All about the bean
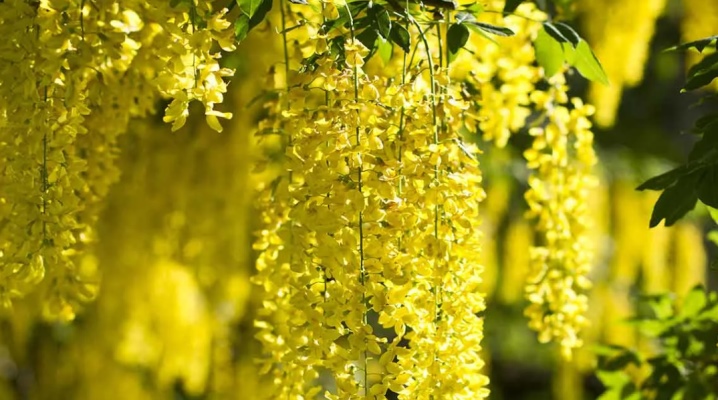

Describing a shrub like the legume will prove to be very valuable to many farmers and gardening enthusiasts. Alpine laburnum and other species are quite different, but in any case, it is useful to know how the tree blooms. You will also have to pay attention to planting and care in the open field.
Description
By itself, the name bean hints at an entry into the legume family, and this is indeed the case. Moreover, this is not one species, but albeit small, but a genus. It consists of 4 types of different plants. Botanists have established that its natural area covers the Mediterranean coast and the countries of the center of Europe. However, after its introduction into culture (dating from about 1560), laburnum (alternative name) can be seen growing and blooming in many other places. Experience has shown that it can thrive in the Russian climate - only due care is required.


The demand for this elegant plant is very high, which allowed it to gain popularity in different places. It is believed that the word "laburnum" is from the ancient Etruscan language, from where it got into other languages, not excluding Russian, through Latin. The specific name focuses on the similarity with stinky anagiris in the appearance of leaves and flowers. The legume is primarily a shrub, less commonly known in the form of a relatively tall tree. In Russia, this culture has been known since the 19th century.
First of all, they began to grow it in warm regions, such as the Crimea, Central Asian territories and the North Caucasus. It was found that the legume has limited frost resistance - no more than - 26 degrees. Therefore, in a winter with little snow, one-year growth can be severely affected. In more severe conditions, problems arise with relatively old specimens. Already at the latitude of Moscow, it will be problematic to grow a tree above 3 m, and you can completely forget about normal flowering.


At the same time, to the south of Rostov, the legume does not just bloom profusely. There he is able to reproduce by self-seeding. In the middle lane, it will be difficult to maintain optimal conditions. It is highly recommended that you purchase North German planting material rather than Italian or Dutch planting material. Bobovnik sheds its leaves for the winter.
It is important to remember that for all its beauty, this is a poisonous shrub, and especially children should be protected from contact with it. A characteristic feature of the external appearance is the density of elongated inflorescences hanging down. The foliage and flowers bloom at the same time, which adds visual appeal to the culture. For its appearance, the bean plant has received the nickname "golden rain".


Main features (by the most common type):
-
height - up to 7 m;
-
the formation of a spreading crown with a large density;
-
light brown bark;
-
frequent formation of several trunks in one tree;
-
weeping type of branches;
-
trifoliate foliage, slightly pubescent below, initially light green, but darkening by mid-July, 15-25 cm long;
-
flexible peduncles 20-50 cm long;
-
extremely abundant flowering, taking from 14 to 20 days;
-
bean-shaped fruits with a maximum length of 8 cm, containing flat seeds no longer than 0.3 cm (these are the fruits that are most poisonous!).


Types and varieties
Ordinary
A perennial plant with a pronounced deciduous cycle is known under this name; frost resistance - up to - 20 degrees.Its crown is oval and differs in spreading; synonym - anagirolisny bean. The total height of the tree reaches 7 m. Flowering covers May and June. In this case, the following are formed:
-
golden;
-
white;
-
pink;
-
lilac inflorescences.


