Magnolia Cobus: characteristics and cultivation
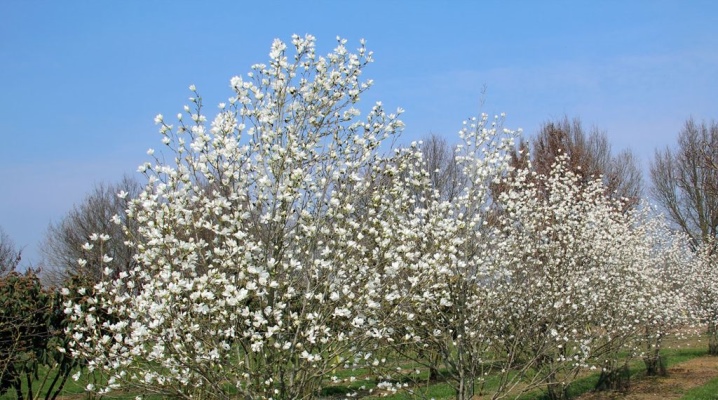

Magnolia kobus was first studied at the end of the 18th century. botanist Thunberg, and in 1817 the tree got its current name. In the wild, the plant grows up to 20-23 m, in a cultivated state it does not exceed 10-15 m. In our article we will tell you more about how to plant and grow this ornamental plant.
Description
Magnolia Cobus is widely used in gardening and landscaping. It is a deciduous tree with an annual growth of 20-25 cm. At the age of 10, the cobus grows up to 2.5 m in height and up to 1.5 m in width. In adulthood, it has a size of 10 m, the crown diameter is 4-5 m.


The flowering of decorative magnolia begins no earlier than 10 years of age, therefore, for planting on the site, it is best to purchase an 8-9 year old seedling.
The flowers give a strong vanilla-citrus aroma. Flowering occurs in April-May before the leaves open and lasts about 2 weeks.
Ripe fruits resemble a pine-shaped bunch 10-12 cm long. The seeds are in a scarlet shell - it is visible from the side and gives the plant an exotic look. The shell protects the seeds from drying out, so you should never buy dry magnolia seeds - their germination is minimal. Fruiting usually occurs in October.


Planting and leaving
For planting, it is better to use 8-year-old seedlings, preferably with a closed root system, then the rhizomes will not be injured during transshipment, and this will facilitate the survival of the culture in a new area. You need to land the cobus in September - early October. At this moment, the plant is in a dormant stage, due to which it takes root well. When planting in April, the seedling may grow ahead of time and fall under recurrent frosts.


It is very important to choose the right site for planting a culture. This should be a well-lit area, protected from gusts of wind.
It is best to plant magnolia on the west or east side of your garden plot.
Placement in the north is allowed only when the plant is illuminated by the sun for at least 3-4 hours a day. Magnolia is not planted in the south.


Kobus prefers peaty soil. It should be nutritious, slightly hydrated and drained. Although magnolia cobus can grow and develop successfully on loamy and sandy loam substrates.
When planting magnolia, it is necessary to prepare a 1x1 m planting hole. Expanded clay, crushed stone, pebbles, broken brick or other drainage material are laid on the bottom, then sprinkled with prepared soil mixture - and a young bush is planted. In this case, the root collar should rise 3-5 cm above the ground level. After that, the land is thoroughly compacted and irrigated. When the water is completely absorbed into the soil, the trunk circle is sprinkled with mulch - coniferous bark or wood chips.


In order for the kobus to please with its bright colors, the shrubs will need useful substances. After the snow melts at the root, granular complex fertilizer is applied, with the arrival of summer, they switch to liquid formulations, alternating mineral components and organic matter.


