The cotoneaster is brilliant and the peculiarities of its cultivation
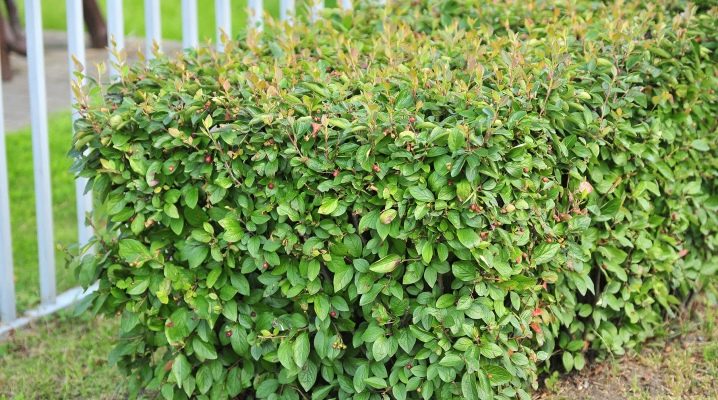

The brilliant cotoneaster (Cotoneáster lucídus) is a shrub from the genus Cotoneaster of the Rosaceae family. More recently, more precisely since 2000, it is believed that the plant is a type of holly cotoneaster. It is widely used as a decorative culture.
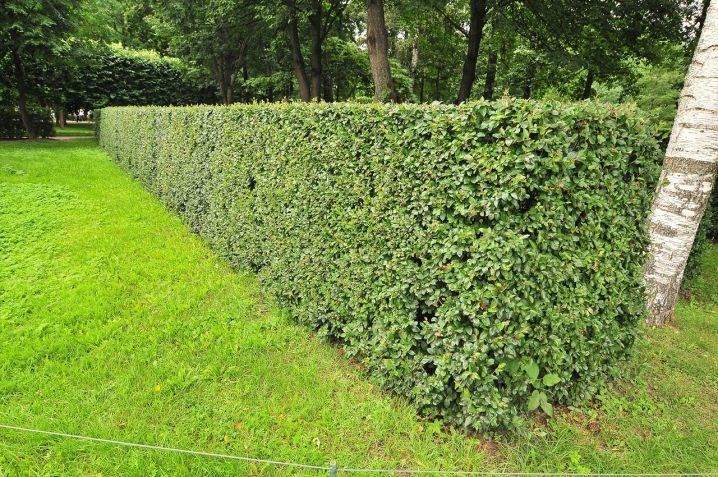

general description
In the modern world, it is impossible to imagine landscape design without ornamental shrubs and tree-like crops, the brilliant cotoneaster is one of the representatives of this family. With its help and thanks to its size, hedges of various heights and purposes are grown, the plant is used for zoning, and without any special financial costs.
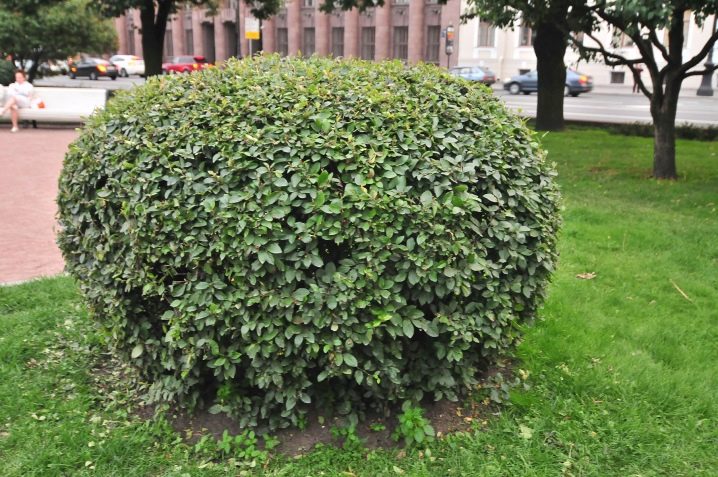

