Insulation for the walls of the house outside: types of insulation and features of materials

No matter how comfortable and modern the house is, without high-quality thermal insulation it will not become comfortable for living. Properly organized insulation can significantly reduce heating costs, protect the facade of the house and its premises from dampness, freezing, the appearance of mold and fungi, which will significantly extend the life of the building. The most popular is the exterior or facade insulation of the house.

Advantages and disadvantages of outdoor insulation
All load-bearing elements of the structure must be insulated, however, for the outer walls of the house, this is especially important, since they are the ones leading in terms of heat loss.
By insulating the outer walls, it is possible to protect them from the negative effects of high and low temperatures, as well as their abrupt change. As a rule, the insulation is closed with a facade, which also performs a protective function, taking on the atmospheric effect on itself. All this contributes to the preservation of the strength of the walls, an increase in the period of their maintenance-free operation.
Insulation outside can be quite voluminous, but this does not in any way affect the usable area of the premises in the house. This cannot be achieved when insulating rooms from the inside, because even the thinnest layer of thermal insulation leads, albeit to a slight, but decrease in the usable area.


In addition, with external insulation, it is possible to avoid the formation of "cold bridges", which inevitably arise between the floor and walls, walls and partitions during internal insulation of the room. User reviews suggest that "cold bridges" are practically not formed when the facade is insulated. Otherwise, they can be easily eliminated by using special gaskets at the joints of the insulation sheets.
The task of thermal insulation of external walls is to bring the total indicator of their resistance to heat transfer to a calculated indicator that is optimal for a particular area. More details about such calculations will be discussed below.

Usually they resort to insulation already on the erected walls. Thanks to the variety of modern materials and insulation techniques, it is possible to solve the problems of heat transfer and, accordingly, protect the walls from freezing, the appearance of erosion on concrete surfaces, rotting of wooden structures.
In rare cases, you can do without additional wall insulation in frame houses in the first place. Others, for example, foam block houses, definitely need thermal insulation.



The ways
Depending on the type of facade, structural features and the selected option for exterior decoration, one or another method of installing insulation is selected. Today's thermal insulation materials have a small thickness with high thermal efficiency. They are suitable for both wet and dry facades and can also be poured into wall voids. The first involves the use of building mixtures for decoration, the fixing of the insulation is carried out with glue.

Suspended facades involve the use of fasteners. As a rule, panels and tiles are used for decoration, which delight with a variety of designs.The user can choose calm muted shades of the panels or, on the contrary, bright ones. Facade materials like stone, wood, imitating plaster or brickwork, are very popular.


Thermal insulation with bulk material, for example, granular foam glass, is used when erecting walls using the well method. Also, materials of this type are suitable for mixing masonry mortars and plaster mixtures. Regardless of the chosen method of laying the insulation, the surface of the walls should be prepared. All protruding elements must be repulsed, cracks and gaps must be repaired with cement mortar.


It is necessary to remove all communications from the facade - wires, pipes. The surface must be level, clean and dry. After that, it is necessary to prime the facade in 2-3 layers. The primer will provide additional protection for the walls as well as better adhesion of materials. It is recommended to pre-treat wooden surfaces with an antiseptic or choose a primer containing antiseptic additives.

Under plaster
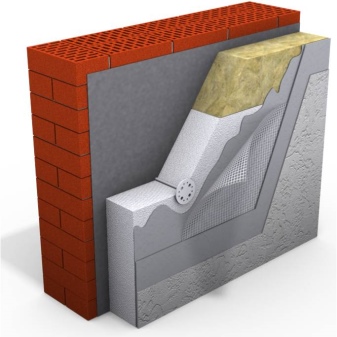
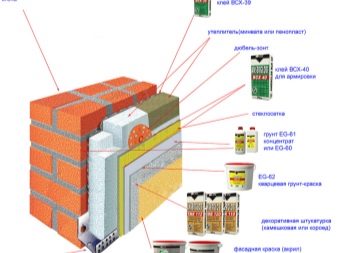
Insulation in the form of sheets or plates is glued to the prepared wall with special glue. Additional fixation is provided by umbrella dowels, which are inserted into specially made holes on the surface of the glued insulation. Each subsequent row of insulation is attached with an offset of ½ sheet of the previous row. For some time after gluing, the material remains mobile, so it is possible to align it and correct minor flaws.
After the insulation is fixed, a thick layer of glue is applied to it, into which the reinforcing mesh is pressed. First, it is attached to the corners of the building, for which special corners are used. After about a day, the facade mesh is securely installed at the corners and you can start attaching the mesh to the rest of the facade surfaces.


