All about gas silicate blocks

Knowing everything about gas silicate blocks, the characteristics of gas silicate and reviews about it is very important for any individual developer. A shed with a pitched roof can be created from them, but other applications are also possible. In order not to be disappointed, you should choose the right partition gas blocks from Zabudova and other manufacturers.

What it is?
Everyone knows that the main costs and difficulties in construction are associated with the materials used for the external walls. Manufacturers diligently improve their products and offer a wide range of design solutions. One of the modern popular options is just gas silicate blocks. All of them must be manufactured in accordance with GOST 31360, in force since 2007.


The sale of other structures is allowed only if they comply with the TU or foreign standards, which are not worse than the domestic standard.
Technologically, gas silicate is a subtype of aerated concrete. The technology for its production is quite simple, and sometimes it is even produced in artisanal conditions, directly at the sites. True, for artificial stone made in factories, the overall quality and service life are noticeably higher. In industrial conditions, special autoclaves are used, in which, along with high pressure, a decent temperature also affects the raw materials. The manufacturing method of the product is well developed and involves the use of quicklime, Portland cement, water, aluminum powder and special components that force hardening.


Advantages and disadvantages
The undoubted advantage of gas silicate even for skeptics is the ease of single structures. This circumstance greatly simplifies loading and unloading, especially when it is carried out on its own. It is also pleasing that the construction requires a transport of lower carrying capacity - usually it is possible to do without complex lifting machines. Moreover, it becomes possible to work even alone, which is quite optimal for individual developers.


Sometimes building blocks have to be processed, but gas silicate is at a height here too, almost all the necessary manipulations are done with a simple hacksaw.
This material suppresses extraneous noise well. This effect is achieved due to the abundance of voids. Another advantage is limited thermal conductivity. Gas silicate houses are quite energy efficient even in comparison with brick and wooden buildings. The increase in size in comparison with brick makes it possible to build walls faster, and it will be possible to move into the house in a few months, even if serious finishing is needed.

Since gas silicate structures are slightly flammable, they can be used much wider than the same tree. And no processing is needed to achieve this result. In terms of comfort and environmental friendliness, there are also no complaints about this material.

But one cannot ignore the disadvantages of gas silicate blocks, which developers also need to know about in advance. It is unacceptable to build three-story and higher buildings.
Violation of this rule threatens the destruction of the underlying rows - because it will happen gradually, it does not get any easier. Intense water absorption can also be a serious nuisance.And in the event of a fire, thermal deformation of the house is a threat. As soon as the block is warmed up to 700 degrees or more, its destruction begins. Then even a special reconstruction does not allow returning the dwelling to its normal state.
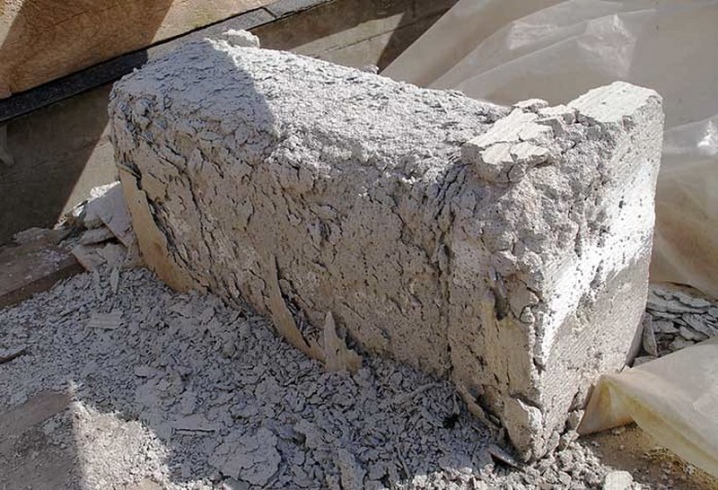

As soon as water gets on the structure, almost all of it seeps inside. Further, as soon as the temperature drops, the material is torn to pieces. In this regard, the brick is much more reliable and does not lose especially strength or thermal characteristics when moistened. The solution to the problem is a special waterproof shell. It is not required to form a weighty expensive foundation for gas silicate.