Description of the brilliant cotoneaster.
-
Deciduous shrub of upright form, up to 3 meters high, has a dense crown formed by straight shoots growing in different directions with a large number of lateral branches.
-
The diameter of the crown usually exceeds the height of the cotoneaster by one and a half times, and the rate of annual growth of dense leafy shoots is considered average.
-
Dark green leaves with a dense leathery structure have a glossy upper surface, for which the cotoneaster was defined as "shiny". The lower surface of the leaf is yellow, pubescent, almost tomentose at the beginning of development, gradually becomes almost naked in adult form. In autumn, the leaves are painted in dark tones from red-brown to dark burgundy palette.
-
At the time of flowering, the cotoneaster forms loose inflorescences in the form of corymbose brushes, consisting of 5-12 pink flowers. Each flower consists of wide-triangular sepals, petals 2.5-3 times longer than the sepals, as well as stamens and 3-4 columns. Small flowers cover the vegetative mass so densely that greenery is practically invisible from under them. The shrub blooms in May or early June, flowering lasts a month, maybe a little more.
-
After flowering, spherical black fruits with a shiny surface and reddish-brown flesh are formed on the cotoneaster. The size of the berry is from 7 to 9 mm, there are 3, sometimes 2 seeds inside. Fruits ripen in the last decade of September and early October, berries remain on the bushes for a long time, up to frost. The fruits are edible, but have almost no taste and have no nutritional value. The first fruiting occurs in the fourth year of life.
-
The plant is an excellent honey plant, comparable to linden and raspberry - flowers emit a large amount of nectar that attracts many insects. Bees actively collect sweet liquid and “graze” on the bush from dawn to dusk.
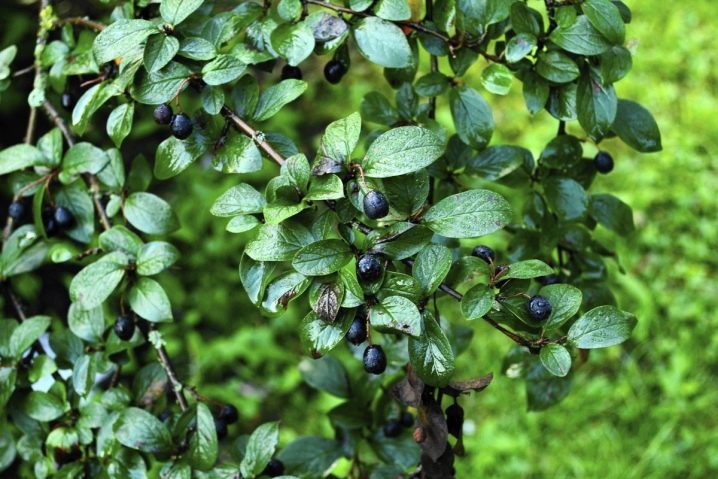

Among the ornamental shrubs, the cotoneaster is perhaps the most popular due to its unpretentiousness and high decorativeness. The culture is used for landscaping the urban landscape, garden and private plots.
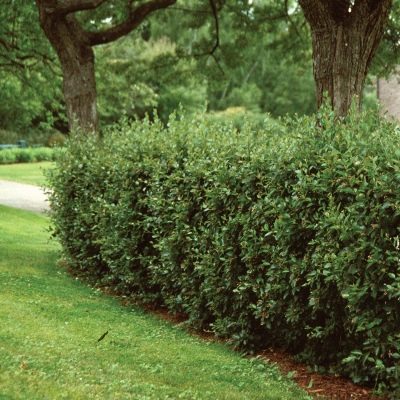

