All about screw sizes

A screw is a hardware for fastening different parts, one part of which must have a thread. The screw resembles a threaded pin, on the one hand, on the other, a structural element for transmitting torque. The screw is designed to connect and fix different types of products. In addition, it can serve as an axle for rotating parts of the product.


Basic dimensions
A standard is a conformity assessment that defines the technical characteristics of a product, including strength, material of manufacture, and test methods. Meeting the requirements of the standard means making a quality product.
The dimensions of the screws are determined by GOST 1491-80 (identical to the international standard ISO 4762: 2004). This means that the screws are made according to the standards of the production technology of classes A and B. The standard sizes according to GOST are from M1 to M64, but in practice there are often those that differ from the standards, on the markets you can find options up to M100. If the characteristics do not comply with GOST, you must use other international standards: ISO 261, ISO 888, ISO 898-1, ISO 965-2, ISO 3506-1, ISO 8839 and ISO 4759-1.

Screw sizes by class
|
View |
Bar diameter mm |
Head outer diameter mm |
Screw length |
Additional Information |
|
M2 |
1.86 to 2.0 |
3.48 mm |
from 3 to 20 mm |
Only class A is produced for the hexagon. |
|
M3 |
from 2.86 to 3.0 (0.14 mm discrepancy is allowed) |
2.7 mm |
from 5 to 30 mm |
The top of the screw head can be rounded. |
|
М4 |
3.82 to 4.0 |
6.53 mm |
from 6 to 40 mm |
Produced only in class A, the length tolerance does not exceed 10% of the nominal value. |
|
M5 |
from 4.82 to 5.00 |
8.03 mm |
from 8 to 50 mm |
According to the standard, it is produced in a single version of the thread pitch - 0.8 mm. |
|
M6 |
5.82 to 6.0 |
9.38 mm |
from 20 to 60 mm |
The maximum rounding limit above the screw head should be 1.7 degrees. |
|
M7 |
6.0 to 7.0 |
10.20 mm |
from 12 to 105 mm |
Non-standard type of screw. |
|
М8 |
from 7.78 to 8.0 |
12.33 mm |
from 12 to 80 mm |
Rounding and countersinking on a recess for a hex key are allowed. The standard turnkey size is from 6.00 mm to 6.14 mm. |
|
M10 |
from 9.78 to 10.00 |
15.33 mm |
from 16 to 100 |
It can be made in three variants of the thread pitch: 1.0 mm, 1.25 mm, 1.5 mm. |
|
M12 |
from 11.73 to 12.0 |
17.23 mm |
from 20 to 120 |
The standard thread pitch is 1.75 mm. |

M3x6 (6x20) - these hardware are used when working with any metals and hard plastics. The size of the screw length is from 6 to 20 mm. When installing products with this hardware, it is necessary to drill a thread of a suitable size or use a nut of the required diameter in order to improve the fastening.

М3х10 used in the assembly and fastening of parts in mechanical engineering and other industries. The length of the fastener is 10 mm. Sometimes it is the only option for construction use.


M4x10, M4x16, M4x20 are made of carbon steel, they are galvanized. Length, respectively, 10, 16, 20 mm.



M5x8, M5x10, M5x20 used for different types of buildings (in the process of their assembly and installation). There is a possibility of fastening using an anchor or a dowel. Parts are connected using a washer. The length of the fastener is 8, 10 and 20 mm, respectively.




M6x10, M6x12, M6x16, M6x20, M6x25, M6x30 - screws with lengths of 10, 12, 16, 20, 25 and 30 mm. Buyers are pleased with the versatility of use and the variety of applications. Such a screw is fastened with an anchor and a dowel, or using a washer or nut.



М8х25, like М8х45, it is used for the installation and fastening of various products and parts, the length of the hardware is 25 and 45 mm, respectively.


There are several types of screw hat shapes, and all of them are made according to certain standards:
- a cylinder with an internal hexagonal opening is regulated by standard No. 11738-84;
- the semicircular head is regulated by the standard No. 17473-80;
- the half-open view of the head is regulated by the standard No. 17474-80;
- the hidden head is regulated by the standard No. 17475-80;
- the square headrest is regulated by the standard No. 1482-84, No. 1485-84;
- straight slot with a smooth head is regulated by standards No. 1476-93, No. 1477-93, No. 1478-93, No. 1479-93.






