How to propagate viburnum?
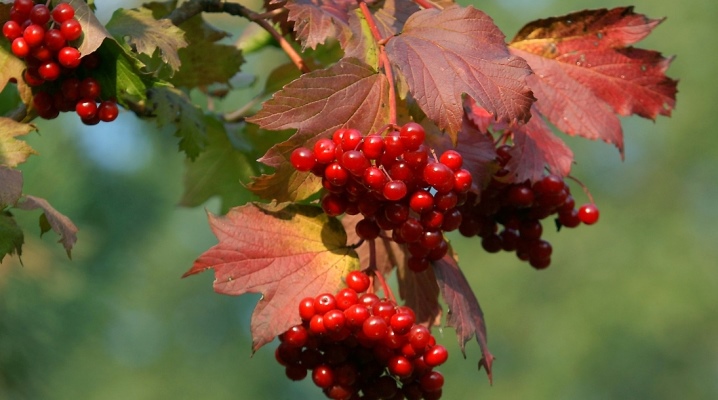

Viburnum is a perennial shrub or small tree, especially appreciated by gardeners for its medicinal properties. Viburnum is used to prepare drinks and jam, pie fillings. All kinds of ailments are successfully treated with bark, leaves, flowers and berries. The decorative viburnum made this culture a favorite inhabitant of gardens, delighting with beautiful foliage, lush bush shape, snow-white or pale pink inflorescences. She is unpretentious, so it is not difficult to grow her.
Viburnum propagation can be done by seeds (seeds) or by vegetative methods: cuttings, layering, root shoots, dividing the bush. The most productive methods are vegetative. When using them, the plants retain all the characteristics of their variety with 100% survival rate. Saplings begin to bear fruit already in the second year. But each of the types of reproduction has its positive and negative sides.

Features of cuttings
Cutting is the best agricultural technique to preserve the varietal characteristics and decorative properties inherent in the mother plant. A feature of the grafting method is to obtain an unlimited number of planting specimens, but this is associated with high labor intensity. When grafting, winter already lignified or summer green cuttings are used. Each type of cuttings preparation has positive aspects.
The easiest way to propagate is winter cuttings. Suitable for harvesting 20 cm annual shoots, cut from the bush in the winter months. You can distinguish a one-year-old by a lighter shade of the bark.
To preserve the prepared cuttings until spring, they are pre-soaked in water for several hours. After that, wrapped in foil, they are perfectly preserved until transplanted on the lower shelf of the refrigerator.
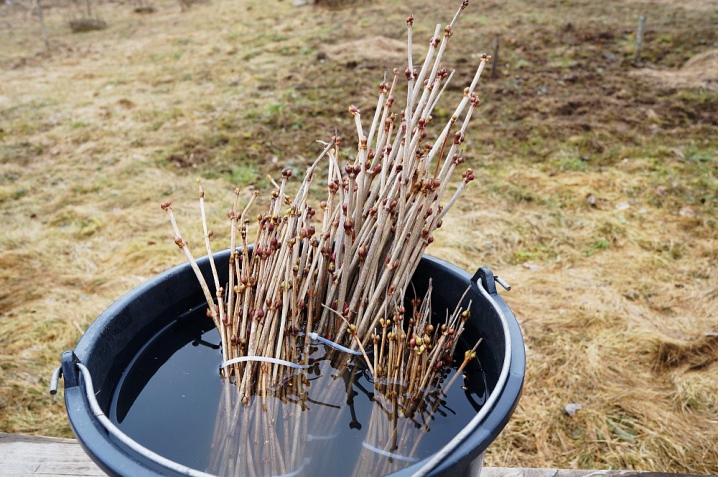