Culture advantage:
-
height from 2 meters or more;
-
dense crown, allowing the cotoneaster to be used as a hedge;
-
high decorative qualities throughout the growing season;
-
life span - the shrub fully lives for at least half a century.
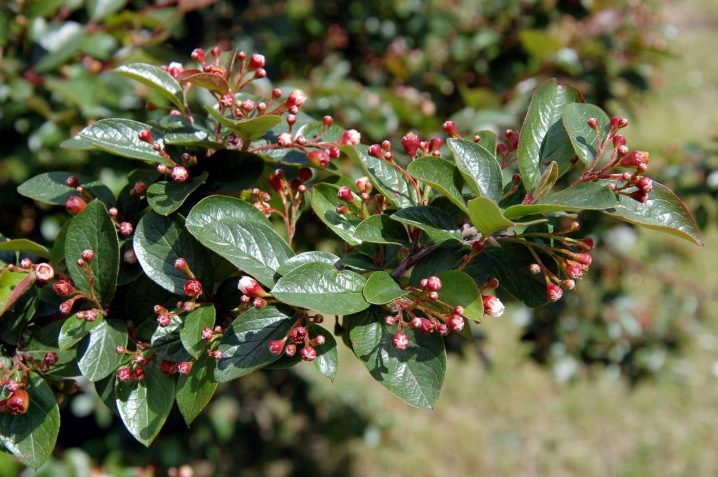

One significant drawback of the cotoneaster is that it is believed that the bush grows quite quickly, in fact, you can wait up to 10 years for a three-meter height, but the end result is worth the time spent.
It is possible to penetrate through such a hedge only if a passage is cut out; it is absolutely impenetrable to the eye in summer and gives very little clearance in winter. An ornamental bush will serve as a highlight of the garden.
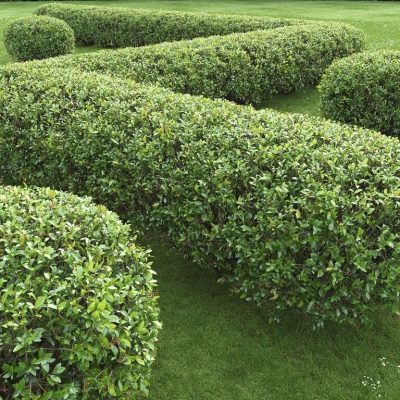

Landing
In order for young seedlings who have changed their place of residence in a nursery to a garden or city plot, feel good and develop actively, several rules must be followed. The practice has developed the most optimal algorithm.
-
Seeds can be sown all year round, creating greenhouse conditions for good germination.
-
For planting young plants, choose a site with protection from winds and drafts. The constant direction of the wind gives the shrub the same direction of growth of the shoots, therefore, if you do not pay attention to this factor, you can get a one-sided bush.
-
The cotoneaster does not have special requirements for lighting, but it grows faster in sunny places.
-
Seedlings with ACS (open root system) are planted at the beginning or at the end of the growing season, with ZKS (closed root system) can be planted in a permanent place in spring, summer, autumn.
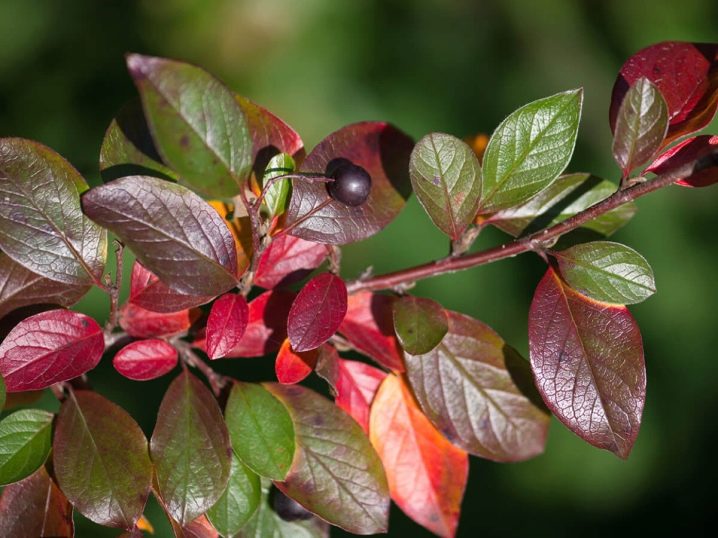

The half-century life of the shrub requires a thoughtful approach to the place of constant growth and landscape planning. To create a hedge, you will have to make mathematical calculations: measure the length of the covered perimeter and divide it by the optimal distance between the roots. In turn, the last parameter depends on the final goals. To obtain a high, but thin barrier, 3 roots are planted per running meter. A denser and less tall wall will require 4-5 plants.
The right approach to this issue will allow the owners of the site and their descendants to admire the colorful green design for decades.