But you have to fill in the support tape. If there is no desire to do this, then you will need to prepare the grillage. Even a slight distortion immediately provokes the formation of cracks and the subsequent destruction of the walls. In terms of mechanical strength, gas silicate loses to bricks, therefore it must be chosen deliberately, taking into account all the strengths and weaknesses of such a solution. With skillful use, it brings a lot of benefits.

How are they different from other blocks?
It is necessary to answer other questions, first of all, what is the difference between a silicate product and a gas block. It is not easy to answer it, first of all, because both bright representatives of the category of aerated concrete are difficult to distinguish by eye, even for professionals. The confusion is exacerbated by the marketing policies of manufacturers and illiterate descriptions in which names are assigned arbitrarily. During installation, no special differences were found, but the difference still manifests itself - however, at the operation stage.
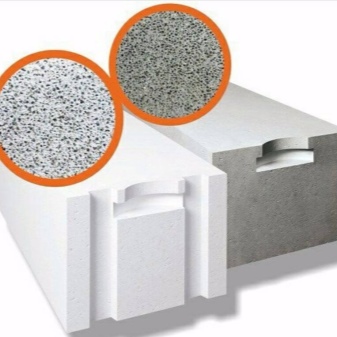
Aerated concrete can be made with your own hands at a sufficiently high quality, however, one must understand that the technology must still be strictly followed.
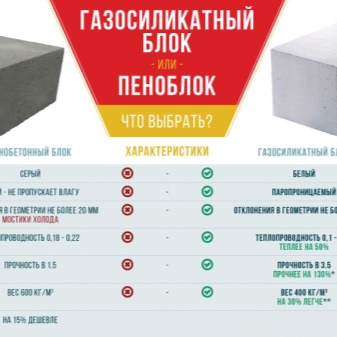
From a practical point of view, gas silicate is preferable to aerated block. However, the situation is reversed when considering moisture capacity. Therefore, silicate blocks cannot be used if the humidity exceeds 60%. But it is also necessary to figure out which is better - a foam block or still a gas silicate structure. And again, the comparison will go with another common representative of aerated concrete.

The ratio of properties is as follows:
- the foam block is more susceptible to open fire;
- foam concrete is easier to handle by hand;
- gas silicate has a slightly higher thermal protection;
- foam concrete loses in geometric shape perfection;
- their cost, scope and complexity of application are more or less identical;
- these materials are hardly distinguishable in terms of resistance to water absorption, for use in diverse climatic zones;
- it is easier to apply certain types of finishing materials to the foam block, which require the roughness of the substrate.



Stamps
D600
Gas silicate of this category is quite suitable for the construction of load-bearing walls - in fact, this is its main use. An alternative solution is to equip a facade with ventilation inside. Fastening the necessary external structures to products of this density does not cause any problems. The mechanical strength ranges from 2.5 to 4.5 MPa. The standard coefficient of thermal conductivity is 0.14-0.15 W / (m ° C).

D500
Such material is in high demand for low-rise construction. But monolithic structures can also be built from it. The strength level ranges from 2 to 3 MPa. It is obviously unsuitable for the construction of four-story buildings. But increased insulation is guaranteed.

D400
The characteristics of this block allow even less heat to pass through. Therefore, it is quite possible to use it to form insulation layers. A similar brand is also suitable for private buildings. An excellent balance of strength and thermal performance is achieved. Nevertheless, these products are unacceptable for the most loaded structures.
D300
This type of blocks has a density, as you might guess, 300 kg per 1 cubic meter. m. Thermal conductivity - 0.072 W / (m ° C).Therefore, no special additional insulation is required. The composition is the same as for other brands of gas silicate. The buildings are relatively light.

Types
Wall
Under this name, they supply building materials intended mainly for low-rise buildings - no more than 14 m. If you need to build a high-rise, then silicate with gas is no longer suitable, you must give preference to a reinforced concrete slab. The size of the products is very different, but even the smallest in size significantly exceed the brick. Moreover, they are inferior to him in density. If the thickness of the element does not exceed 40 cm, use is guaranteed at temperatures up to - 35 degrees without additional thermal protection.