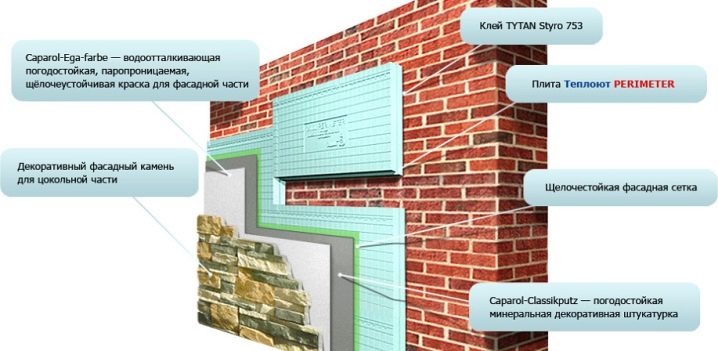
The next step is to plaster the surfaces. The composition is applied in several layers. Each subsequent - after complete drying of the previous one. To improve the adhesion of the layers and eliminate small irregularities on the dry layer, you should walk with fine sandpaper.
The finishing layer of plaster is covered with decorative plaster or painted with facade paint. The latter usually has an acrylic base, the presence of polyurethane in the composition is permissible to increase the strength and wear resistance of the painted layer.

Ventilated facade
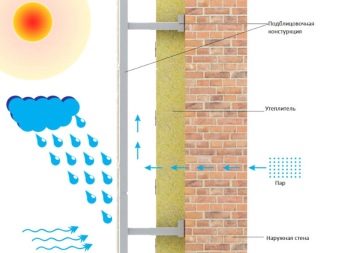
To increase the thermal efficiency of a building, they increasingly resort to organizing a ventilated facade. Its feature is the presence of air space between the insulation fixed close to the wall and the facade material. This distance is usually 25-50 mm.
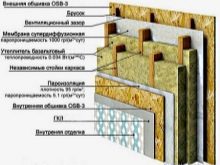
In addition to preparing the facade, it is necessary to install a crate - a system consisting of metal profiles or wooden bars, which is a frame. Facade materials are attached to this frame.
For the lathing, metal profiles are increasingly used, which is associated with their greater bearing capacity, as well as durability and fire resistance. An important point - the profiles of the lathing should be made of stainless steel. Other metals may be used, provided that they have anti-corrosion protection.
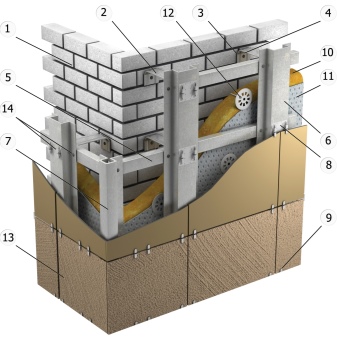

Wooden logs are also used as a frame. Before installation, they are treated with fire retardants and compounds that increase the hydrophobicity of the wood. The frame is attached to the entire surface of the façade by means of brackets. Insulation (in the form of sheets, mats) is laid between the guides of the crate, which is attached to the brackets (as if hung on them).
A waterproofing windproof membrane is laid on top of the insulation, which serves to protect the thermal insulation layer from moisture and blowing out. The membrane together with the insulation is fixed to the wall by means of disc dowels. The fastening element must necessarily be in the center of each heat-insulating sheet, 2-3 dowels are installed along the edges.