Alpine
This view is also very elegant. Alpine bean is often a full-fledged tree with a height of up to 12 m. His shoots and branches are arranged in an erect pattern. However, the edges do droop a little. A characteristic feature of this species is a very beautiful impressive flowering, the bunches are even compared in descriptions with garlands.
As part of the Alpine bean, a number of varieties are distinguished, each of which is widely demanded by gardeners because of its uniqueness. Thus, in the Pendula variety, the shoots are unusually long in comparison with the species norm, and this immediately creates an unusual effect. The Quercifolia subtype stands out for its non-standard cut leaf shape, which sometimes even leads to confusion with oak. But upon closer examination of the whole plant, the dissimilarity between them is clearly revealed. The Aurea variety is distinguished not by the shape, but by the color of the leaves.
With the beginning of spring, they have a distinct yellow tint, which will smoothly change into the usual green. But the Automnale variety also has its own unique feature. Only he demonstrates the ability to bloom in the spring and autumn months equally productively. It looks especially impressive in September.



Vaterera
Such a plant is closer not to a tree, but to a bush. Its compactness pleases many gardeners. It should be noted that the Vaterer bean is a hybrid that does not exceed a height of 3 m. Shoots develop upright. Only at their tips are small falling spots noted.
The shoots are foliated very intensively. Flowering is not just active, but even stormy. At the same time, a strong pleasant aroma appears. The inflorescences can reach 0.5 m in length. The fruits of the Vaterer bean have a low degree of pubescence.


Pink
This species is also called the Norwegian bean, Adam's bean. Strictly speaking, it is a hybrid of the classic bean and broom. It can be a shrub or tree up to 8 m. This culture has lilac and pink, lilac-pink inflorescences from 0.2 to 0.4 m. It is worth noting that this name is often mistakenly given to pink almonds, but this is a completely different plant.
The red bean grows up to only 1.5 m. Bright flowers contrast perfectly with the foliage. This explains its wide popularity in landscaping home gardens. It should be borne in mind that it is still quite possible to grow such species and varieties in the Moscow region. But in the Leningrad region, and even more so in Siberia, this will require remarkable skill and great effort from gardeners.



Landing
To grow such a crop in the open field, you do not have to overcome special difficulties. It needs sunlight and land with increased water permeability. If there is little light, flowering later or does not come at all. Stagnation of moisture in the ground is critical for a tree, but the poverty of the soil and its calcareous composition are not so harmful. It is quite possible to breed laburnum without adding large amounts of organic dressings.
It will be possible to grow a tree or bush of this type if you protect it from the effects of the wind. A group planting is recommended, not a solitary one. This will increase resistance to cold climates and enhance flowering. Experience has shown that the legume grows best when planted in early spring. The optimum moment comes immediately after the snow cover melts.
Planting pits are prepared in advance. Fresh humus soil mixed with lime is laid in these recesses. Simultaneously with the seedling, a support structure is buried, which is immediately used for a garter.



Mulching the trunk circle is done using:
-
peat;
-
bark;
-
ordinary moss;
-
a film designed to retain water in the ground.
The legume bean tolerates penumbra, but no more. Great attention should be paid to the quality of the drainage layer. Deep burial of the seedling is unacceptable. It is recommended to tie young flexible shoots to strong supports in order to exclude deviation in different directions and destruction. The choice of nutrient soil is preferable.
Better if it has an alkaline reaction. Sour soil is improved by adding wood ash or a small amount of lime. Such manipulations are carried out in the fall, and then the effect will be achieved by the spring. Seedlings with a closed root system can be used throughout the growing season.
When the roots are open, a choice must be made between the very beginning of spring and the warm October weather.


