All about high strength bolts
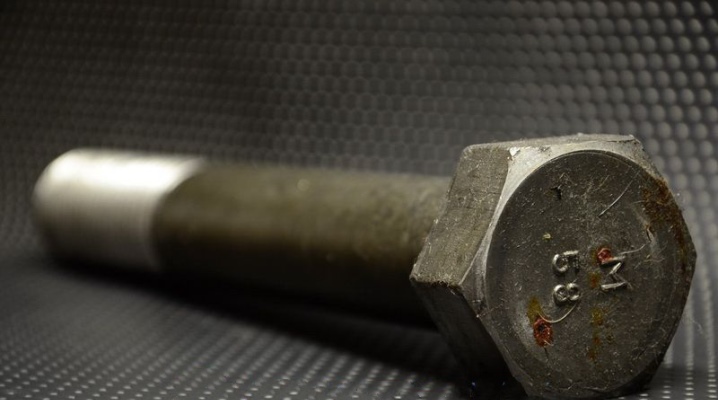

Knowing everything about high-strength bolts is necessary not only for employees of machine-building enterprises. This information is also needed by the most ordinary people who are trying to create complex structures. Differences in types and markings, features of operation, dimensions and weight are extremely relevant.


Description
For high-strength bolts there is an official valid GOST 52644-2006. This act standardizes:
bolt dimensions;
the length of the thread of such a fastener;
variations of structural elements and designs;
twisting coefficients;
theoretical weight of each product.
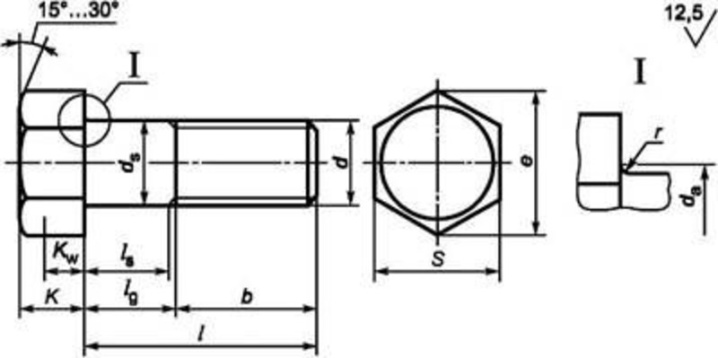
They are also covered by the DIN 6914 standard. By default, this product has a wrench hex head. It is intended for highly stressed steel joints. The diameter of the fastener can be from M12 to M36. Their size ranges from 3 to 24 cm.
Such bolts can be used in mechanical engineering, in engine building. They are also useful for areas where strong vibration is active; finally, they can be used in building structures of various kinds. However, the correct tightening torque plays an important role. Too little pressure often leads to premature destruction of the connection, too strong - can harm the fasteners or the structures to be connected.
The designation of high-strength bolts in the drawings is made using the triangle symbol, at the top of which (but not at the very top!) Vertical and horizontal lines intersect.


Areas of use
Several areas of use for extra strong fasteners have already been mentioned. But it can be used not only for metal structures in construction and mechanical engineering, as is often thought. These products are also needed for agricultural machinery and rail fastenings. The main feature is the suitability for such assembly joints that are exposed to very heavy loads, and where therefore standard fixing methods cannot be used. Such fasteners are in demand even in the most "heavy" construction - in the construction of bridges, tunnels, high towers and towers.
Any parts of high-strength bolts, of course, must have increased reliability and mechanical strength. All connections where such fasteners are used are classified in the shear-resistant category. When using such fasteners, you do not need to ream or clean the holes. You can screw a high-strength bolt not only into metal, but also into reinforced concrete. Separately, it should be said about the hexagon bolts.

Outside hex thread can be either standard size or small size turnkey.
There are also products with a reduced head height (and one of their subspecies is designed for small keys). However, products with an internal hex are good due to:
more convenience;
increased strength;
optimal reliability.


Types and marking
The strength class of bolts in Russia must correspond to the official GOST. It is customary to distinguish 11 categories of such fasteners. The high-strength group includes only products not lower than class 9.8. The first number, when multiplied by 100, gives the indicator of the greatest strength. Multiplying the second digit by 10 allows you to set the correlated maximum strength.
The high-strength bolt must be designed for use in harsh climates if it is marked with the letters "HL". The designation "U" indicates that the product will withstand an average degree of cooling. Tension-controlled connections must be recorded in a special log.The calculated value of the twisting force must not be exceeded by more than 15%.


Returning to the marking in accordance with GOST 22353-77, it is worth noting the following structure:
first the letter designation of the manufacturer;
short-term resistance (in megapascals), reduced by 10 times;
Climatic performance;
number of the completed melt.
As for GOST 2006, the corresponding marking indicates:
company mark;
strength category according to the current standard;
climatic category;
number of the completed heat;
letter S (typical for products with increased turnkey dimensions).


Materials (edit)
High strength bolts are made on the basis of carbon steel with the addition of alloying components. Choose only those steel grades that are particularly strong and resistant to mechanical stress. Proven modern technologies are hot or cold "heading of blanks". Such techniques make it possible to significantly increase the strength of the alloy being produced.
Additionally, heat treatment is carried out in an electric furnace, which guarantees increased anti-corrosion characteristics and long-term preservation of the product; it also increases the strength of the product.