For finishing apply:
- wood;
- siding of various types;
- brick;
- spray plaster imitating the appearance of a stone.
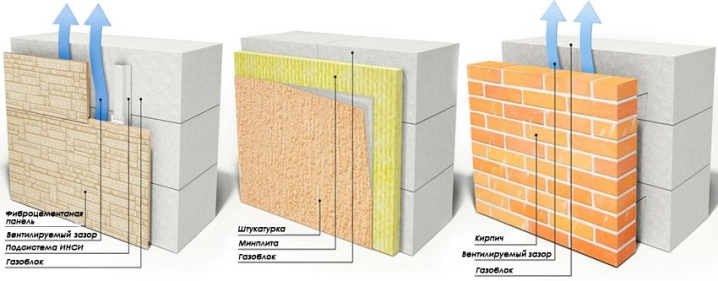
Partition
An important feature is the reduced size (compared to wall models). However, at the same time they have quite acceptable strength. Internal load-bearing walls are constructed of solid material. Secondary partitions can be made from hollow elements. The lightest structures are erected from 2 hollow parts.

Groove-ridges
These types of blocks are needed to build partitions and secondary walls. An alternative use is wall cladding. In geometry, they resemble a regular parallelepiped. For your information: instead of gas silicate, you can take gypsum structures. Their practical characteristics are almost the same, some models contain special additives that increase the resistance to moisture.

Common parameters:
- sound absorption not less than 35 and not more than 41 dB;
- density is usually 1.35 tons per 1 cu. m .;
- water absorption from 5 to 32% (depending on the type).


U-shaped
Such blocks are used to connect structures of unusual shape and geometry. Basically, we are talking about:
- window openings;
- door openings;
- reinforcing belts.
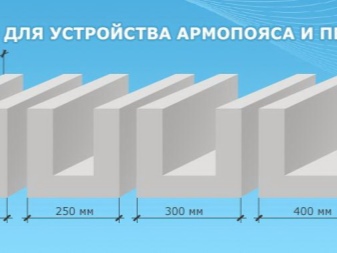



Such products can also be used as a base for solid formwork. Another possible application is for bridging. Finally, you can consider them as props for fixing the rafter complexes. If you make a cut, a tray-like structure appears. Steel rods are placed in the gutter niches, which help to increase the strength of the assemblies. Power belts proved to be very good with uniform spreading of the load, and the total length of the structures is approximately the same, regardless of size.


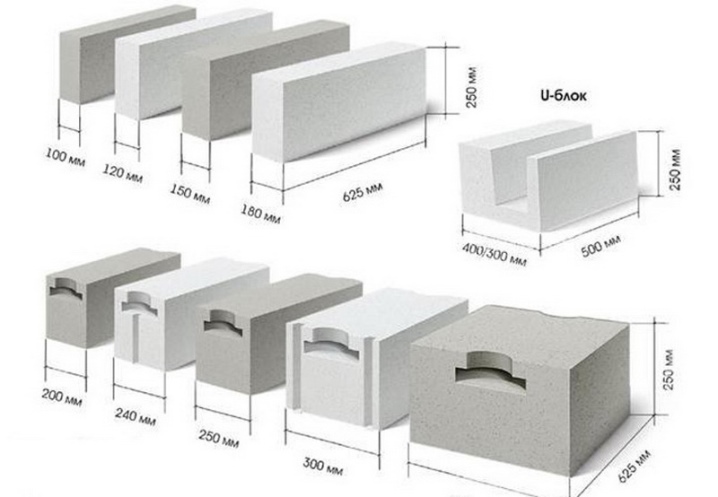
Dimensions (edit)
On sale you can find many gas silicate blocks differing in parameters. The difference in height, length and width determines how many pieces will be in the package. The dimensions are selected taking into account the intended purpose of the structures. The size also affects the mass of specific elements. Models are widespread:
- 600x300x200;
- 200x300x600;
- 600x200x300;
- 400x300x200;
- 600x400x300;
- 600x300x300 mm.
Applications
Often, various modifications of gas silicate blocks are bought for use in construction:
- private houses;
- separate load-bearing walls;
- thermal insulation layers;
- heating networks (as insulation).