Care
When the laburnum has faded, its brushes need to be removed. You will also need to continue watering regularly. Weeding around this plant should be done with the utmost care. Bean roots develop on the very surface and are highly ramified. Inaccurate loosening can lead to their sudden deformation.
Frosting of branches in winter is very likely. If this happens, the unique flowering quality will be compromised. In the center and in the north of the Russian Federation, in many respects and in the middle lane, such a plant should be covered for the winter. In heavy snow, the branches will be subject to heavy stress. It is better to shake off snow from them more often.
In the north, it is very important to insulate the main trunk to protect it from the cold.
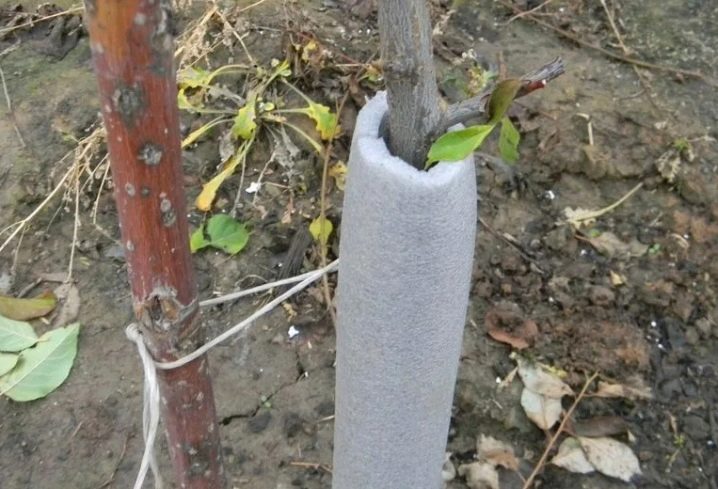

In the springtime, the plant should be examined and all frozen branches should be immediately cut off. Young bushes and trees need to be shaped so that their crown looks more graceful. Key fertilizers are used twice a year. In the spring months, it is necessary to apply nitrogen mixtures to activate the growth of green mass. When the plant prepares for the dormant season, it must be supplied with phosphorus and potassium.
The bean plants endure arid moments much more persistently than waterlogging. Watering is required only against the background of prolonged and persistent drought, as well as during flowering. Regular feeding is necessary for a pot crop, which for obvious reasons cannot get enough nutrients. During the active growing season, mineral fertilizers in liquid form are added every 14 days. Such dressings are introduced into wet, abundantly watered soil, since in dry soil the roots can be severely burned.
They are engaged in top dressing from the moment the first young branches and leaves appear. In the fall, their activity is gradually reduced to nothing. Bobovnik tolerates well the impact of both mineral and organic fertilizers. Often used:
-
humus;
-
manure;
-
humus.


The manure must first be overheated. Otherwise, root burn is almost inevitable.
An unsaturated poultry manure solution can also be used. Excessive nutrient intake is best avoided altogether. Formative pruning is carried out very carefully, since when a significant number of shoots are removed, the development of the plant will be suppressed.
It is more correct to avoid pruning of adult branches altogether. Basically, the bean branch branches on its own. If he lays the side shoots as it should, then there is no need to cut him. For work, sharply sharpened tools are traditionally used. All trimmed areas are immediately treated with garden varnish.
During the summer months, the bean plants (shrub forms) are best kept outdoors rather than indoors in a tub. But even in this case, protection from rain and wind is required.
In the fall months, the legume may lose foliage. This is completely normal and should not be alarming.
Reproduction methods
Seeds
The seeds can be used within 3 years after harvest. But, naturally, fresh planting material is preferable. Processing before sowing itself is optional. However, stratification has a positive effect on the development of culture.This procedure is carried out for 12-14 days in the refrigerator; the seeds are pre-mixed with damp soil or wrapped in wet gauze - and in this form are placed in a plastic bag.
Sowing is carried out into fertile land. It is advisable to give it maximum looseness. Bean is sown sometimes even before winter. However, it is best to do this in the spring, as soon as a confident thaw begins. Seeds are covered by 10-20 mm, the gaps between them are left within 100-150 mm.