These attachments are also distinguished according to other criteria. An important aspect of mounting and dismounting a fastener is the type of slot. There are several standard types.
- Straight slot. To mount and dismantle this slot, you need a wedge-shaped screwdriver. If one is not at hand, it is possible to replace it with a knife, chisel or other handy tool.
- Slot type "Torks". This is a patented type of 6-beam or 5-beam slot. It has a range of sizes: from 1 to 100 mm.
- Snake-eye head. Use a fork screwdriver to attach parts with this type.
- Polydrive slot. It is a star spline used in mechanical engineering and has a powerful tightening torque.
- Cross recess. It has two types: the first is "Phillips", and the second is "Posidriv". Visually, they are very similar to each other, so a layman can easily confuse them.
- Slot HEX. This is a slot patented by a German company, it has a hexagonal head shape. In stores, you can also find slots with anti-vandal action.
- The slot is a 12-pointed star. It has a recess in the form of 12 beams with an apex angle of 60 degrees.
- Vandal-proof slot One-way. This slot is used exclusively for screwing in and does not have a screw-out function. For dismantling, one should resort to slotting or drilling a screw.
- Tri-Wing slot. It has a large thread pitch, similar to a nail with helical grooves and a hemispherical hat.
- Bristol Slot. It is equipped with either 4 or 6 radial recessed beams. This slot is used in soft metal screws.
- Square spline in the head called Robinson spline. It has indentations for screwing in and out in the form of a square.
- Triangular slot. As the name implies, it has the shape of a triangle and is used to prevent illegal admission.
- Hi-Torque. This type of spline is very good for frequent loosening and screwing, as it has excellent torque.
- Cross slot. Has two flat splines at an angle of 90 degrees. They duplicate each other in case one of them becomes unusable.
- French slot. It has a cruciform stepped shape.
- JIS B 1012. This slot is Japanese standards, often found on Japanese technology. It is very similar to the Phillips slot, but the screw-in tool will need an original one; it is available in the markets of our country.

- Carbon steel Is an alloy containing up to 99% iron and up to 2% carbon. Its advantages are: high quality and good quality, hard top and soft inner layers, ease of finishing, long service life, general availability. Hardware have their own strength class when manufactured from carbon steel: 3.6; 4.6; 4.8; 5.6; 5.8; 6.8.
- Carbon hardened steel with additives. Strength classes - 8.8; 9.8; 10.9.
- Alloy hardened steel. Strength class - 10.9.
- The screws are made of corrosion-resistant steel. The composition includes chromium and nickel, and chromium should be present more than 13%.

- Austenitic steel has excellent thermal conductivity. It contains chrome and nickel. The most common steel for the manufacture of hardware for fastening. It is designated as follows: A1, A2, A3, A4, A5.
- Martensitic steel. The steel grade is designated C1, C3, C4.
- Ferritic steel. It is designated by the letter F1.


The screws are made of various expensive metal alloys. Basically, these are screws that are used in energetic conditions, are subject to gravity, and require high thermal conductivity. Propellers made from these alloys are lighter than other types.
According to the requirements of GOST 1759.0-87, screws can be made from the following alloys of expensive metals:
- alloy No. 31 - designated as AMg5, PAMg5, controlled by standard No. 4784-74;
- alloy No. 32 - designated as L63, LS59-1, controlled by standard No. 15527-70;
- alloy No. 33 - designated as brass L63 anti-magnetic, LS59-1 anti-magnetic, controlled by standard No. 12920-67;
- alloy No. 34 - designated as bronze AMts9-2, controlled by standard No. 18175-78;
- alloy No. 35 - designated as D1, D1P, D16, D16P, controlled by standard No. 4784-74.


How to choose the right size?
Choosing the right screw, consumers often make the wrong size. Considering that it will do well, they fasten the parts with it and operate the product. This absolutely must not be done.
An incorrectly selected screw size will cause the thread to loosen in the product and thereby render the item unusable. It is highly likely that no further repairs to this product will be possible.
While in the store, you will find over a hundred screws with different hats, similar types of threads, different lengths and diameters. These screws are also made of different metals. First of all, you need to decide for what purpose the screw will be used. After that, you need to think about what loads it must withstand and whether it needs heat and electrical conductivity. For products that do not require high tightening, semicircular and cylindrical heads can be used.