The completion of the work is the installation of hinged panels or tiles, which are fastened with self-tapping screws to the crate and interlock with each other by means of a locking mechanism. The latter ensures the wind resistance of the facade, the absence of gaps in it. For the design of corners, window and door openings, various architectural elements, special additional structures are used.
It is a mistake to think that only a curtain facade can be ventilated. Wet technology is quite applicable to a ventilated system. For this, the facade is also decorated with a wooden crate, between the guides of which insulation is glued. A protective membrane is installed on top of it.

This "pie" is covered with a solid sheathing of plywood or boards. They are mounted on wooden logs, thus creating a solid wooden "facade". It is primed, and after drying, finishing plastering is performed.
Finally, there is the so-called integrated approach - the organization of a ventilated facade using thermal panels. The latter are insulated facade slabs (for example, clinker), which are glued or fixed to the lathing. There is no need for additional wall insulation, the main thing is to select the required thickness of the thermal panel insulation (standard thickness is 30-100 mm) and seal the gaps between the facade tiles.



Three-layer system
This insulation technology is possible only when building walls at home. As a rule, it involves laying walls according to the principle of a well. As the level of the facade rises, an air space forms between the walls. It is filled with bulk insulation or liquid thermal insulation mixtures.
An option for such a construction can be the use of overall aerated concrete blocks with large cavities for the construction of walls. At the same time, the cavities in the blocks are filled with bulk insulation (expanded clay, perlite).


A simpler and less laborious way to build warm walls is to use blocks of non-removable polystyrene foam formwork. The installation of blocks is somewhat similar to the assembly of a children's designer - the elements of the wall structure are fastened by means of spikes and grooves. After the wall has risen somewhat, a reinforcing belt is installed and concrete mortar is poured.
The result is reinforced concrete walls equipped with an inner and outer thermal insulation layer. In this case, the facade finishing is carried out using ½ brickwork, facade tiles, or simply plastered. The choice of interior finishing options is also wide.


The only way to organize a three-layer insulation system is to cover the structure with brickwork. In other words, the masonry acts as the outer layer of the "pie", as well as the finishing of the facade.
The technology implies the insulation of the main wall with insulation, and then facing it with bricks. This method is only suitable for reinforced foundations that protrude at least the width of the brick. If the bearing capacity of the existing foundation is low, then the brick cladding requires the installation of its own foundation. He, in turn, must be associated with the base of the main walls.


Varieties
Depending on the composition and production technologies of manufacturing, heaters have a different appearance, technical characteristics and scope. There are materials that are used exclusively on flat surfaces, while others are only suitable for curtain-sided ventilated facades.
However, modern heaters are quite versatile.So, bulk materials are suitable not only for insulating flat surfaces or filling in the inter-wall space, but can also be added to the cement mortar for pouring or screed floors. Mineral wool materials are used for wet and curtain walls, and are also suitable for thermal insulation of interior walls, floors and ceilings. Moreover, due to the heat resistance of stone wool, it can be used to insulate baths or saunas.



Stone wool can insulate both non-stressed structures and those that are under pressure. To do this, you just need to choose the right density of cotton wool.
Due to the variety of release forms, it is possible to choose a more convenient option from the point of view of installation for a specific site. So, it is convenient to use roll materials to insulate flat, flat areas. Plates will help out, if necessary, to cover large flat vertical surfaces. Loose materials or foam insulation are suitable for basement insulation.



Styrofoam and extruded polystyrene foam
Previously, styrene foam insulation was almost the only one, and therefore was widespread. Today the situation is different, and the owners of private houses are in no hurry to use it for thermal insulation.
Expanded polystyrene materials are presented in two types - non-pressed expanded polystyrene (more commonly known as polystyrene) and an analogue obtained during extrusion. Polyfoam is a light rectangular white blocks that can have different thicknesses. At the base - foam balls filled with air. It is they who provide significant indicators of the thermal efficiency of the material.