For planting, you will need to work on the structure and composition of the soil. Saplings love soil of approximately the following composition:
-
lime - 300 g / sq. m .;
-
sod soil - 2-5 parts;
-
compost or peat - 1 part;
-
coarse river sand - 2-5 parts;

The hedge density is achieved by planting in a checkerboard pattern, so that later the crown closes and the overgrown bushes become impassable. During planning, do not get carried away with the quantity: border plantings in 3 rows are not recommended, since they will look untidy for a long time, and then too thickened.

Pits for seedlings are dug to a depth of 0.6 meters, the bottom is covered with a drainage layer and the prepared nutrient mixture is poured. For mass plantings, it is much more convenient to use the trench method, when a trench of the appropriate depth is dug over the entire length. It is necessary to plant it carefully, carefully spreading the roots and filling it with the remnants of the nutrient soil. The root collar is left flush with the surface.
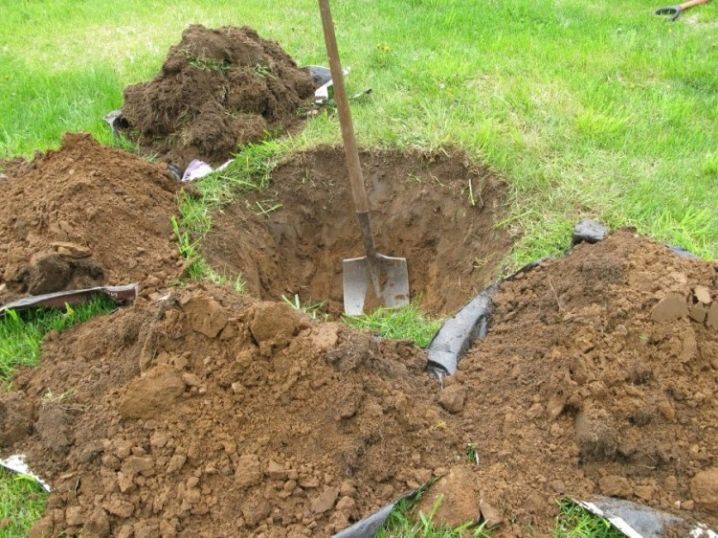

During backfilling, the soil around the plant should be carefully compacted to prevent the formation of voids. The root surface is covered with a 5-7-cm layer of high-moor peat mulch.
Care
For a cotoneaster to look perfect, it must be cut properly, and cutting requires a certain level of skill and experience. On an adult shorn shrub, the slightest flaws are noticeable. If you think in advance about the planting scheme, the type of future plantings, the plan for the location of the shrub and its shape, follow the cultivation technique, the final result will be great. In winter, plant care is not required, all events are held in spring, summer, autumn. The cotoneaster begins to form in 2-3 years.

Watering
The shrub belongs to the drought-resistant group - with a sufficient amount of natural precipitation, it does not need artificial irrigation. If there is no rain, the bushes are watered at the rate of 10 liters of moisture once every 2 weeks under each root. The shrub is able to survive the drought perfectly, but it will lose its decorative effect. The foliage will become dull, dull, flowering may be rare, the flowers quickly crumble without forming an ovary, which ultimately deprives the culture of such decorations as sparkling coal-black berries.
Weeding will help rid the planting of weeds that are competing for nutrients.

Loosening provides oxygen access to the depth of the root system, mulching - long-term preservation of moisture, helps the development of beneficial microflora.
Top dressing
Additional nutrient introduction begins from the second or third year after planting. During this time, the bush will have time to use up the applied fertilizers, the more the phase of active growth begins. Consequently, it will need much more micro- and macroelements to ensure the full development of the entire system than is contained in the soil.
Fertilization scheme:
-
in early spring, nitrogen-containing preparations are used that stimulate the active build-up of green mass;
-
during the flowering period, the cotoneaster needs phosphorus and potassium compounds, while the introduction of granules into the soil ensures the prolongation of the supply of nutrients;
-
closer to autumn, the culture is fertilized with complex compositions of the corresponding direction.