Several types of screws are used to fasten furniture parts, depending on the connection point, material and load on this part of the product. There are three ways to use screws to assemble furniture:
- fastening parts from chipboard;
- collection of upholstered furniture frames.
- collection of wood products.
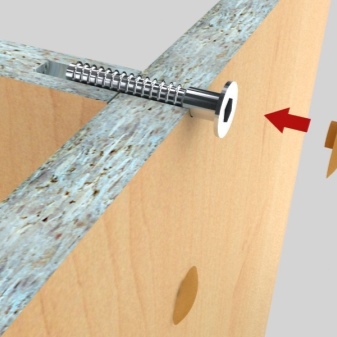

There are these types of screws that are used exclusively to fasten certain items. For example, screws for fixing shelves with a lock. It is not worth using such varieties for fastening other products: they can break and spoil parts.
The confirmat has a countersunk head and a slot for hex and Phillips screwdrivers. The hidden hat is followed by a flat, main part, which easily fits into the fastened part. The size of the flat part directly depends on the purpose of the screw. For example, if the width of the chipboard is 16 mm, then screws with a smooth area of 16 mm should be used to fasten it to another (same) part. According to GOST, this is a screw with a diameter of 7 mm and a length of 50 to 60 mm.


The most popular screws are with hex. To screw in these screws, use a hex bit, which is attached to a screwdriver, or such a tip has a screwdriver. The second tool that can be used to screw in or unscrew the hexagon is a z- or l-shaped hex key. The Phillips slots on the screw do not allow the part to be tightened quite tightly, which leads to the destruction of the screw-in socket.


When choosing the correct screw, you should pay attention to the fastening system of the parts. It can be a turnbuckle. The system looks like this: outside - a screw thread, inside - a barrel-nut for screwing in. With this connection, the screw and nut are perpendicular to each other. Basically, this mount is used in the furniture industry. Using a screw tie, the manufacturer achieves strength and rigidity at the junction of the parts. This is a very high-quality method of fastening, but without skills it is rather difficult to practice it.

The pan head screw is the most common type of fastener. It is always used to join upholstered furniture body parts. There are several types of such hardware. The difference between them is in the shape of the head and fastening parts.
The next important point in determining which screw you need is the material of manufacture. The above describes what raw materials can be used to make fasteners. They can be uncoated or galvanized. All these standards are governed by GOST.


How to determine?
It seems that in order to select the correct screw, it is enough to know the length and diameter of the screw. But it is not always the case.
To correctly determine the size, you should refer to the GOST standards - all the parameters that determine the size of the screw are spelled out there.

First of all, you need to have the right tool. To determine the diameter of the screw and its length, you can use a vernier caliper, micrometer, or a stencil ruler. If you need to find out the size of the metric thread, use a special tool - a pedometer. If such a tool is not available, then it is allowed to measure the pitch of the turn using a vernier caliper. But it is worth noting that the exact result will be obtained only with coarse threads. If it is shallow, measure several turns and divide the result by the quantity to be measured.
There is one thing to keep in mind when determining the length of a screw: when measuring a screw with a protruding head, the measurement should be taken to the base of the head.
- M - metric thread indicator;
- D is the diameter;
- P - thread designation;
- L is the length.



In order to install or dismantle a product that is fastened with a screw, you can use a wrench. There are 16 types of wrenches to match the size of the screw head. Masters of their craft pick the key by eye and almost never make mistakes. The amator in this case will have to choose the key by the test method.
If the key is correctly selected, the distance between it and the screw head does not exceed 0.1-0.3 mm.

|
Screw size |
М4 |
M5 |
M6 |
М8 |
M10 |
M12 |
M14 |
М16 |
M18 |
M20 |
M22 |
M24 |
M27 |
M30 |
M34 |
M36 |
|
Key size |
3 |
4 |
6 |
6 |
8 |
10 |
12 |
14 |
14 |
17 |
17 |
19 |
19 |
22 |
24 |
27 |

Prepare the site before the start of technical events. Check the availability of the tool necessary for the operation and its serviceability. In this case, the occurrence of problems during operation is excluded. Be careful when measuring so as not to make unnecessary purchases and do not waste your time on a second trip to the store for the necessary propeller.
















The comment was sent successfully.