You can make a universal cobus feeding for magnolia with your own hands. To do this, dissolve 15 g of urea, 20 g of ammonium nitrate and 1 kg of manure in 1 bucket of water - the consumption per adult plant is 12-15 liters. In August, the plant needs phosphorus and potassium - these elements increase the winter hardiness of the crop.
Starting in September, the introduction of dressings is stopped.
Magnolia cobus is demanding watering, especially its young plants. It is very important not to allow the soil to dry out - for the full development of this crop, intensive irrigation and mulching is required.
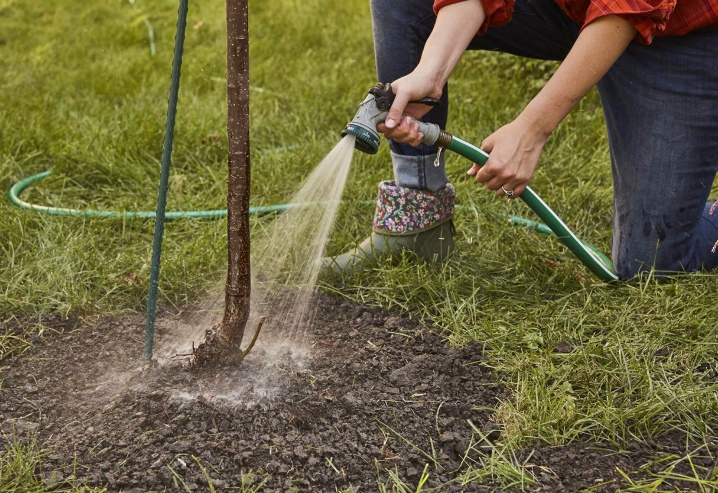

The advantage of this magnolia variety is that it does not require shaping, since pruning does not affect either the flowering intensity or crown formation. And here sanitary pruning should not be neglected. All damaged and dried branches should be cut off, and the cut area should be lubricated with garden varnish.
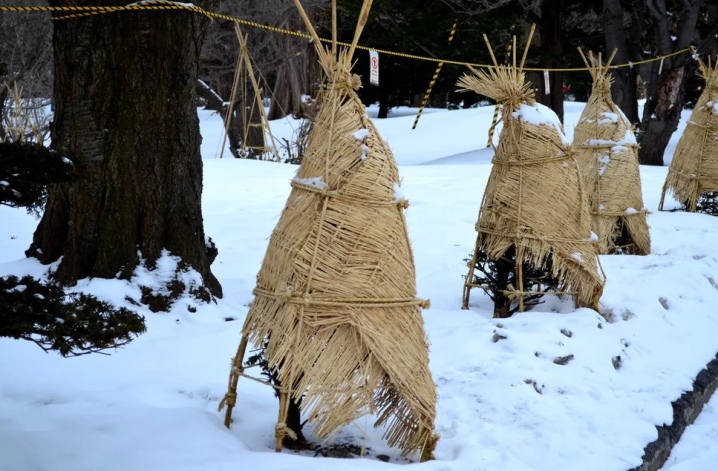
For the winter, the kobus is covered with burlap or agrofibre. This increases the frost resistance of plants and protects them from birds. A non-woven material can also be used to cover the trunk circle - then the mice will not be able to damage the roots and young stems.

Reproduction
Magnolia can be propagated by seeds, as well as cuttings and layering. If you want to preserve all the main varietal characteristics, then vegetative techniques should be preferred. When growing magnolia from seeds, sometimes a new variety is obtained, different from the parent.
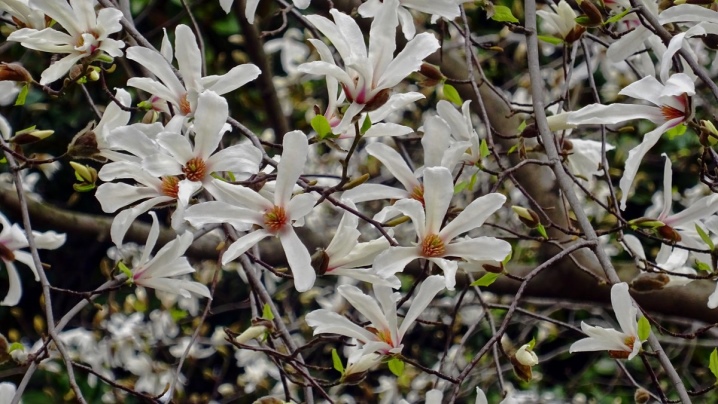

