When and how to plant honeysuckle?

The honeysuckle plant belongs to the shrubs of the Honeysuckle family. It can be curly or creeping, evergreen or deciduous. There are about 200 species in nature, some of which bear fruit with edible berries. There are also poisonous and ornamental plant varieties.





Growing honeysuckle is a favorite pastime of farmers. To obtain a tasty harvest, varietal varieties are selected based on the growing region, and also adhere to simple planting rules.
Timing
In late April - early May, buds bloom on the bushes. When planting in spring, you need to focus on these dates. In the case when a honeysuckle seedling was purchased in advance, while the soil on the site has not yet been prepared, it is recommended to plant it in a volumetric pot and later plant it in the hole.

A potted seedling can be planted in an open area throughout the season. For ordinary seedlings with bare roots, early spring (until the buds have blossomed) and autumn, optimally September, will be suitable periods. For most regions, the deadline for planting is mid-October.
Spring
Honeysuckle with edible fruits is planted in spring. In early spring, a transplant or division of the bush is usually planned. From the container, the shrub is transplanted into the open ground by the transshipment method, keeping the earthen lump. This is done to protect the roots. The procedure is performed before the buds appear, otherwise the seedling will not have enough strength to grow and develop.
Spring planting of a crop in an open area has its own individual terms, depending on climatic zones:
- end of April - March: in a southern climate (in the Crimea, in the Caucasus, in the Kuban);
- April: Moscow region, middle zone of the Russian Federation;
- end of April - first days of May: Ural, Siberia, Leningrad region.
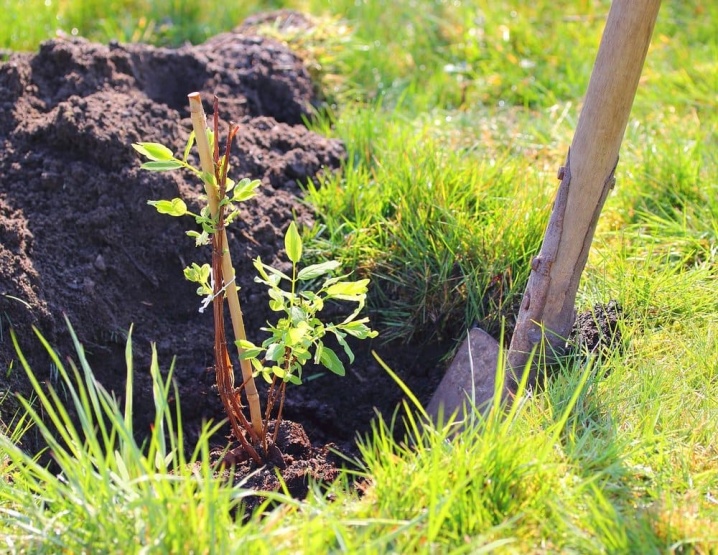

Summer
According to the experience of gardeners, it is worth planting honeysuckle in the last week of summer, or you can choose the first half of September for this procedure. At this time, the culture will be able to quickly adapt to new conditions. The plant is less likely to get sick and take root better.
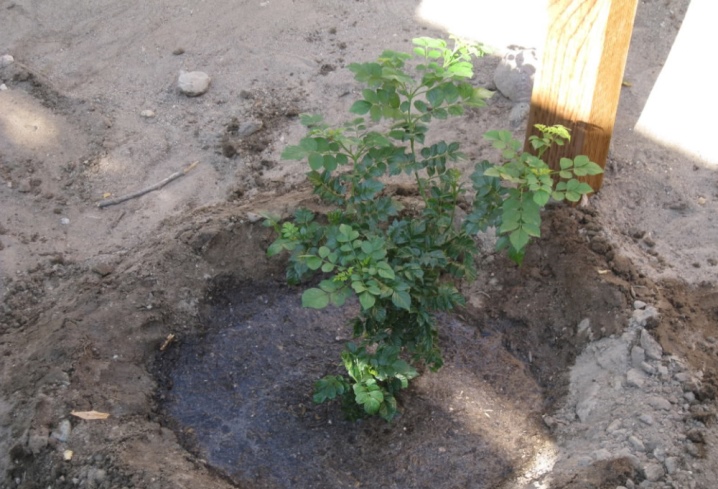

