Pool heat exchangers: what are they and how to choose?

For many, the pool is a place where you can relax after a hard day's work and just have a good time and relax. But the high cost of operating this structure does not even lie in the amount of money spent on its construction. We are talking about high-quality heating of water, because its volume is large, and heat loss is very high. The best solution to this problem would be constant circulation of water at different temperatures. And a heat exchanger for a pool can cope with this task. Let's try to figure out what it is and what types it can be.


Peculiarities
It should be understood that heating a pool with a large amount of water is not a cheap pleasure. AND There are 3 ways to do this today:
- use of a heat pump;
- the use of an electric heater;
- installation of a shell-and-tube heat exchanger.



Of these options, the best would be to use a heat exchanger due to the following features:
- its cost is relatively low;
- it consumes less power than 2 other devices;
- it can be used with alternative heating sources, the cost of which will be lower;
- has a small size;
- it has a high throughput and excellent hydraulic characteristics (with regards to heating);
- high resistance to corrosion under the influence of fluorine, chlorine and salts.
In general, as you can see, the features of this device allow us to say that today it is the best solution for heating water in the pool.

Principle of operation
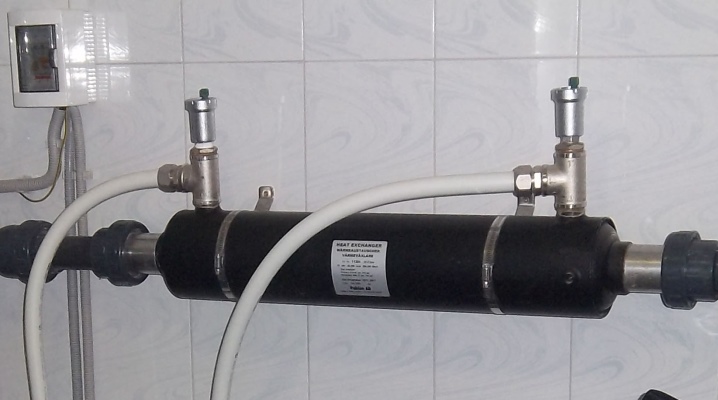
Now let's figure out how a pool heat exchanger works. If we talk about the design, then it is made in the form of a cylindrical body, where there are 2 contours. In the first, which is the direct cavity of the device, water circulates from the pool. In the second, a device is located where hot water is moved, which in this case acts as a heat carrier. And in the role of a device for heating a liquid, there will be either a tube or a plate.
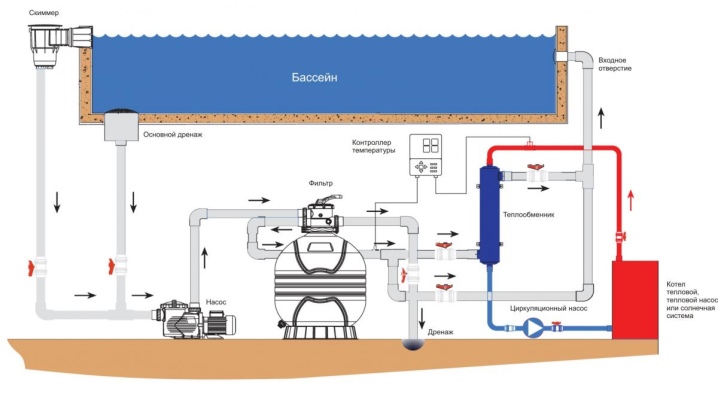
It should be understood that the heat exchanger itself does not heat the water... With the help of external fittings on the second circuit, it is connected to the heating system. Because of this, it is an intermediary in the transfer of heat. First, water goes there from the pool, which, moving along the body, heats up due to contact with the heating element and returns back to the pool bowl. It should be added that the larger the contact area of the heating element, the faster the heat will transfer to cold water.

Species overview
It should be said that there are different types of heat exchangers. As a rule, they differ according to the following criteria:
- by physical dimensions and volume;
- by power;
- by the material from which the body is made;
- by type of work;
- by the type of internal heating element.



Now let's say a little more about each type.
By volume and size
It must be said that the pools differ in design and in the volume of water placed. Depending on this, there are various types of heat exchangers. Small models simply cannot cope with a large volume of water, and the effect of their use will be minimal.
It often happens that you have to carry out calculations for a specific pool and order a heat exchanger specifically for it.