The seedlings obtained in this way do not need any complex care and will actively develop. When choosing a seeding method, sowing in containers is carried out in February. Seedlings will develop well with optimal lighting and limited watering. For transplanting to the final place, it is recommended to use trees with a lump. Seed-grown laburnum begins to bloom in 4 or 5 years.
Whenever possible, seeds should be collected from those plants that have bloomed most effectively. Harvesting is best done in September, when the fruits are ripe. It is advisable not to delay sowing after harvesting. The first full-fledged shoots appear in the container in 15-20 days.
The picking should be done at least on the 60th day of development, and the transfer to the final place should be done after the weather has stabilized in the spring.


Cuttings
It is also possible to propagate legumes in this way. Moreover, vegetative propagation is rated the highest by gardeners. For a varietal culture, this is the only option for preserving valuable properties. Young shoots should be cut in July or August. Such planting material can be rooted in partial shade using loose soil.
Until the roots appear, the cuttings must be kept under a hood. Irrigation should be done carefully so that the ground does not erode and nothing breaks. Laburnum grown from cuttings requires shelter in the first year of a full-fledged growing season. You shouldn't forget about supports either. The use of lime and organic substances can help the development of the plant.


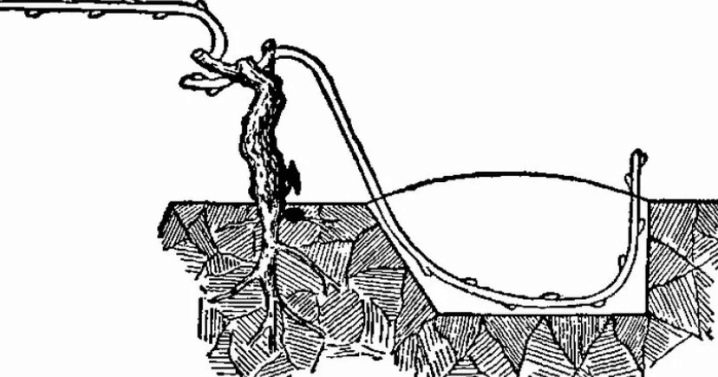
Layers
You can turn young growth into layers. She is pressed to the ground. Roots will appear at the junction. To make them appear faster, an incision is made or the bark is exposed. Reproduction by layering is carried out in early spring. Success is indicated by the emergence of a new vertical shoot, but in this case, replanting should only take place next year, otherwise the plant that has appeared will not be able to survive on its own.
Laburnum also lends itself to dividing the bush. The procedure is carried out in the autumn months. In this case, the plant itself is left in the ground.
In the spring months, the prepared part can be dug up without hesitation and planted in a permanent place. Growth stimulants will help speed up adaptation.
Diseases and pests
It is extremely rare to see that the leaves of the bean tree turn yellow. Its toxicity repels many harmful insects and prevents them from feasting on greens. However, even poisons do not affect the pathogen of powdery mildew. It can occur with long-term stagnant water.
It is best to avoid such a situation altogether, and if it does arise, you need to immediately apply potent drugs, not relying on folk remedies.

Application in landscape design
You can use legumes in the garden very widely. It looks harmoniously against the background of any house, but it is optimally combined with stone buildings. To emphasize the visual beauty, it is recommended to use group plantings. When blooming massively, they look especially elegant. Laburnum is also planted on lawn glades; you can also play on its contrast with conifers.
This plant should be planted where there is no cover during daylight hours. However, for 3-4 hours in the summertime, the legume must be protected from too bright sun. On its basis, you can form lovely hedges. The optimal companions of such a culture are:
-
scumpia;
-
wisteria;
-
chubushnik.









































































The comment was sent successfully.