Dimensions and weight
The easiest way to find out these parameters is in the table below:
Category | Weight | Turnkey dimensions |
М16х40 | 0.111 kg | 24 mm |
М16х45 | 0.118 kg | 24 mm |
М22х60 | 0.282 kg | 34 mm |
М20х50 | 0.198 kg | 30 mm |


For M24 bolts, the key indicators are:
head 15 mm high;
turnkey dimensions - 36 mm;
thread intervals - 2 or 3 mm;
length - not less than 60 and not more than 150 mm.


For M27, the same parameters will be:
17 mm;
41 mm;
2 or 3 mm;
80-200 mm, respectively.

Exploitation
Preparation
Back in the 1970s, experts noticed that even high-strength fasteners require careful observation in the first 1-3 years. At this time, "shooting" is likely even without visible manifestations of external loads. Therefore, very careful preparations are required before starting to use. The hardware will be re-preserved throughout the procedure and cleaned of dirt and rust. Additionally, the threads are driven on the rejected bolts and nuts, after which the lubricant layer is renewed.
The preparation is carried out in two different ways. One of the options involves the use of a lattice container (and for small sizes of work, they just use a bucket in which they punch holes with a nail). Water is boiled in a barrel, where it is desirable to add a randomly selected cleaning agent. Even hand wash powder will do.
When the boiling point is reached, the container is immersed there and kept there for 10 minutes to ¼ hour.


After draining the water, the high-strength bolts will need to be immersed for 60-120 seconds in a tank containing 85% gasoline and 15% autol. The hydrocarbon will soon evaporate from the heated metal products, and the special oil will be distributed in a uniform layer over the surface. As a result, the tightening factor will be 0.18. If the twist factor is to be reduced to 0.12, waxing will be required. Cleaning in this case is done in a standard way. The next step is to place the nuts in liquid paraffin for 10-15 minutes; after removing them, it is required to allow the excess of the reagent to drain off.

Fastening
If it is planned to install bolted fasteners with the possibility of further disassembly, it is recommended to draw up a special project that takes into account the design load. First of all, they inspect all structures and find out how much they correspond to the instructions of the project and section SNiP III-18-75. The holes are aligned and then all parts are connected using mounting plugs. Next you will need:
insert fasteners into free (not closed) channels;
evaluate the linear parameters of the manufactured assemblies;
tighten the package tightly;
tighten the bolts exactly to the force prescribed in the project;
pull out the plugs;
insert the remaining fasteners into the released passages;
pull them up to the required effort.


The variation in the thickness of the elements, when tested using a feeler gauge and a pad, can be maximum 0.05 cm.If this difference is more than 0.05 cm, but not more than 0.3 cm, then a smooth bend is achieved by smoothing with an emery stone. The procedure is carried out in an area up to 3 cm from the cut line of the part. The slope should not be steeper than 1 in 10.
When calculating the length of the bolts used, consider primarily the thickness of the package. When drilling holes in machined surfaces, only oil-free coolants can be used to install the bolts. Important: wherever high-strength bolts are to be used, other types of fasteners cannot be used, even at the assembly stage. This devalues all efforts to improve bond strength. Each bolt is fixed using two washers of increased strength: one under the bolt head, and the other under the nut.
The nuts must be tightened with the force recorded in the project. Any other fixation is not needed. The moment the bolt is put in, these nuts must rotate indefinitely in the grooves when applied by hand. If this condition is not met, the problematic fasteners are replaced, and the products recognized as defective need to repeat the preparatory procedures.
It is recommended to tighten the bolts by adjusting the actual conditions precisely and varying the tension accordingly.


The required parameter is calculated using the formula M = PxdxK. These multipliers denote, respectively, the tensile force (in kilogram-force), the nominal diameter, the twisting factor. The latter indicator is taken at the level of either 0.18 (for bolts in accordance with GOST 22353-77 and 22356-77), or 0.12 (when applying other standards). The tightening factors stated in the company certificates cannot be used for calculations. If there are no more than 15 bolts per unit, as well as when working in hard-to-reach places, the tension level can be determined using torque wrenches.
The torque generated by the key is recorded when a movement is in progress, increasing tension. This work must be carried out smoothly and without the slightest jerk. Important: all torque wrenches must be numbered and calibrated. The last procedure is carried out before the start of each shift. The actual tightening torque cannot exceed the calculated value by more than 20%.
Inspectors check all high-strength bolts regardless of how they are tensioned. They should find out if all fasteners are properly marked. The setting of washers under each head, under each nut is also controlled. The density of the screed in the bag is assessed using a feeler gauge with a thickness of exactly 0.3 mm. This probe must meet an obstacle in the area bounded by the puck.

All connection points must be covered with the contractor's mark and the controller's mark.
When bolted fasteners are prepared by waxing, the letter "P" is applied near these stamps with the same core. For small-scale work, the tensioning force must be adjusted with a manual device for bolts with a cross section of 20 to 24 mm. In this case, the thickness of the package can be up to 14 cm. The serviced package can include up to 7 working bodies.
The bolt tightening procedure is as follows:
tighten all fasteners using an installation wrench with a handle up to 0.3 m;
nuts and protruding parts are covered with risks using paint or chalk;
the nuts are rotated at an angle from 150 to 210 degrees (any key is already suitable here);
control the tension simply by the torque.

For information on how to unscrew a high-strength bolt, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.