Autumn
Planting of honeysuckle this season is carried out from mid-September and lasts until the second decade of November. The timing depends on the region of growth. Honeysuckle's vegetation ends early, at the end of summer it is already preparing for rest. This time is optimal for transplanting seedlings into open ground. The process starts from the end of August to November.
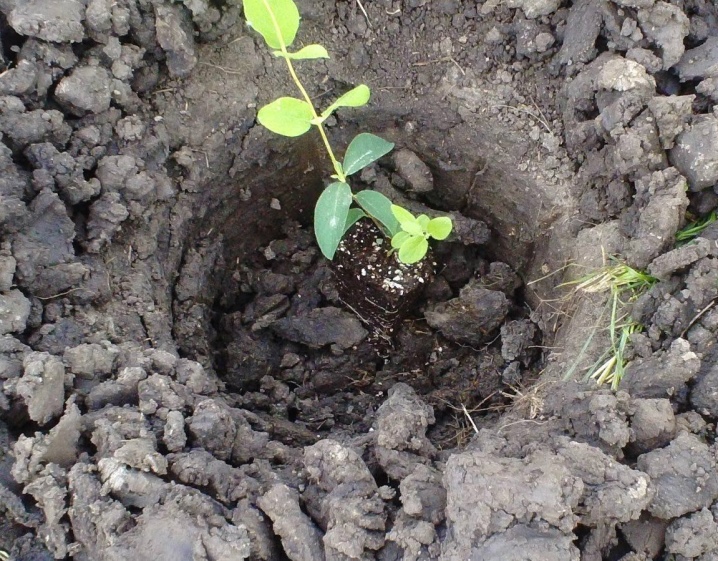

For those who want to grow honeysuckle in the fall, it is important to remember that it is necessary to plant seedlings before the onset of frost. Rooting will take about a month, at least three weeks.
Selection of seedlings
For a stable and plentiful harvest, you need to plant 2 or more seedlings, it is advisable to choose different varieties. A feature of honeysuckle is that a plant requires a group planting for pollination.
For planting material, it is recommended to go to a special store, and it will be even better and more convenient to order seedlings in the nursery. Such vegetative specimens are grown in special containers or boxes with a capacity of up to 3 liters.
On sale there is an assortment of seedlings from local nurseries or you can choose from imported ones. At the same time, the varieties from the Bakcharsky nursery located near Tomsk are considered the best. As a rule, over 20 varieties of honeysuckle varieties are available for free sale in horticultural centers.
The most suitable seedlings are 2-3 year old plants with a developed root system. They should be intact, with branches, up to 40 cm high, buds on the shoots, developed root processes. They must be kept in water for a couple of hours with the addition of "Kornevin" or a preparation similar in composition.

This method can revive even slightly dried roots.
Choosing honeysuckle for your site, you can take into account the main indicators of the plant, its characteristics:
- type and variety: edible / decorative;
- crown shape, plant height;
- sprawling shoots;
- size of edible berries and yield period;
- seasonality of flowering (depending on the place of cultivation).

To increase yields, gardeners practice mixed planting, that is, they simultaneously plant paired bushes of the same variety. In each specific area, taking into account climatic conditions, optimally suitable varieties are grown. They should be chosen for a good decorative effect or generous fruiting.


With an open root system
These seedlings are abbreviated as OKS. Their roots are not covered with an earthen clod, so the planting material can be planted exclusively in the fall, after the end of the active growing season. In this case, plant roots must be soaked in a liquid growth stimulant for 24 hours before planting. This measure will help start the rooting process.
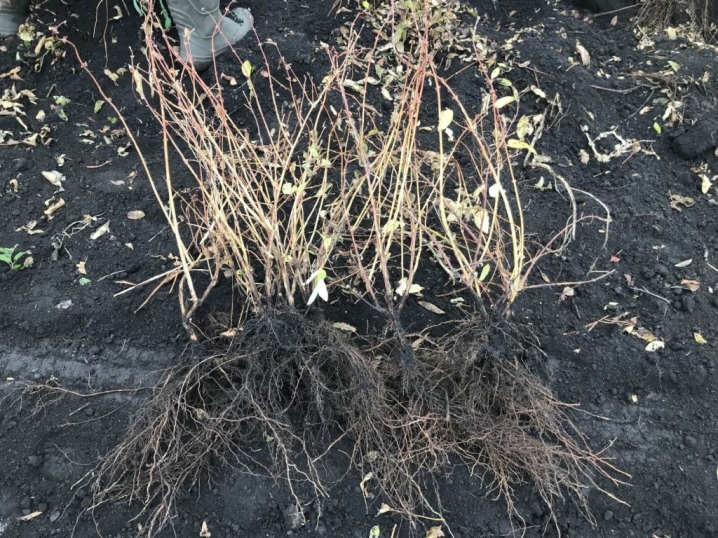

