, for this they use a layer of peat of 5-7 cm. It is introduced around the circumference of the plant's trunk. It is worth loosening the soil after each watering, then the weeds that appear are chosen.


Pruning
For the first time, a boxwood bush can be pruned when the plant is 2 years old.The procedure is carried out with a garden pruner or scissors, the tools must be taken sharp and preferably with short blades. To protect the plant from possible infection, they must be used only clean. As a rule, the trunking is carried out in April - May. Boxwood lends itself well to decorative haircut, already three-year-old plants perfectly keep any given shape.

The crown of the bush allows you to form a wide variety of shapes, but most often the axle box is given a geometric shape: a cone, a cube or a ball. Mostly new branches are suitable for cutting, old shoots are shortened only when the bush has completely lost its shape. Experts advise updating the shape of the shrub monthly, besides, it does not require much effort - you just need to maintain the shape that was set earlier. After such an event, the boxwood crown acquires a greater volume, but the plant needs additional watering to compensate for the loss of useful elements.
It is not necessary to cut the plant when the weather is hot, the leaf plates are then prone to sunburn. The optimal time for such a procedure is evening or morning.



Transfer
It is worth replanting the beech bushes in the spring, in which case it will have time to get stronger by winter. An adult shrub is planted together with a lump of earth, while the same manipulations are carried out as when planting seedlings.

Such a plant is quite painless and steadfastly withstands a change in habitat. With proper care, the bush will continue to grow in a new area.
When buying a plant in the fall, you should not immediately plant it in the place of growth; experienced gardeners recommend digging it in the shady part of the site and wrapping it with a net.
For the winter, such a bush must be well covered to avoid icing.



Preparing for winter
Although a green tree is unpretentious, it should be taken thoroughly to winter. Preparations for frost begin in early November. First of all, the bush is watered abundantly, thus providing the roots with a supply of moisture for the winter period, and the soil around the trunk is mulched with rotted needles or peat. When carrying out such actions, you must avoid touching the mulch to the trunk.
Also, do not use fallen dry leaves as mulch, they will begin to rot and the bush can become infected with rot from them, in addition, eggs of harmful insects are often found in the foliage.


During the cold weather, it is recommended to wrap the bushes with non-woven cloth or burlap so that the plants do not freeze. In order to avoid the wind blowing off the coating, the canvas should be tied with a rope. If live fences are covered, then it is better to sprinkle the edges of the cover with soil. Before covering the plant, it must be tied with twine so that the branches do not break under the pressure of the snow. As a cover, the film is not very suitable, since moisture collects under it and high temperature indicators are kept.



After removing such a coating, a sharp change in temperature occurs, which negatively affects the state of the plant until its death. Wood shavings, straw are well suited as a heater; fallen leaves can also be used. Creating a shelter for the winter, you can build a frame made of slats, in height it should be 20 cm higher than the bush. The free space is filled with insulation, and the structure is covered with roofing material on top. With the beginning of spring, it is taken apart, the straw is shaken off the branches, but this must be done gradually, so that the boxwood gradually gets used to the bright spring sun.



The subtleties of growing in different regions
In nature, on the territory of Russia, only Colchis boxwood can be found. It grows in the Krasnodar Territory and the Caucasus. The plant is characterized by slow growth and resistance to low temperatures. Now you can often see bushes of buxus growing on the streets in the Moscow, Vologda or Leningrad regions, in the south of Siberia, the Far East and the Urals.These are mainly frost-resistant, decorative varieties that do not need excessive care, but have attractive characteristics for landscape design.

The Moscow region, as it turned out, is quite a suitable region for growing boxwood. Although large shrubs cannot be grown here, the plants grown here are well suited for a variety of geometric shapes or creating labyrinths. Cold regions such as Siberia and the Far East are not scary for the buxus. Thanks to the efforts of breeders, now here, too, it is quite successfully possible to cultivate some varieties of this species. The main thing in this business is to choose the right landing site.



To grow bushes in such weather conditions, you need to take into account several nuances:
- the place should be closed from the wind;
- shake off snow from the shoots to avoid breaking them off;
- the last pruning must be done before the beginning of September;
- young plants should be shaded from the early spring sun;
- equip a drainage system to remove excess moisture.
These simple rules will help you grow beautiful boxwood bushes even in such a difficult climate.

Housekeeping in a pot
Buxus is well adapted to growing in pots, but here it should be borne in mind that the state of growth of the bush directly depends on the volume of the container. In a large container, boxwood will grow much more slowly. Watering the shrub in such conditions should be done every day.
As a top dressing for potted boxwood bushes, it is recommended to use special fertilizers in liquid form. They are added to water for irrigation and used every two weeks.

When the leaf plates redden, it is worth adding nitrogenous fertilizer. For the winter period, the tub with the tree should be placed in the same, but slightly larger size, and the empty space between them should be filled with crushed bark. The containers with the plant are placed on the blocks to exclude contact with the ground. Boxwood also feels fine at home as an ornamental plant, it is great for this type of cultivation due to its unpretentiousness and compact size. Evergreen, Balearic and small-leaved buxus are popular as domestic crops.



The location for an indoor green tree should be selected with moderate lighting and constant temperature and humidity.
To retain moisture, the soil around the trunk should be covered with moss or small stones, they also give the tub a more aesthetic appearance.
Caring for indoor boxwood is regular, but not vigorous watering and spraying. In addition, bux is very often used for bonsai-style compositions, due to its beautiful appearance, good tolerance to pruning and the ability to feel normal in small containers.