Compliance with all of the above steps allows you not only to keep the bushes healthy, but also helps their further development.
Pruning
Since we are talking about a shrub that needs to create an image, it is regularly cut, trimmed, and contoured. Any geometry is suitable for solo bushes: from a ball to a spiral, but for a hedge, a rectangular or cuboid shape is usually chosen so that the wall looks monolithic. Sanitary pruning is needed to get rid of dry, damaged and diseased shoots from shrubs.

So:
-
pruning is carried out in early spring before the start of sap flow or in late autumn, removing defective shoots;
-
when planting seedlings, pinch (cut) the top, which stimulates the active formation of side shoots;
-
the height of the cut is determined by the height of the plant and the wishes of the owner.
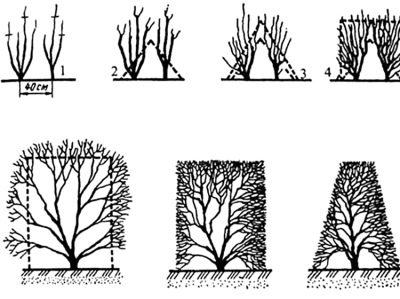
Pruning, as part of the shaping process, can be done several times during the growing season. This technique allows you to correct mistakes and maintain the shape of the plant in perfect condition. A brush cutter and trellis shears should be used as cutting tools.
Transfer
The ideal time for transplanting is in autumn, but the event can also be held in the spring. As mentioned above, a pit or trench up to 60 cm deep is prepared for planting. In this case, the width should exceed the earthen lump with roots by half. The plant is removed from the container in which it grew, with the greatest care so as not to damage the delicate roots.
A simple technique will help to do this: you need to stop watering a few days before this, so that the soil in the pot dries out.
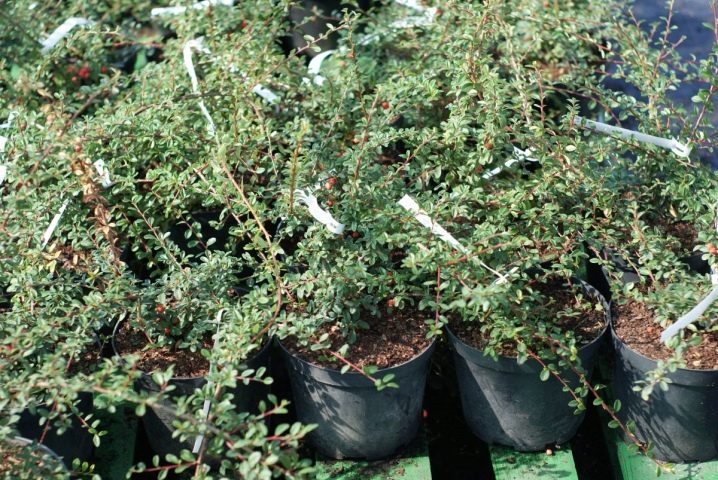

A dry clod of earth perfectly holds its shape and roots, while a wet clod easily crumbles from the slightest shake - instead of a plant with ZKS, you can get a bush with open roots. And this is much worse for any seedling. If the location is chosen near a blank fence, then the more beautiful side can be turned outward. After planting, the trunk circle is compacted, watered, loosened the next day or covered with a layer of mulch.
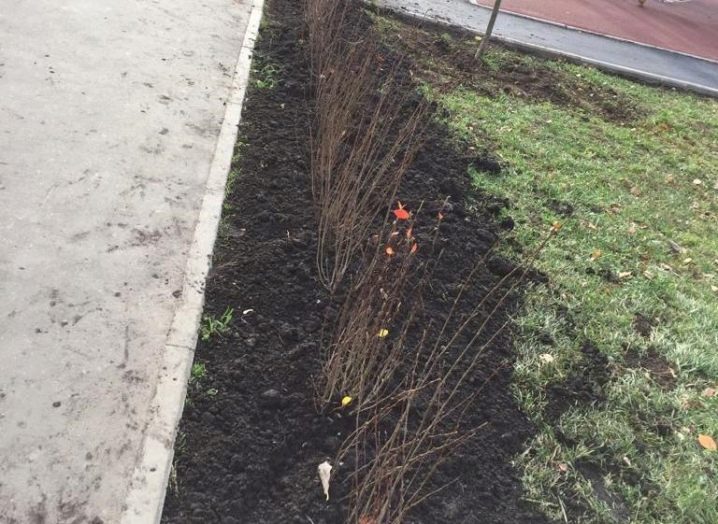