When using such material for main walls and under the foundation, care must be taken to protect against water. For this purpose, apply:
- plaster;
- facade paints;
- siding;
- putty (thin layer);
- facing brick.




In some cases, there is even room for broken blocks. Of course, not during the construction of a house or even a shed with a lean-to roof, but during ancillary, secondary work. They are used for backfilling under floors.
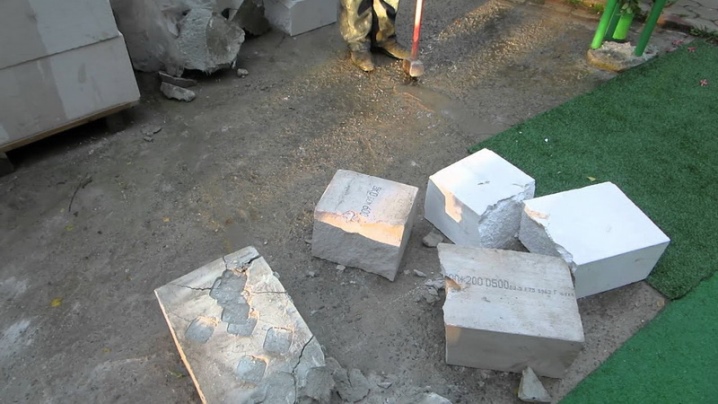

Attention: it is not recommended to use this material in the pits of buildings. The reason - periodic freezing and thawing deprives the fight of its main valuable qualities.
But in addition to using gas silicate for a partition or in a blind area, many people are interested in the question of whether it is possible to build a bath on its basis. On the whole, the answer will be yes. This solution is especially good in places with strong winds. Insulation and waterproofing must be performed at the highest level.

It is still advisable to equip only dry parts of the baths from gas silicate.
How to calculate?
An approximate calculation of the wall thickness can be done using online calculators. However, when building on difficult ground or with a deviation from the typical project, it is advisable to contact professionals. In the middle lane, one can proceed from the formation of single-layer walls 40 cm thick. Be sure to consider:
- corner joints of blocks;
- the size of the assembly seams;
- trimming for window sills;
- framing door and window openings;
- bearing capacity of the foundation.

Manufacturers
Relatively worthy production of blocks is carried out by the Belarusian plant "Zabudova". The company manufactures products of density grades from D350 to D700. The manufacturer insists that its products have a perfectly adjusted geometry. There are compression resistance classes B1.5, B2.5 and B3.5. An important advantage is its comparative low cost.

Poritep blocks have a very good reputation for quality in Russia. Their production is deployed in the Ryazan and Nizhny Novgorod regions. It is worth noting that this company officially sells both the main assortment and defective products (with a corresponding mark). Therefore, it is necessary to carefully look at what exactly is being acquired. In general, high-quality models meet the needs of consumers.

Bonolit products are also quite popular with customers. The structures are distinguished by the evenness of the sides and mechanical strength. The cost is low. But it should be noted that sometimes the thickness of the blocks "goes for a walk." But cracking practically does not occur.

Review overview
Gas silicate blocks require careful selection in terms of the balance of strength and thermal protection. Therefore, floor slabs and Mauerlats must be supported by reinforcing belts. Due to their low resistance to mechanical stress, structures are easily processed with hand tools, but they also break easily. We will have to use monolithic slabs for foundations, which will be stable even when the corners are sagging. Other reviews point out:
- speed of construction;
- the possibility of using special glue instead of cement;
- long-term operation without the appearance of cracks;
- the need to make relatively thick walls or radically insulate buildings;
- the need to work with gas silicate very professionally and responsibly;
- the impossibility or extreme difficulty of arranging the basement (if it is done, then no waterproofing will save the house from gradual destruction).

















The comment was sent successfully.