Features of sulfate resistant cement

There is an opinion that reinforced concrete products are the strongest and most durable. However, this wording is a delusion. Under inappropriate operating conditions, concrete structures are also susceptible to serious deformation and damage. They are adversely affected by severe frosts, subsidence of soil layers, oxygen oxidation, precipitation and the effects of various chemicals.

Sulphate-resistant cement is considered the best option for construction. This building material is most popular in those regions where the weather conditions leave much to be desired. This applies to areas that are characterized by sharp temperature changes and a large amount of precipitation.


What it is?
Sulfate-resistant cement or Portland cement is a special building material that differs from the usual analogue and is resistant to the negative effects of chemical compounds and the changeable whims of nature. The main area of application of Portland cement includes the construction of pumping stations, spillways and water outlets. Zinc sulphate concrete and piles are used to build most industrial structures.

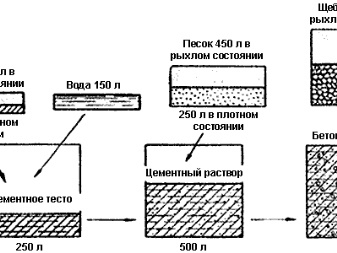
Sulphate-resistant cement hardens rather slowly, but in the hardened state it has a very high density. The latter factor is its main advantage among other building materials.
Views
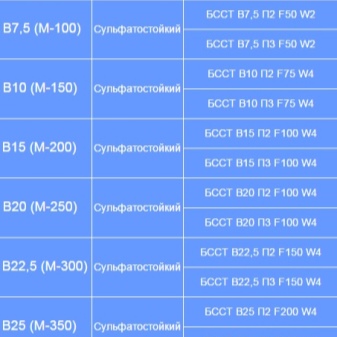
According to its composition, sulfate-resistant cement is divided into the following types:
- pozzolanic Portland cement;
- sulfate-resistant slag Portland cement;
- sulfate-resistant Portland cement;
- sulfate-resistant Portland cement with the addition of minerals.




Now let's take a quick look at each of these building materials:
- Pozzolanic Portland cement contains a mixture of granulated blast-furnace slag and pozzolans. The latter refers to products of volcanic origin in the form of ash, tuff and pumice. Pozzolans are active mineral additives in the manufacture of Portland cement. This building material relatively poorly tolerates the regime of alternating moistening and drying, as well as thawing and freezing.
- Sulfate resistant slag Portland cement is made by mixing clinker with blast-furnace slag in granular form (about 50-60%) and a small amount of gypsum. The slag used for production should contain a limited amount of aluminum oxide (up to about 10-12%). Sulphate-resistant slag Portland cement is assigned grades M300 and M400. It is relatively resistant to sulfates, but it does not tolerate severe frosts.


- Sulfate-resistant Portland cement has the brand M400... It is prone to slow curing and low heat generation. It is versatile and can withstand any kind of temperature and humidity conditions.
- In sulfate-resistant cement with minerals about 15-20% of the total cement mixture of blast-furnace slag in granules or 5-10% of minerals is added. This type of building material is produced with the M400 and M500 brands. Sulfate-resistant cement with mineral additives is excellent for the construction of various structures, has increased frost resistance and resistance to strong moisture and drought.


Application
Due to the main components of Portland cement, which can be characterized as resistant to adverse environmental factors and harmful chemical compounds, the structures created with its use are durable and strong.
Portland cement is used to create sulfate-resistant concrete, as well as the following structures:
- sulfate-resistant piles;
- reinforced concrete structures;
- bridge supports;
- hydraulic structures.

Special attention should be paid to sulfate-resistant piles in order to understand what it is. Piles are large rods made from Portland cement. Their main application is to strengthen structures and create a solid support during the construction of the foundation.
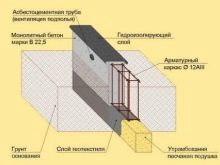


The quality of these products completely affects the durability and safety of buildings. The piles are buried deep in the soil. They are resistant to moisture, precipitation, groundwater and chemical elements in the soil cover. Most often they are used for the construction of large-sized bridges, hydraulic stations and dams.
Sulfate-resistant concrete can even be made from ordinary cement if mineral additives are included in the solution. However, it is better to use Portland cement when creating a mixture for sulphate-resistant concrete. This will increase the strength of the structure at all stages, from the concreting process to guaranteed protection throughout the entire service life of the reinforced concrete product.


