Sizes of gas silicate blocks

A gas silicate block made of silicate concrete with a porous structure is nowadays one of the most popular building materials. It contains quartz sand and lime. Due to their density and other, equally important characteristics, gas silicate blocks are used for most construction work.
The main indicator that you should pay attention to is density, it shows why it will be more rational to use the block: load-bearing and serious structures or any partitions and racks. Also, an important factor is the heat engineering calculation of the blocks, which determines where it is better to use the block: for external or internal work. Today we will consider equally important parameters - the dimensions of the gas silicate blocks. This will allow you to understand the question of what size blocks to use, depending on the task at hand.
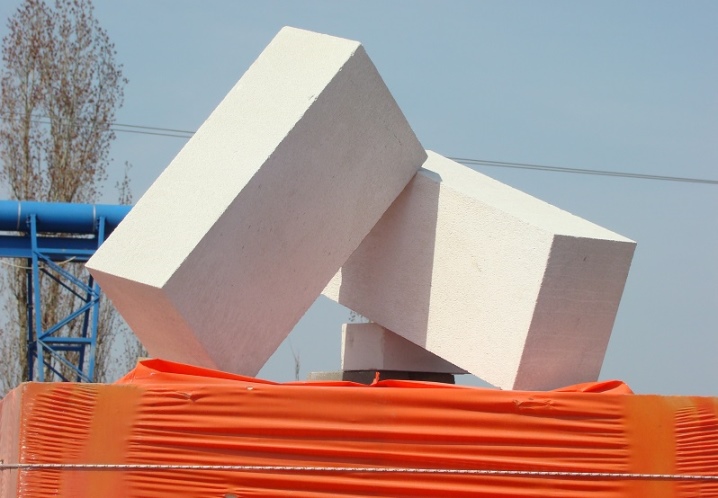

Standard dimensions
Gas silicate products can be of various sizes. But even with all this diversity, certain standards have formed that are most often used for the construction of certain structures. For example, in all kinds of tables on the websites of manufacturers, the following dimensions prevail: 600x200x300 mm, 600x100x300 mm, 500x300x200 mm, 250x400x600 mm, 250x250x600 mm. There are also quite massive and dimensional samples for floors.
The block is a rectangular product, the thickness of which is slightly less than its width. Most often these are specimens of a regular rectangular or square shape, with in rare cases additions in the form of serifs and locks.
A special type are the so-called U-blocks, which are mainly used to build jumpers.

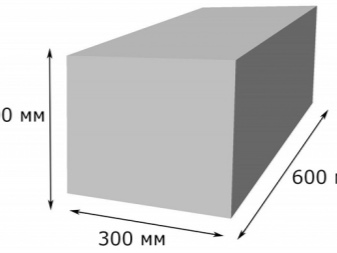
There are standardized sizes that are regulated by GOSTs, they depend on where and how the blocks will be used, by what technology the concrete hardens. But, as a rule, most manufacturers produce gas silicate blocks according to TU, thanks to this, a wide selection of standard sizes, shapes and dimensions is provided. However, there is a certain standard that does not allow making blocks smaller than the given sizes:
- length - from 600 or 625 mm;
- thickness - from 100 to 500 mm;
- height - from 200 to 300 mm.
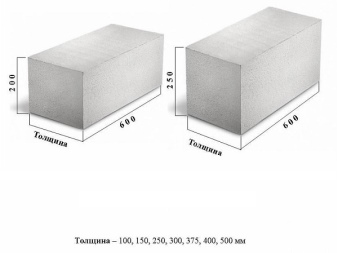
What else are there?
There are many types of gas silicate blocks, but three types are clearly distinguished.
- Aerated concrete. They are an artificial stone, where concrete holes form closed cells that do not touch each other.
- Foam concrete. This material is similar to aerated concrete, but here the pores are open and are also distributed throughout the volume.
- Gas silicate. Cellular building material. Its components are: crushed sand and lime, aluminum powder using autoclave treatment (necessary to accelerate hardening). Distinctive features of the raw materials in question are light weight and better thermal conductivity compared to those presented above.

We will also describe other types of gas silicates.
- Rectangular with finger grooves. It has a small mass and a convenient shape, suitable for the construction of high walls without the involvement of auxiliary equipment. The recesses for the hands also serve as a place of additional rigidity, because they, in turn, are filled with mortar.
- Partitional. For interior partitions inside the building, rectangular blocks are used, but with a smaller thickness - 105–155 mm. Manufacturers also offer their own modifications, so the sizes can be from 75–80 mm.
- Aerated concrete with groove and ridge. This view is a kind of lock, in which the joint is hidden, as a result of which destructive factors do not act on it. The monolithic and solid construction also has a plus in that, thanks to such a coating of the seams, cold bridges are excluded.
- U-shaped, or tray. In the block, a cavity is created inside for a solution and a reinforced frame made of reinforcement. It turns out a kind of formwork, with the help of such blocks, all kinds of jumpers and openings are made.



What size should I choose?
Most often, for the construction of low-rise buildings outside, blocks are used whose density varies from D300 to D600 (the number indicates a kilogram per cubic meter). The warmest option is the D300 blocks, but they, in comparison with others, have lower strength and, therefore, are suitable only for one-story construction. The dimensions in this case are as follows:
- the width of the block for the construction of walls - 200, 250, 300, 350, 375, 400, 500 mm;
- for partitions - 100–150 mm;
- length - 600, 625 mm;
- gas silicate height - 200, 250, 300 mm.
To build wall partitions and all kinds of niches, special blocks are used that have a smaller thickness. In most cases, their thickness does not exceed 100–150 mm, block width - 600, 625 mm, block height - 200, 250, 300 mm.

The lintel has a width that depends on the thickness of the wall. For this, prefabricated structures come to the rescue:
- for an opening of 300 mm - a lintel 300 mm wide;
- for an opening of 400 mm - 2 jumpers 200 + 200 mm;
- for an opening of 500 mm - 2 jumpers 300 + 200 mm.
For the construction of a garage, blocks of 600x300x200 mm are most often used. This thickness is sufficient for an unheated building.
Aerated concrete has entered modern life so actively that completely different structures can be erected from it, even outdoor barbecues and barbecue ovens. This material is fire resistant and harmless to people and the environment.
Gas silicate blocks are excellent raw materials for construction due to their technical characteristics and flexibility of use. Also, do not overlook their properties, such as frost resistance, moisture resistance and ease of processing.
This material can be easily cut with a conventional hacksaw, which allows you to deploy a small workshop on your site for the production and fitting of blocks of the size that you need.














The comment was sent successfully.