By power
Models also differ in power.Here you need to understand that on the market you can find samples with a power of 2 kW and 40 kW and so on. The average value is somewhere around 15–20 kW. But, as a rule, the required power is also calculated depending on the volume and size of the pool where it will be installed. Here you need to understand that models with a power of 2 kW will not be able to effectively cope with a huge pool.
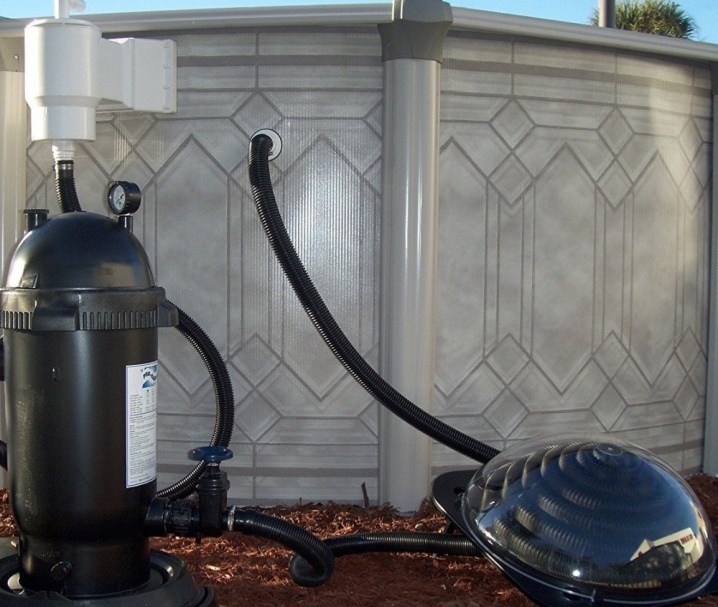

By body material
Pool heat exchangers are also different in terms of body material. For example, their body can be made of various metals. The most common are titanium, steel, iron. Many people neglect this factor, which should not be done for 2 reasons. First, any of the metals reacts differently to contact with water, and using one may be better than the other in terms of durability.
Secondly, the heat transfer for each of the metals is different. So, if you wish, you can find a model, the use of which will significantly reduce heat loss.


By type of work
By the type of work, heat exchangers for the pool are electric and gas. Typically, automation is used in both cases. A more efficient solution in terms of heating rate and energy consumption would be a gas appliance. But it is not always possible to supply gas to it, which is why the popularity of electric models is higher. But the electric analogue has a high energy consumption, and it heats the water a little longer.


By type of internal heating element
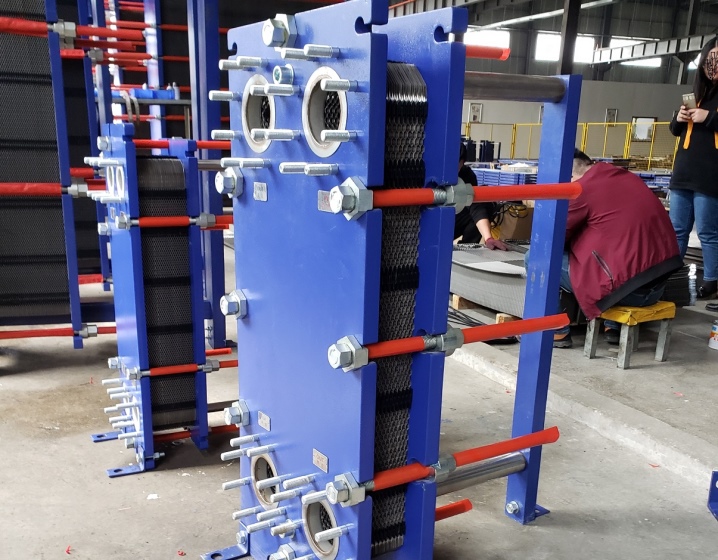
According to this criterion, the heat exchanger can be tubular or plate. Plate models are more popular due to the fact that here the contact area of cold water with the exchange chamber will be larger. Another reason is that there will be a lower resistance to fluid flow. And the pipes are not so sensitive to possible contamination, unlike the plates, which makes it unnecessary for preliminary water purification.
In contrast to them, the plate counterparts are clogged very quickly, which is why it makes no sense to use them for large pools.