Closed root system
The so-called ZKS seedlings are on sale in retail chains and nurseries. They are placed in pots with a volume of 0.2 to 10 liters. Sometimes the roots can be wrapped in a moist layer made of clay talker with the addition of sawdust, or packed in a special box. From the latter, it is convenient to transplant the plant directly into the ground.


With closed roots, planting material is easier to protect from drying out, the development of infections and death. Saplings adapt better and take root after planting.
Seat selection
In the realities of the wild, honeysuckle bushes are found in groves and forest edges. In such an area, the plant gets to the best of the sun and shade. If you overdo it with scorching rays and plant a bush in an open space, the berries will become bitter. If you place the honeysuckle in the shade, there is a chance of getting a sour crop.
A compromise solution would be to plant the plant in diffused shade, with sufficient lighting. This condition can be met by planting honeysuckle next to tall trees, just not directly under them. Most often, honeysuckle is planted near the fence.


In the Russian northern regions it is usually rainy, and the summer is not too hot, so sunny areas would be a suitable place for honeysuckle. There they develop more actively, the berries ripen fully. Adult bushes are quite cold-resistant, but drafts are destructive for them, as well as for young specimens.
It is optimal to plant honeysuckle in the southern regions in partial shade or in a sunny place, providing the plant with constant watering. On dry soil, the bush will turn out to be weak and low, it will bring a meager harvest. Also, shrubs are not "friendly" with acidic soil.
Areas with very close groundwater flow are unsuitable for honeysuckle. If it is impossible to find the best place, it is worth planting a seedling on a high ridge. The soil is desirable fertile, light, with neutral acidity.


There should be no anthills in the place where shrubs grow.
After planting the seedlings, it is necessary to check the surrounding areas from time to time for the timely detection of insects, since where ants live, such a dangerous pest as aphids, set up to destroy all kinds of cultivated plants, settles next. Honeysuckle is also to her taste.
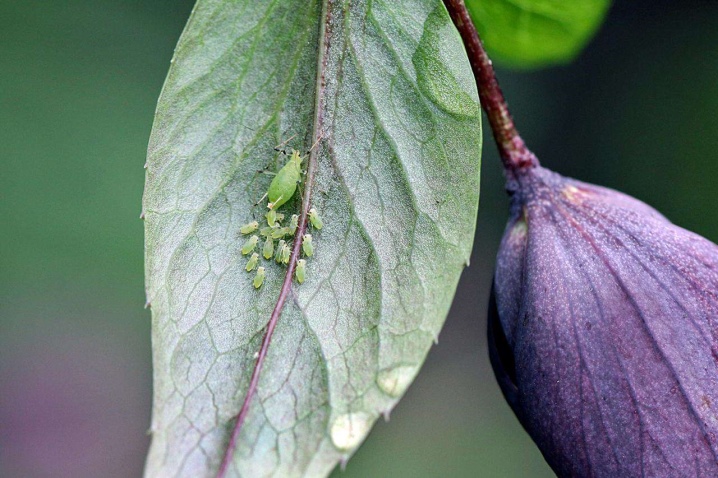