Transplanting into the ground is carried out in the spring, when it warms up well. They are planted in rows. Finish the planting process by loosening the soil around the cuttings and watering. This is done regularly, until the already rooted shoots are transplanted at the onset of autumn.
There is another technique when the cuttings are soaked for several days and then planted in the cuttings. The soil in it is moistened and covered with polyethylene. A month later, the root system will grow, and by autumn the seedlings will be ready for planting on open soil.
A more common agricultural technique is planting viburnum in summer with cuttings, harvested when cutting perennial, already faded bushes, since elastic green cuttings have the best survival rate. From a young branch, 15-centimeter pieces are cut, with two upper leaves previously cut in half. This will help reduce moisture evaporation.
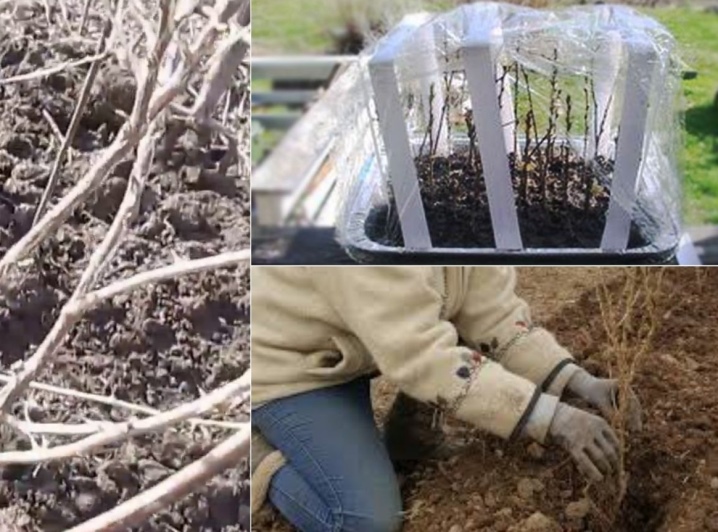

The cuttings are soaked for some time in a growth stimulator and planted in small greenhouses. Cover with foil from above. Cuttings that have released roots are gradually hardened, giving access to open air, regularly opening the film before removing it completely.
In the spring, without removing the earthen lump from the container, the shoots are moved to the garden bed for growing. After that, they are transplanted to a permanent place. Young bushes grown from seedlings will bloom only after a few years.


Growing from seeds
Experienced growers do not advise planting ornamental varieties with seeds. In such seedlings, varietal characteristics are not reproduced. Therefore, it is possible to obtain high-quality planting material with the varietal characteristics of the mother plant during reproduction only by vegetative methods. Otherwise, varietal species will grow with bitter and small fruits. Only non-hybrid varieties of viburnum can be planted from seedlings grown from seed.
Seeds retain their germination capacity for up to 2 years, but germinate poorly. They can be sown both in spring and autumn. If you sow freshly harvested seeds directly into the ground in late autumn, then the process of their germination will be long, since the seed will begin to germinate only after 18 months. This is an uncomplicated method that does not require special preparation and effort.
It is necessary to sow well-ripened seeds on the soil surface in the shade of bushes, trees, buildings, because moisture is better retained here. The seedbed should be protected until germination and rooting of seedlings. Therefore, you cannot even weed out. In order to avoid damage to the underground shoots of viburnum and to prevent the death of shoots from drought, it is better to mulch the site. The seedling will begin to develop only in the spring, in the second year of planting, and only then will it have shoots.
It is possible to achieve early germination by adding a small amount of wet sand to the seeds and keeping this mixture for several weeks, first at room temperature at home, and then in the cooler conditions of the refrigerator.
The seeds saved in this way and sown in April will sprout this spring. But a bush of seedlings will be able to bloom after 5 years.