Reproduction
The brilliant cotoneaster can be propagated in two ways: vegetatively and by sowing seeds. The first method is very popular, due to the low germination of seeds and the extremely long period of stratification: the seeds are kept in the refrigerator for a whole year.
-
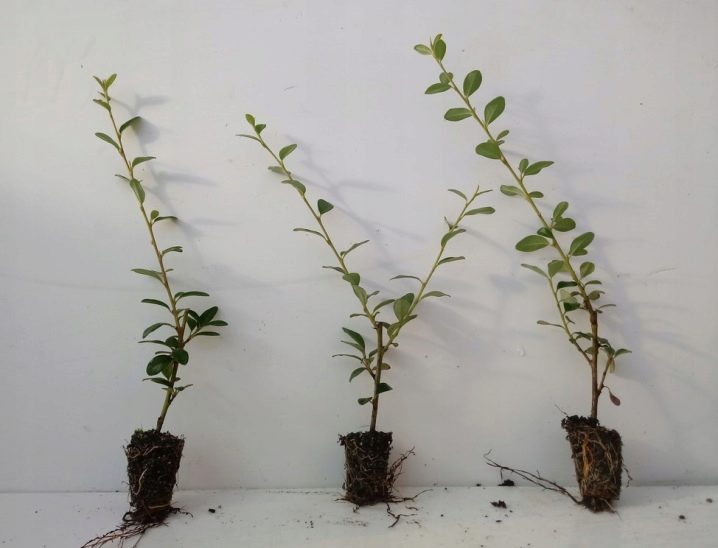
The vegetative method is cuttings. Healthy shoots are suitable for harvesting, they are cut into cuttings 15 cm long. Before planting, the lower oblique cut is treated with a root formation stimulator. Then the cutting is dipped obliquely into soil with a neutral pH level, whose structure consists of river sand, peat or vermiculite. Placed under a glass shelter or covered with agrofibre.The use of the second will avoid daily ventilation. Planting needs regular moisture.

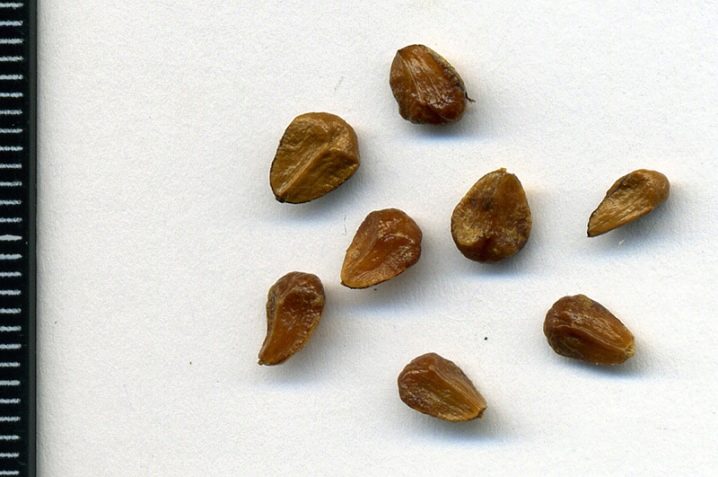
- Sowing seeds is carried out after stratification, after soaking them for 24 hours in warm water. During this time, non-emerging (empty) seeds will emerge, viable ones will remain at the bottom. High-quality seeds are immersed to a depth of 3-4 centimeters and left for a long time - you can wait up to a year for seedlings. During this time, care must be taken to keep the soil moist.