Neighborhood
Honeysuckle is rarely damaged by various pests, so it is permissible to plant it near other shrubs. The closeness of the black currant turns out to be especially successful for her.And from raspberries, gardeners recommend planting honeysuckle at a short distance - because of the powerful root system of the first.
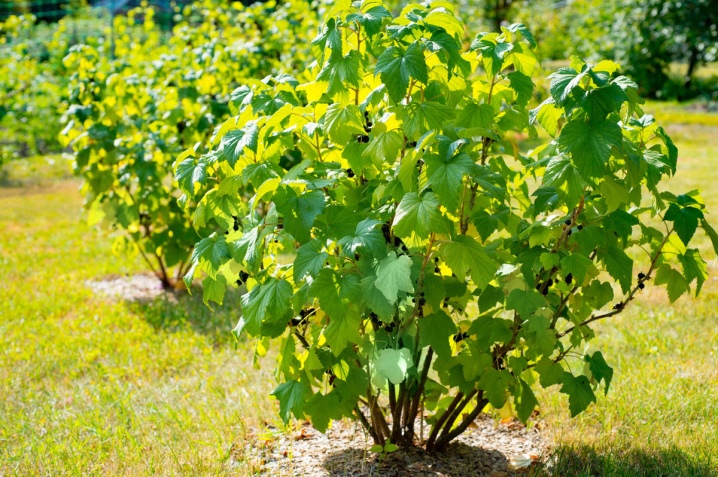

Do not place any plants in the honeysuckle tree trunk circle.
Otherwise, we can say that the plant is picky, it "gets along well" with most trees and other berry bushes. It is only important that the plant crops growing nearby do not cast a shadow on the berry.

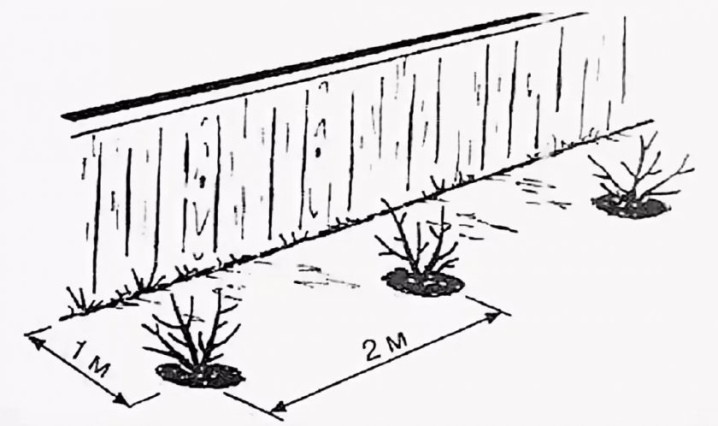
Saplings placement scheme
This is a fairly large plant, so if you want to grow a lot of honeysuckle on the site, you need to correctly arrange the plantings. Each bush will require its own nutritional area, otherwise it will not be able to grow and develop normally, let alone bear fruit.
You need to adhere to the following scheme: 1.5-2 m between honeysuckle bushes in rows and 2-2.5 m between rows. It is important not to skimp on indents, since the culture will be uncomfortable in thickened plantings.
Landing technology
Low-growing decorative varieties of honeysuckle are planted in pots or spacious tubs. The rules for planting a plant in a pot are the same as those that are adhered to in an open area:
- the first layer is drainage;
- planting a seedling in a fertile substrate;
- full watering.

The containers should be placed on a warm loggia or placed on the veranda on the south side. For uniform growth of the shrub along the edges of the pot, it is advisable to build supports in the form of sticks, wooden pegs, slats, etc. The trunk and central branches are carefully fixed on the supports.
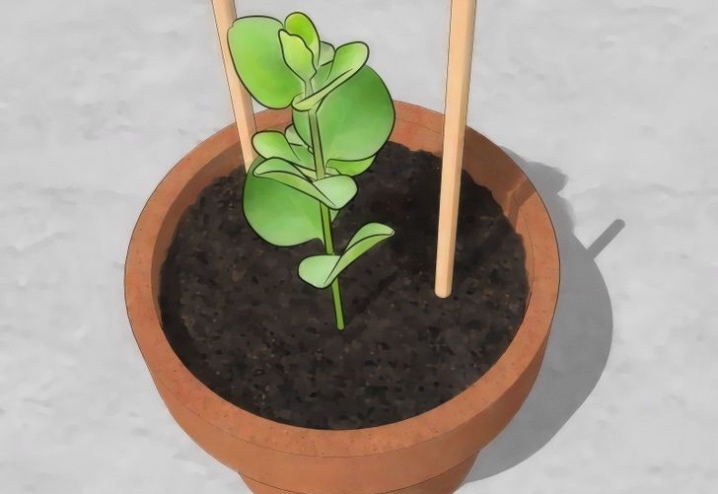