Seedlings are stratified before planting, and then germinated in moist moss. Germination rate is usually 50-60%. Transplanting into open ground is carried out only at the end of May, and it is best to transfer the seedlings by transferring them together with an earthen clod.
When grafting, the material is obtained from young plants, the workpieces are cut off until the concrete is blooming. It is desirable that the lower part of the cutting be lignified, and the upper one green.
The prepared material is planted at the end of June - the first half of July under a greenhouse, in which the optimum temperature and an increased level of moisture should be maintained. Rooting usually takes at least 5-10 weeks; in a cold room, this process slows down significantly. But overheating is also dangerous for cuttings: at temperatures above +25 degrees Celsius, young seedlings may die.


To propagate a cobus by layering, in the spring you should choose a branch that grows as close to ground level as possible. It is pulled down and fixed in this position. In the place where the branch comes into contact with the substrate, it must be sprinkled with earth. With the onset of autumn, the seedling is separated from the parent plant, and they grow at home for another year.
Diseases and pests
For decades, it was believed that the kobus resisted pests and infections. However, this kind of magnolia can also have problems. The most common is chlorosis, from which yellow spots appear on the leaves, but the veins retain a green tint. Chlorosis indicates that an excessive amount of lime is present in the soil. An unfavorable situation can be corrected by adding acidified peat or coniferous substrate to the soil, and you can also use iron chelate.


The development of magnolia kobus can be suspended due to the fact that the earth is oversaturated with minerals - this leads to soil salinization. A sign of a problem will be the wilting of the edges of the sheet plate.
In this case, you should increase the amount of irrigation, and completely stop the application of nutrient dressings.
Thrips can live on magnolias, as well as mealybugs and spider mites. These insects feed on vital juices and weaken the plant, as a result of which the magnolia sheds its leaves early. In addition, pests are active vectors of viruses for which there is no cure. It is possible to destroy insects with acaricidal agents: the greatest effect is given by "Actellik" and "Aktara".


In winter, the tree is harmed by rodents. If you notice any bites, you need to spray the affected area with a solution of Fundazole.
When grown in the middle lane of our country, magnolia can be affected by fungal pathologies. For the treatment of plants, fungicidal solutions are used, but they are effective only at the initial stage of the lesion.

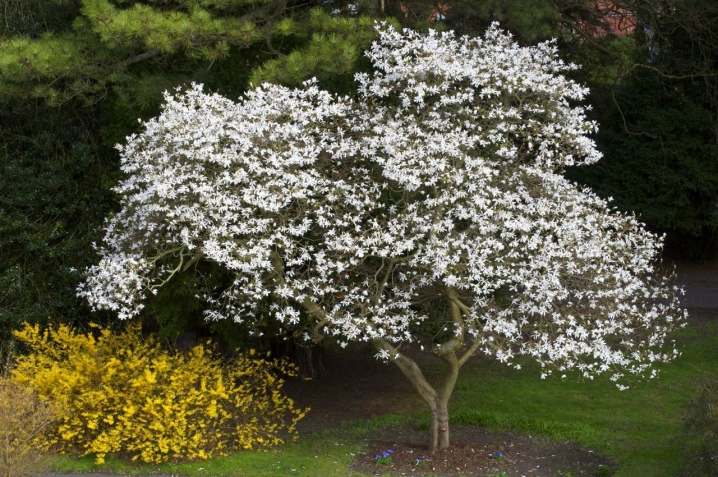
Use in landscape design
Magnolia Cobus is widely used in landscape gardening, and is also planted in personal plots. This ornamental shrub looks beautiful as a single planting and in combination with conifers.


































































The comment was sent successfully.