Reproduction methods
Boxwood is bred in several ways, although the vegetative method is most often used. Cutting is considered the best option for reproduction of the axle box. For him, you can use the shoots that remain after cutting.
Cuttings can be cut throughout the year, but experts recommend doing this in March - July.
Shoots cut off earlier are too fragile and poorly withstand the sun's rays, therefore they need shading.



Using this method of reproduction of the buxus, you need:
- cut off young cuttings along with a part of the shoot (about 10 cm);
- in a container with holes at the bottom, pour a universal substrate for ornamental plants and sand in equal proportions;
- remove the lower leaves from the branch, and process the cuttings themselves in the rooting machine (you can use "Kornevin");
- place sprouts in small holes and press down with earth;
- It is good to moisten the plants, place the container in a shaded place (in the winter time - in the basement, and in the summer - in any dark part of the house, but it is worth covering with a film).
The sprouts take root after 1-2 months, after which they can be planted (recommended together with an earthen clod) in a permanent place in open soil. Seedlings need to be moistened and sprayed with water every other day.

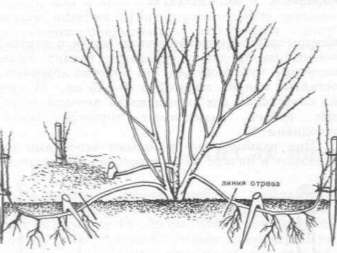
Reproduction by layering is distinguished by its simplicity and effectiveness at the same time. For him, you need to tilt a healthy lateral shoot to the ground and dig in. Watering and feeding is done in the same way as for the parent bush. When the roots appear, the cuttings are separated from the shrub, dug up and transplanted to a chosen place with an earthen lump.

You can try to propagate boxwood with seeds. To do this, the recently harvested seeds are soaked for 5-6 hours in warm water, after which they are placed on a damp gauze or napkin and kept for 1-1.5 months on the bottom shelf of the refrigerator. The seeds need to be moistened regularly. After this period, their day is kept in a solution of a growth stimulator, then the seeds are placed between two wet wipes for about a month. It is constantly necessary to maintain a humid environment, after this time sprouts hatch.


Seeds are sown in a container with equal proportions of peat and sand, but they need to be placed in the soil with the sprouts that have appeared. To create a mini-greenhouse climate, the container must be covered with a film and placed in a warm, dimly lit place. After the emergence of shoots (after 2-3 weeks), the film can be removed, and the shoots can be moved to a semi-darkened place with a temperature of + 18-20 degrees. Caring for the bushes consists in moisturizing, fertilizing with complex mixtures, weeding. It is worth planting in open soil in the spring, after the threat of night frosts has passed.


Diseases and pests
Boxwood is susceptible to attacks by a fairly large number of pests, in addition, it is prone to fungal infections, and if you do not take any measures, the plant will disappear. Among the harmful insects, the greatest danger to the buxus is the boxwood gall midge, also called the mining fly. She lays her eggs in young leaf plates, which begin to turn yellow, the plant dries up. Treatment of the plant consists in its periodic treatment with insecticidal preparations, for example, "Karbofos" or "Aktara" every 10 days.


Among other insects, axle boxes damage:
- felt - causes drying of shoots and the formation of bulges on the leaf plates, the fight consists in the use of "Fufanon" or "Tagore";
- the spider mite reveals itself by the formation of thin threads of cobweb on the leaves, the protection of the plant consists in the treatment with the preparations "Karbofos" or "Aktara";
- the boxwood flea provokes the appearance of a whitish bloom and stickiness of leaf plates, the treatment consists in breaking off the infected foliage and washing the bush with mineral oil;
- The boxwood firewood is characterized by the fact that its caterpillars braid the bush with a whitish cobweb, fight against it with insecticides "Fury" and "Fastak".
In addition to parasitic insects, boxwood also attracts such insects, which, on the contrary, help in the fight against pests. Among them are a ladybug, a flier, a hoverfly, an earwig.






Among the diseases for buxus, fungal lesions are considered the most dangerous; they are manifested by characteristic spots on orange leaves. To heal the plant, all affected parts must be removed and burned outside the garden. There is also such a disease as shoot necrosis, when the ends of the stems begin to die off and the leaves become covered with spots.
The bush is treated with multiple treatments with fungicidal preparations. Sometimes buxus can develop cancer, with such a disease it is necessary to remove all diseased areas, while cutting off the healthy part. All sections must be moistened with "Fundazol".



Use in landscape design
Boxwood is a fairly popular shrub for use in landscaping. Its application is quite wide:
- curbs;
- live fences;
- mixborders;
- alpine slides;
- rockeries;
- green walls;
- edging tracks.




The green tree is beautifully combined with various ornamental plants; blooming crops such as hosta, for example, are beautifully set off against its background. Also, boxwood serves as an excellent addition to the site near water bodies. It makes great decorations for both the garden and the terrace. - standard trees in tubs. The spherical shape of the shrub on a long trunk will appeal to many, moreover, it is easy to make it yourself.



Boxwood is an undemanding plant, quite resistant to various factors. - knowingly acquired the love and admiration of gardeners, its compactness and delicate appearance make boxwood more and more popular. It has become a real decoration of city flower beds and parks and is increasingly becoming a pet in the garden or summer cottage, as well as in apartments.

If you want boxwood to decorate your site with its beauty as soon as possible, you need to know the nuances that will accelerate its growth and increase the volume of greenery. This is detailed in the video below.






























































The comment was sent successfully.