How to propagate chokeberry?
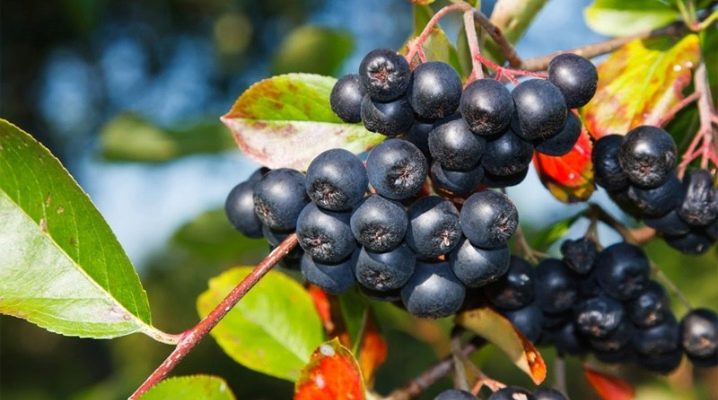

Chokeberry is considered a very popular horticultural crop. Its significant advantage is the ability to multiply in multiple ways.


Propagation by cuttings
It will be possible to propagate chokeberry with both green and lignified cuttings.
Green
Since the planting of green cuttings is carried out only in a cold greenhouse or greenhouse, cuttings can be cut in this way either in the spring, in the last days of May, or already in the summer. It is important that the soil for rooting the material consists of deciduous soil, compost and a small amount of coarse sand. Cuttings no more than 15 centimeters long must be cut only from healthy bushes. Their lower leaves are completely cut off, and the upper ones are shortened by half. It is also recommended to create several shallow cuts in the lower part of the twig and one under its upper leaf blade.
Immediately before planting rowan, cuttings are immersed in a stimulating drug for 8-12 hours. After this time, the material is washed in clean water and dipped into the ground at an angle. It is important that a gap of 4 centimeters is maintained between individual plants. Planting in a greenhouse should be at a temperature of about +20 degrees and irrigated periodically.
Aronia moves to a permanent place only in September of the next year.


Lignified
To carry out cuttings of chokeberry with lignified twigs, and to prepare and root the material will have to be in the fall, having time before the arrival of frost. Last year's shoots are separated from the adult mother bush in the second half of September. The upper part of the cutting is cut at an angle, and the lower part is shortened in a straight line, literally under the ovary. It is necessary that the length of the planting material be about 15-20 centimeters, and several full-fledged buds, at least 6 pieces, were observed on its surface. The twig should be rooted at an angle in a moist, nutritious soil.
The cutting is deepened so that no more than a couple of full-fledged buds remain above the surface. You will need to keep 10 to 12 centimeters between individual copies. The procedure ends with abundant irrigation and mulching of the trunk circle. For a month, autumn cuttings should take root, and with the arrival of next spring, they should already begin to fully develop. It should be mentioned that if the frosts came ahead of time, then the cuttings collected in the fall will need to be left for the next season.
The twigs must be sorted and tied with a bundle. Its lower part is immersed in moistened sand or wrapped in a wet cloth, and then covered with a bag. The stored material is regularly checked and, if necessary, moistened. It should be located in a cool room. With the onset of spring, the cuttings are planted in plastic cups, and when the earth warms up, they are transplanted to a permanent habitat.


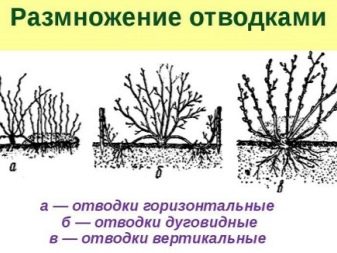
Breeding by layering
The propagation of black chokeberry by layers growing along the root area is carried out in early spring, as soon as the ground warms up for mechanical processing. The procedure begins with digging the soil under the selected bush with a half-bayonet deepening of the shovel. As a result of such processing, a neat groove should form, where 2-3 last year's shoots with a young growth are bent.
Annual branches can be used both horizontal and arcuate. Biennial specimens with abundant growth are also suitable. On the ground, they are fixed with special brackets or stones, before that, the top of the branch must be pinched. It is also recommended to break them slightly to speed up root formation. The groove is filled with loose nutrient soil.
Layers require the same care as adult bushes: they will have to be irrigated and protected from weeds. When young shoots emerging from the buds of the cuttings reach a length of 12 centimeters, they will need to be sprinkled with humus. The procedure is repeated another 12 centimeters later.
The transplantation of the culture to a permanent habitat, as well as the separation of the new bush from the mother, is organized next spring.