The second method is almost never used for obvious reasons, because its productivity cannot be compared with the vegetative one. Reproduction by cuttings is carried out in late spring and summer, so that they have time to take root before the onset of cold weather.
Diseases and pests
Unfortunately, despite the strong immunity, the cotoneaster can be affected by fusarium. Symptoms of a fungal disease: the leaves turn yellow and fall off. This is due to the germination of the mycelium of Fusarium fungi, which causes the death of the green part of the plant. At the first signs of damage, it is necessary:
-
remove all infected parts;
-
subject the diseased plant and the soil under it to fungicide treatment.

The disease, perhaps, will not lead to the complete death of the bush, however, it will noticeably reduce the decorative indicators.
Of the pests for shrubs are dangerous:
-
aphids and scale insects;
-
sawfly and spider mite;
-
apple moth and yellow bear.
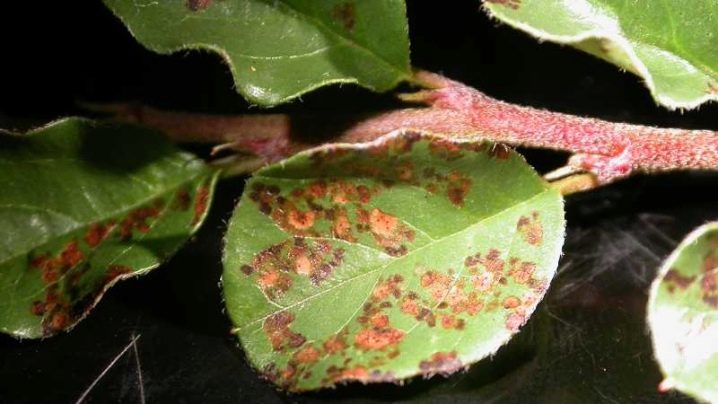

Enemies of green spaces are disposed of with insecticides. You can treat aphids with folk remedies, the recipes for which are available in the network, for example, with a decoction of wormwood or yarrow, infusion of garlic or potato tops.
Application in landscape design
The ornamental shrub cotoneaster brilliant is a real gift for the landscape designer, especially when dealing with large spaces. Not only hedges are created from the cotoneaster - it is a great opportunity to organize green secluded areas or original clusters of bushes with vertical shearing in the middle of the lawns. All this is possible due to the tendency of the cotoneaster to respond well to a haircut. After it, he becomes thicker and his forms after each "hairstyle" look more graphical.
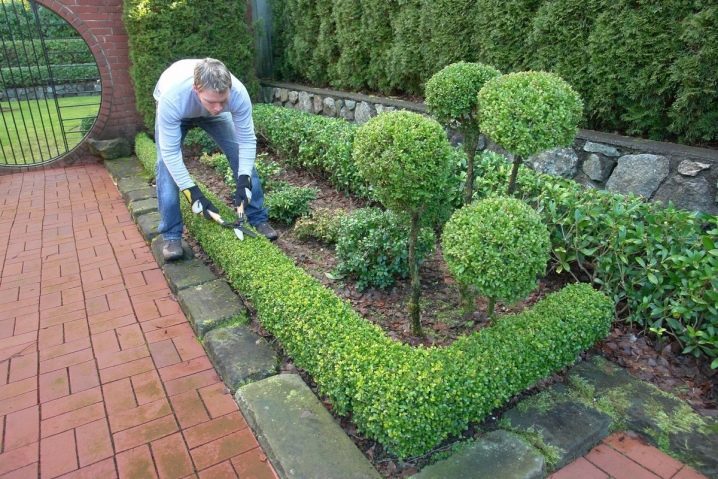

Low curbs are grown from the cotoneaster, bordering lawns, garden paths, city sidewalks, recreation areas, children's and sports grounds - there are endless options.
Planting cotoneaster can serve as a middle tier between the flower bed and tall conifers, with which the deciduous shrub goes well. They are used in topiary - groups of shrubs of the most bizarre forms. They serve as a living floristic basis for creating figurines of animals, birds and a wide variety of objects, for example, flowerpots or balls. Standard agricultural techniques are guaranteed to allow you to grow a cotoneaster in a "stone jungle", where not all shrubs are able to take root.


































































The comment was sent successfully.