Other breeding methods
Layers
Vertical layering is an easy way to propagate viburnum. In the fall, at the selected bushes, the lower shoots with several buds are shortened and each of them is spud up by half.
Next spring, new 15-centimeter growths will form from the existing buds, which are again half-spud. In the fall, they will already form roots. They are cut off from the old bush and planted in the soil for growing until the next season. And next spring they are already determined in open ground for a permanent place.
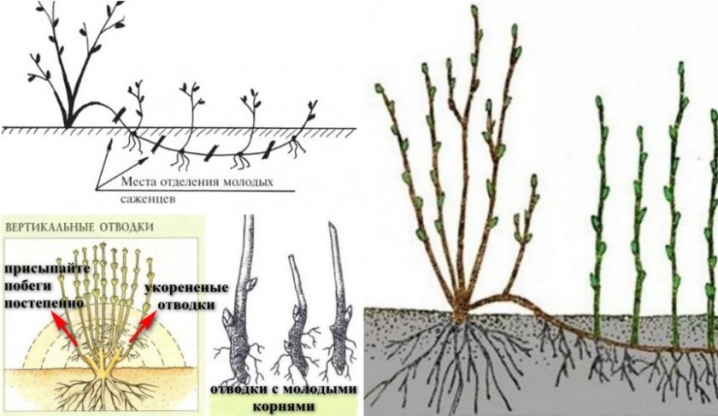
Viburnum has the ability to form additional roots on shoots well. This ability is used when choosing a method of reproduction by horizontal layers, in which the shoots are folded back, pinned with paper clips or spears and moistened. When shoots with a height of 13 cm grow from the buds, they are spud up by a third. With growth, the shoots also increase the height of hilling almost to the height of the shoots. In the fall, the cuttings are dug up, separated from the old mother plant and divided into independent bushes, and then planted in the soil.
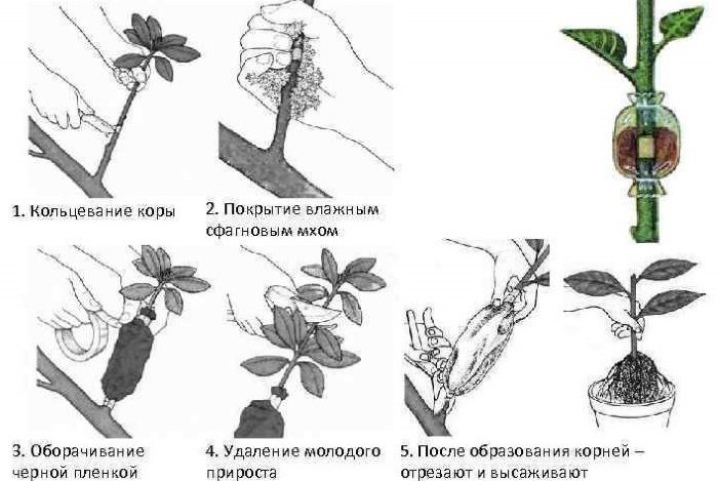
If the plant is the only one, it is propagated in greenhouses using the method of air layers. This rather laborious method consists in dragging the shoot with wire and covering it with sphagnum moss. The sprout is moistened daily, treated with a growth stimulant and wrapped in plastic wrap. As soon as the root system is formed, the cuttings are cut off from a single copy and planted separately.
The bush from which the air layer is taken is not damaged. And the resulting annual cuttings have good roots, so they develop and grow quickly.
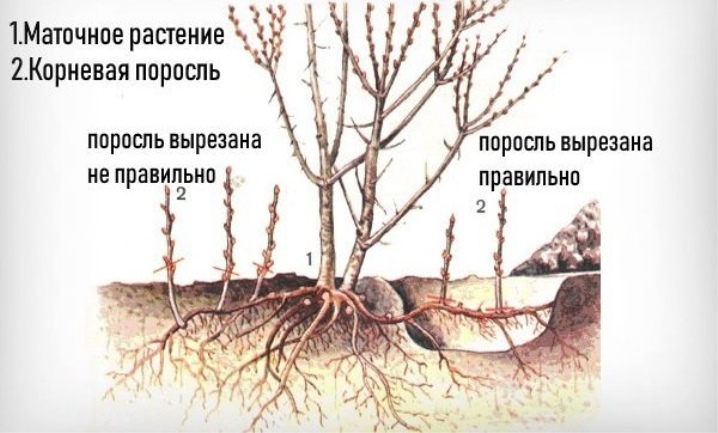
Root shoots
The fastest way to propagate a bush is by root shoots. At the end of spring, the bases of the shoots should be tightened with soft wire. This will significantly speed up their root formation. Then they are spud with humus. Over the summer, hilling is carried out about 3 times so that the mound is at least 20 cm before autumn. In the subsequent spring period, the shoots are separated from the mother bush and planted as an independent plant.
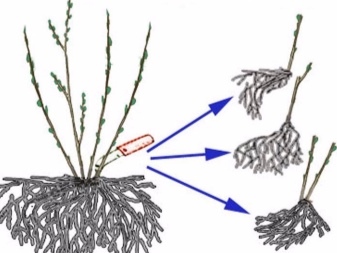
By dividing the bush
This technique is used to transplant a plant or a very valuable species. The advantage is low labor intensity, and the disadvantage is the limited number of obtained seedlings. This method makes it possible to obtain in spring or autumn, when dividing one young bush, no more than 3 daughter plants with their own part of the roots and several growth buds for renewal.
It is possible to apply the method only before the buds of the plant swell.