The pots are placed against the wall as the container can tip over under the weight of the shrubbery.
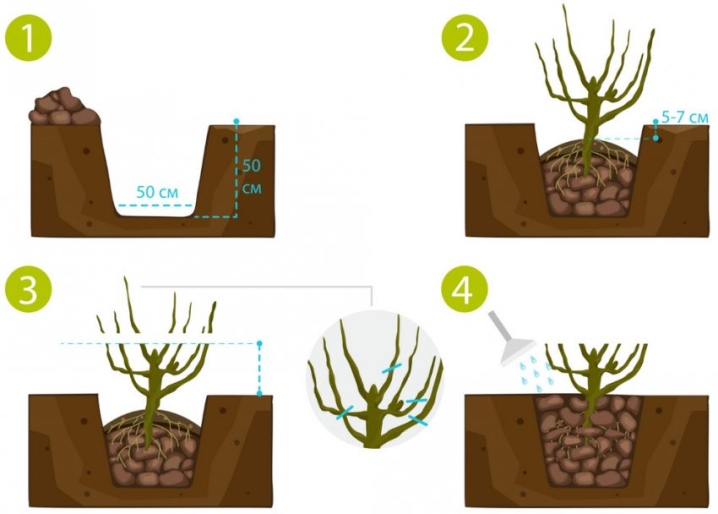
Due to the nature of the rhizome, honeysuckle has to be planted slightly differently than other shrubs. It is important to follow the step-by-step instructions:
- dig a shallow, but rather wide planting hole with dimensions of 35 * 50 cm;
- remove all the roots of perennial weeds;
- form a small mound from the substrate;
- place a seedling in the middle of the hole;
- spread the roots, evenly distributing them over the surface of the hill;
- gently sprinkle the roots with the substrate;
- deepening of the root collar by no more than 4–6 cm is permissible;
- tamp the soil in the near-trunk circle, creating a low side around its circumference;
- spill the near-stem area with 10–15 liters of water;
- when the water is absorbed, the substrate must be mulched using peat or humus, dry herbs, etc. (a 3 cm layer of mulch will prevent the soil from drying out in the future).
In the southern regions, in hot weather, it is especially important to ensure that the soil does not dry out.
In a temperate climatic zone and cool regions, before wintering, the trunk circle must be mulched, pouring mulch in a layer of 10-15 cm. Without insulation, the roots can freeze.

The soil
Edible honeysuckle should not grow on acidic soil, the optimal acidity level is in the range of 5.5-6.5. A month before planting, chalk is added to the site or replaced with lime (dolomite flour). On average, the liming of the soil takes 150-200 g of chalk per 1 square. m.

For growing fruit crops, any type of soil is permissible. Soils and sandstones of poor composition must be regularly fed with organic matter and mineral complexes.
Ideal for honeysuckle is light and loose, fertile soil. Also, the plant will show itself well on sandy loam and loam, black soil. Groundwater in the area where it is planned to grow honeysuckle should lie no higher than a meter above ground level.

The deeper the water, the better for the honeysuckle. This crop should not be planted in swampy low-lying areas, as well as large hills are unsuitable for this.
Landing pit formation
The honeysuckle bush is distinguished by vigorous shoots up to 2.5 m high, so the seedling needs enough space to feed. A separate planting hole must be made for each plant.
Pour a couple of buckets of humus inside or use the same amount of rotted compost, add 80-100 g of superphosphate, potassium salt at the rate of 30-40 g and a full liter can of wood ash. All fertilizers are mixed with the substrate.