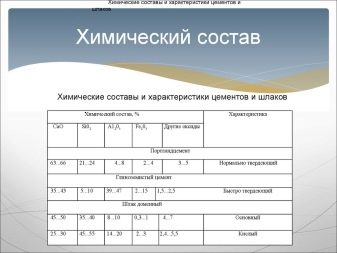
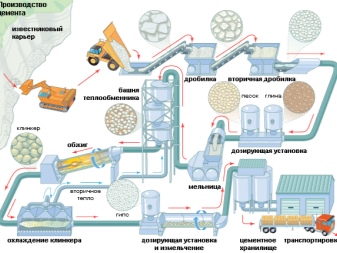
Clinker composition
Clinker is an intermediate product in the production of Portland cement. It was first heard of in 1817, when the French engineer Louis Vica invented cement clinker. This useful discovery later helped to create artificial cement (Portland cement) in 1840.
The composition of sulfate-resistant cement includes components of crushed clinkercomposed of minerals. In the production of the material, the exact dosages of all the necessary components are necessarily taken into account. Typically, the finished product contains 5% aluminate and 50% silicate. This ratio is due to the fact that there are already quite a lot of sulfate compounds in the soil layers themselves and in precipitation.
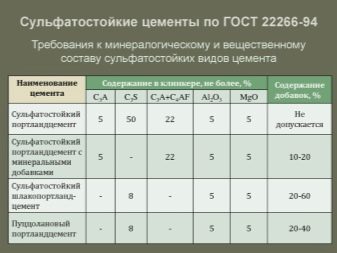
Upon reaction with aluminate, the destruction of sulfates begins and, as a result, the deformation of the structure itself. For this reason, only a small amount of the aluminate phase should be present in the feedstock for the production of Portland cement.
The basic composition of clinker is greatly influenced not only by the raw material, but also by the manufacturing conditions. When raw materials are fired, impurities are placed in it randomly. This factor creates a changeable structure of clinker phases. By the latter, it is customary to mean the basic minerals: alite and belite.
- Alit is an important mineral of great importance in the composition of clinker. It hardens quickly and has high strength. Alite is very active in combination with water.
- Belit in its reaction it is less active in contrast to alita. Also, its heat release is two times less than that of the main clinker mineral - alite. Belite hardens slowly and thus provides high strength of the material.

The main intermediate substance involved in the creation of cement clinker is tricalcium aluminate. The content of this substance in a standard mix of sulfate-resistant cement is only 5-10%. An excessive amount of this material can provoke, as noted above, sulfate corrosion. This process is fraught with negative consequences in the form of destruction of the concrete structure and crystallization of salts on the walls of materials.

As for the last destructive effect, crystallization leaves its mark in the form of a noticeable expansion of the cement stone in volume.Sometimes the influence of sulfates leads to the formation of gypsum, which also contributes to a significant expansion of the stone and the gradual destruction of buildings.
The harmful effect of sulfates on reinforced concrete structures is noted with alternating drying and moistening of the soil and the structure itself. An example is the constantly changing water level in a river. Reinforced concrete piles made of sulfate-resistant cement, during this exposure to moisture, are slowly eroded into the structure of the material and wear of structures until complete destruction.


When choosing cement for work, you should carefully study its basic composition. It is important to take into account that each specific type of soil requires a special type of cement.
How to do it?
Getting sulfate-resistant cement is possible in two ways:
- make cement mortar with special additives from mineral substances;
- the use of a special zinc-sulphate cement-sand mixture produced by an industrial method, which is durable and guarantees the protection of the structure during the entire period of operation.

In the manufacture of solutions, the exact ratios of the components should be adhered to.
In the event that mineral additives are several times higher than the standard rate, the strength of the solution is significantly reduced, and accordingly the fragility of the buildings also increases, due to which their destruction occurs. A solution of sulfate-resistant cement must necessarily comply with the basic norms of state standards.


The use of Portland cement is an expensive procedure, therefore it is not used as often as a simple analogue. However, sulfate-resistant cement is simply incomparable in its characteristics with ordinary concrete mortar.
After all, the durability of Portland cement is several times higher than that of conventional materials. It should be noted that its main distinctive properties fully justify the high cost.
Sulfate-resistant cement reliably protects buildings and structures from the effects of moisture and frost, increases the durability of structures. It can also significantly improve the quality of simple concrete mortar, as a result of which such a building material will last longer than the usual declared life.



For information on how to properly mix the cement mortar, see the video below.













Cool! Thank you!
The comment was sent successfully.