Further care
Proper care of it will help to grow a lush viburnum with excellent fruiting from a seedling. Full development will be ensured by sufficient moisture and fertilization, as well as preventive measures against diseases and pests. And in the future - regular pruning.
The shrub is hygrophilous. In the summer, in the evenings, seedlings need abundant watering. And the older they are, the more water will be required.
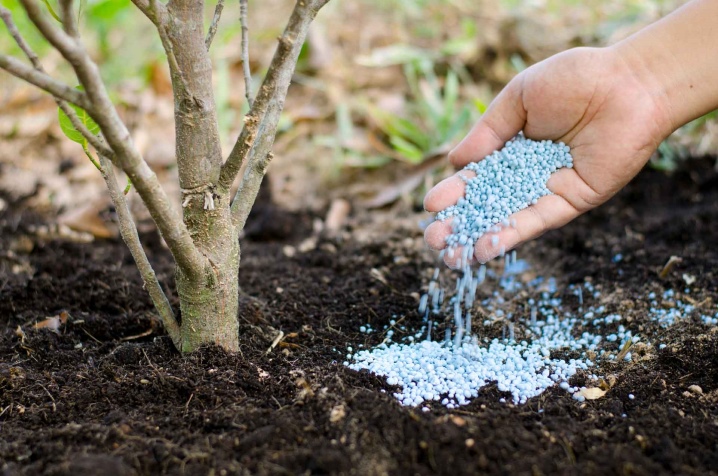
An adult bush can do without feeding. But for the better development of the seedling and increase the future yield, you need to use them. It is advisable to carry out top dressing together with mulching with sawdust.
Before the leaves bloom, spring nitrogen fertilizers are applied. In the summer months - any mineral complex. In the fall, when preparing for winter, the bush is fertilized with a phosphorus-potassium mixture. The next autumn feeding with manure solution or potassium-phosphorus fertilizer is carried out 2 years after breeding, during watering or when digging up the soil.

The shoots must be protected from pests: aphids, leaf beetles, cap moth and comma-shaped scabbard. If necessary, plants should be treated with insecticides before bud break. The use of insecticidal plants is perfect: horse sorrel, dandelion, bitter wormwood.
In high humidity weather, young shoots can be attacked by a fungus. These are various types of rot, spotting and powdery mildew. Spraying with fungicides will help. You can process seedlings with folk remedies throughout the season. For example, solutions of household and tar soap with the addition of soda, tobacco, ash. In case of severe damage, the seedlings are treated with a Bordeaux mixture.
Preventive measures consist in the regular removal of weeds, loosening of the soil cover and the root zone of the seedlings.


For information on how to propagate viburnum by cuttings, see the next video.



































































The comment was sent successfully.