Dividing the bush
Chokeberry can be diluted simply by dividing the old bush into several parts. This method is possible for implementation, since the root system of the culture is actively growing, and the shoots only become stronger with age. The procedure is carried out in the spring, until the buds swell on the bush. In principle, an option is also possible with an autumn division, carried out a month before the cold weather. The plant is first watered abundantly, and then carefully removed from the ground and divided into several parts, which is accompanied by pruning of old shoots and removal of damaged parts. You will have to work with a well-sharpened tool - a pruner or a shovel.
It is important that each resulting specimen has healthy roots and at least a couple of young branches. The exposed wounds are sprinkled with crushed charcoal. For plots, pits are immediately dug, filled with humus and superphosphate. The seedling is carefully lowered into the hole, sprinkled with earth, compacted and irrigated with a warm, settled liquid. A free space of 1.5-2 meters will have to be left between individual plants. Some gardeners prefer to immerse their root system in water for several hours before planting plots so that the roots are saturated with water.
An option is also possible with the use of a clay talker, with which the root processes are lubricated.


Use of suckers
Suitable for reproduction of chokeberry and root shoots created by the root system on an annual basis. These offspring grow especially actively in the conditions of nutrient soil. The shoots are detached from the parent plant using the edge of the shovel.
Pruning must be carried out in such a way as to be sure to leave several buds, which will give rise to new branches. Root offspring are immediately planted in their permanent habitat. It is customary to use root shoots in spring, and the procedure should be preceded by regular feeding.

other methods
Propagation by seeds and grafting is considered the most time consuming method.
Seeds
Chokeberry seed is purchased in a specialized store or harvested independently. In the second case, ripe fruits are kept at room temperature until the stage of fermentation. Then they are ground through a sieve or cheesecloth, and the exposed pulp is washed under clean water. The seeds also need to be stratified. To do this, they are mixed with wet calcined sand and removed to the lower shelf of the refrigerating chamber for 3 months. If there is such an opportunity, then the container with the material is buried in the snow or placed in the basement.
In the second half of April, seeds are planted on a temporary bed, and are transferred to a permanent habitat only next fall. The soil must be nutritious, and the depth to which the grains are buried should not exceed 5-8 centimeters. Landings are necessarily mulched with humus.When a couple of leaves appear on the seedlings, they will need to be thinned out of all weak and underdeveloped specimens. The distance between the shoots is kept equal to 5 centimeters.
Re-thinning is organized when 2 more leaves appear on the plant. This time, the gap between the shoots will need to be left equal to 7-8 centimeters. As part of the third thinning, which is carried out next spring, the seedlings are "moved apart" by 10 centimeters.
The growing mountain ash will need full care: it will need to be irrigated regularly, keeping the soil moist, and also fed with slurry or other organic matter.


Graft
It is better to arrange the procedure for grafting chokeberry in early spring, until the plant begins to move the juices. As a rootstock, an ordinary rowan seedling or any other winter-hardy variety, which is abundantly watered and cleaned of dust, is optimal. It is necessary that its thickness is from 2 to 2.5 centimeters. The shoot is cut off in such a way that no more than 12-15 centimeters remain above the ground. In the place of the cut, an incision is created with a depth of about 5 centimeters, split in the middle for the scion - the place of further connection with the handle. Work should only be done with a disinfected, well-sharpened tool so as not to introduce bacteria or pests.
The graft from the black chokeberry is formed wedge-shaped, since it has to tightly enter the stock. For this purpose, it is recommended to use a strong lignified stalk obtained from the upper shoot and shortened in its upper part. Its length should be about 15 centimeters. It is also important to have 2-3 active kidneys. The junction area is abundantly coated with garden varnish and pulled together with twine, or it is fixed with electrical tape, looking outward with an adhesive layer. The protective material should be removed no earlier than in a month. Additionally, it is worth wrapping the vaccination site with polyethylene, which creates a greenhouse effect. The bag is put on the seedling and fixed below the grafting site. It is also removed after a month, when young leaves appear on the scion.
It is also possible to carry out budding, that is, to graft a bud or a peephole on a self-rooted seedling. The rootstock is cleaned of dust with a damp cloth, after which a T-shaped bark cut is created on its northern side. The latter should be located at a height of 5-8 centimeters from ground level. The varietal shoot of black chokeberry is cleared of leaves, and the bud is carefully cut off from it. The peephole is to be taken with a piece of bark and a heel 2.5-3 centimeters long and 0.3 to 0.5 centimeters wide. The heel of the bud is inserted directly into the rootstock incision. The bark is clamped and tightened with plastic wrap so that only the kidney remains outside. After a couple of weeks, the dressing is removed, and in the spring of next year, the upper part of the rootstock is cut off to an adrenal thorn 5-7 centimeters high.































































The comment was sent successfully.