Sapling placement
For a seedling with an open rhizome, you first have to straighten the roots along an earthen hill.
The seedling with the ZKS must be removed from the pot, spread the roots, planted on a hill or in a planting pit. Such a seedling can be immediately placed in the hole, but the root collar should remain at ground level.
Pour soil into the pit and tamp, quite tightly pressing the substrate to the roots. It is important to compact the earth in stages so that voids do not form around the roots.
It is necessary to deepen the seedling to a depth of 5 cm from the level of the root collar.
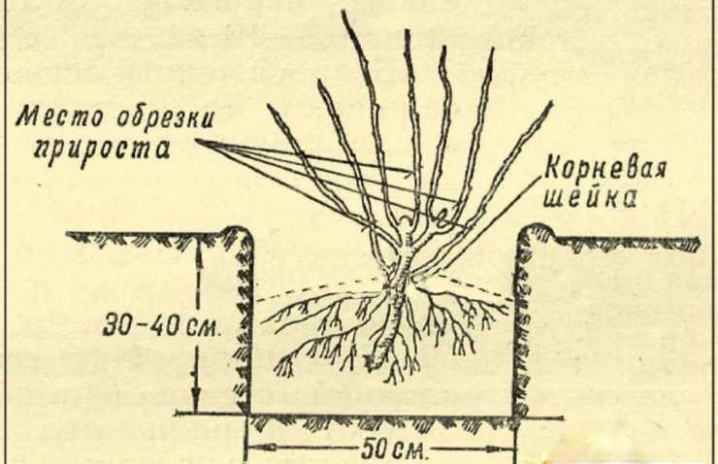
Pour water on top, you can have one or two buckets. Mulch with grass or use wood chips, cardboard or regular newspaper immediately after soaking.


Further care
Growing honeysuckle will not be a problem. The shrubs should be watered as needed. After planting in an open area for 3 years, honeysuckle should be spud high. Moderate watering is important for the plant, and in dry periods, abundant soil moisture.


It is also necessary to periodically remove weeds, fertilize and loosen the soil. Honeysuckle also needs feeding after it is harvested.... Preventive treatments of honeysuckle plantings from pests and infections will be required.

For the prevention of diseases, as soon as the buds hatch on the bushes, they will need to be sprayed with a solution of one of the drugs: "Fitosporin", "Aktara", "Trichodermin" or "Karbofos".
Not only shrubs need to be processed, but also the soil under them. The dosage of a specific drug and the frequency of treatments are indicated in the instructions.

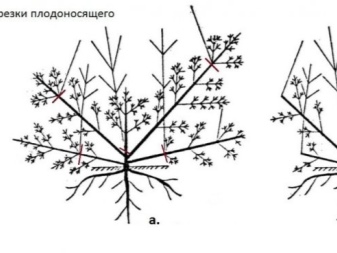
You need to trim it painstakingly and carefully. Even when cracks have formed on the branches, you should not panic, as well as cut off the "damaged" shoots. Observing the rules of caring for honeysuckle plantings, you can get fruits for up to a hundred years in a row.
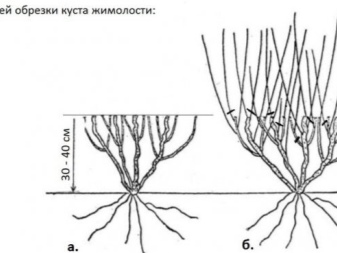
Honeysuckle pruning rules:
- in the first year of life shrub, it is necessary to pick off all the flowers, otherwise the plant wastes energy and does not take root enough;
- in the second season most of the flowers are removed, the color remains only for the sample of berries;
- once in 2-3 years in the autumn period, the rejuvenation of the bush (thinning) is carried out;
- in the sixth year of life in the fall, it will be necessary to remove obsolete, sick and damaged branches - the so-called. sanitary pruning;
- 15 year old and older bushes need updating - the branches are cut "under the stump", the bush is updated after a couple of seasons.
The structure of the roots of honeysuckle is such that they lie shallow in the soil, similar to currants. The near-trunk areas must not be dug up. They are simply loosened carefully so as not to harm the root processes. All weeds are removed.
To retain moisture and activate the soil microflora, you need to mulch the trunks.

Honeysuckle tolerates the "resettlement". The bushes are transplanted to a new place using the transshipment method. After the harvest is harvested, the bush is carefully dug in and transferred to a prepared hole with an earthen lump.
For successful adaptation in a new area, the shrubs need generous watering and replenishment with mineral compounds.
Frost-resistant varieties are not afraid of severe cold weather; in winter, bushes do not require shelter. The branches on them can freeze slightly, but with the arrival of spring heat they quickly recover.
Climbing shrub varieties are less winter hardy. They are usually planted in milder climates.
Honeysuckle pleases not only with amazingly tasty fruits, but also with a decorative look. To preserve these properties for a long time, it is important for a shrub to provide proper care.













Thanks!
The comment was sent successfully.