Calculation and selection
It should be noted that choosing the right heat exchanger for the pool is not as easy as it might seem at first glance. To do this, you need to calculate a number of parameters.
- The volume of the pool bowl.
- The amount of time it takes to heat the water. This point can be helped by the fact that the longer the water is heated, the lower the power of the device and its cost will be. Normal time is 3 to 4 hours for full heating. True, for an outdoor pool, it is better to choose a model with a higher power. The same applies when the heat exchanger will be used for salt water.
- The coefficient of water temperature, which is set directly in the network and at the outlet from the circuit of the device used.
- The volume of water in the pool that passes through the device over a specified time period. In this case, an important aspect will be that if there is a circulation pump in the system, which purifies water and its subsequent circulation, then the flow rate of the working medium can be taken as the coefficient that is indicated in the pump's data sheet.
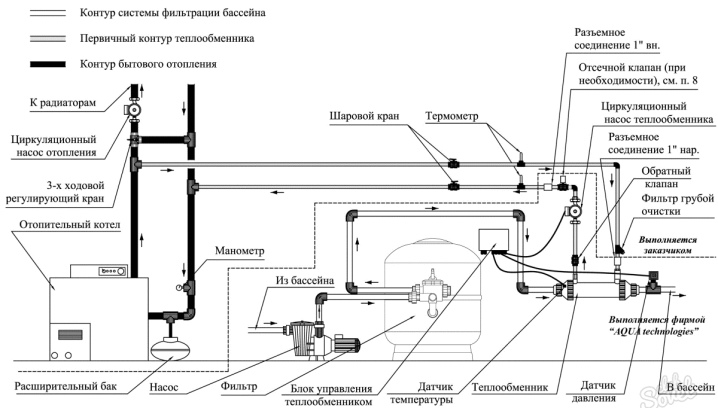
Connection diagram
Here is a diagram of the installation of a heat exchanger in the system. But before that, we will consider the option when it was decided to make this device on our own. This is easy considering the simplicity of its design. To do this, we need to have at hand:
- anode;
- a pipe made of copper;
- a cylinder-shaped tank made of steel;
- power regulator.
First you need to make 2 holes in the end sides of the tank. One will serve as an inlet through which cold water from the pool will flow, and the second will serve as an outlet, from where heated water will flow back into the pool.
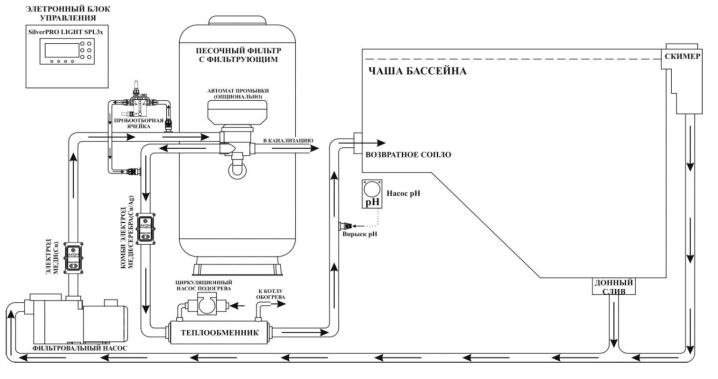
Now you should roll the copper pipe into a kind of spiral, which will be a heating element.We attach it to the tank and bring both ends to the outer part of the tank, having previously made the corresponding holes in it. Now the power regulator should be connected to the tube and the anode should be placed in the tank. The latter is needed to protect the container from temperature extremes.
It remains to complete the installation of the heat exchanger in the system. This should be done after installing the pump and filter, but before installing the various dispensers. The element of interest to us is usually installed below the pipes, filters and air vent.
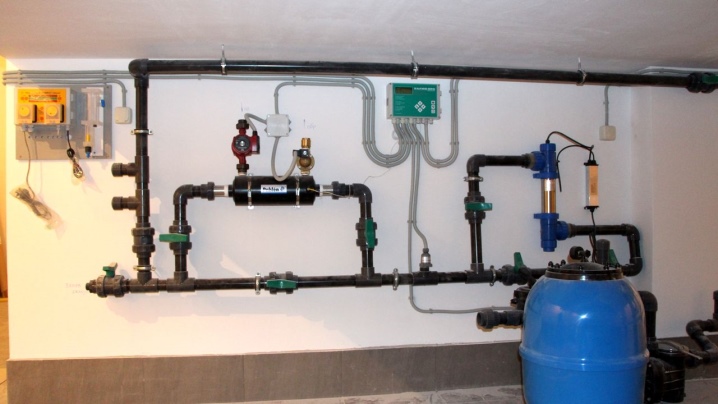

Installation is carried out in a horizontal position. The tank openings are connected to the pool circuit, and the outlet and outlet of the heating tube are connected to the heat carrier circuit from the heating boiler. The most reliable for this will be threaded connections. All connections are best done using shut-off valves. When the circuits are connected, a control valve equipped with a thermostat should be installed on the inlet of the heat carrier from the boiler. A temperature sensor should be installed at the water outlet to the pool.
It so happens that the circuit from the heating boiler to the heat exchanger is too long. In this case, it is necessary to additionally supply a pump for circulation so that the system works smoothly.
What is a heat exchanger for heating water in a pool, see below.



































































The comment was sent successfully.