However, it is important to understand that it is thanks to this structure that the material is able to absorb up to 300% of its mass of water. Naturally, there is no trace of the former thermal efficiency.
Polyfoam does not allow the walls to "breathe", and after 5-7 years its thermal efficiency will decrease by about 8 times. This is confirmed by laboratory studies and is associated with destructive changes in the material (the appearance of cracks, half-lengths).
The main danger of using foam as a heater is its tendency to actively burn with the release of extremely toxic substances into the air. In this regard, it is banned for use in construction in many European countries.


However, in fairness, it should be noted that foam plastic, due to its low weight, does not require strengthening the facade, is easy to install, and has a low cost. A more modern type of foam is extruded polystyrene foam. Thanks to the technological features of production, the material managed to deprive many of the disadvantages of its non-foamed analogue.
The extruded material also consists of many smaller (compared to foam) air bubbles, each of which is isolated from the next. This increases the thermal efficiency of the material, as well as the mechanical strength and moisture resistance.



The components of carbon dioxide or inert gases present in the composition somewhat increase the fire resistance of the extruded insulation, but there is no need to talk about its complete fire safety.
Due to its low vapor permeability, the material is suitable for use only in ventilated facades. At the same time, it is important to stick it tightly to the surface of the walls, avoiding gaps and gaps between the insulation and the wall.
Extruded polystyrene foam is good for insulating a basement or foundation. The increased strength of the material will ensure its resistance to soil pressure, and moisture resistance will protect it from getting wet and deteriorating the base.


Polyurethane foam
The use of polyurethane foam is considered one of the most effective methods of thermal insulation, since in its thermal insulation characteristics it is significantly superior to most thermal insulation materials.To achieve a positive effect, a layer of 2-3 cm is enough.
Polyurethane foam refers to liquid types of insulation, which are applied by spraying. After hardening, a durable moisture-resistant layer is formed. Due to the improved adhesion of the material, such a monolithic "fur coat" is applied to almost any surface. An important advantage of polyurethane foam is its fire resistance. Even when decomposed by high temperatures, it does not release toxins.

It is worth noting the environmental friendliness of the coating. During spraying, the composition contains compounds hazardous to health, however, as they solidify, they volatilize. The material is not suitable for contact finishing (plastering, painting), since it is impossible to obtain a completely smooth and even surface during the spraying process.
Aligning the polyurethane foam "coat" (as well as removing it completely) is a very laborious process. Among the disadvantages is low vapor permeability. This necessitates enhanced ventilation of the facade. Polyurethane foam is not recommended for application on wooden walls, because literally in 5-7 years, wood decays due to constantly high humidity.


Mineral wool
Today this material is becoming more widespread due to its versatility, good thermal insulation performance and affordability. Such material consists of randomly spaced fibers, between which air bubbles are contained in large volumes. It is they who provide not only a high thermal insulation effect, but also good sound insulation.
When insulating facades, glass and basalt wool are usually used. The first is based on glass breakage and quartz sand, which are melted. Long and thin fibers are formed from the semi-liquid mass, after which they are given the necessary shape (mats, rolls).


Glass wool is plastic, which determines, firstly, the simplicity of its transportation and storage, and secondly, the possibility of using it on uneven surfaces. The material is pressed and packed into compact boxes or rolls. After opening the package, the material takes the prescribed shape and volume. In addition, due to its elasticity, glass wool insulation is optimal for cladding wall surfaces with complex configurations.
The material does not melt, does not attract rodents or pathogenic microflora (fungi, insects). The combustion temperature is 500 degrees, which allows us to speak of a low flammability class of the material. Its affordable cost is a definite plus.



A significant disadvantage of glass wool is its hygroscopicity. It is clear that getting wet, the material loses its technical characteristics. In this regard, when using insulation, it is important to consider reliable water protection or the possibility of regular ventilation.
Glass elements, being amorphous, stick together during operation. This causes the material to shrink - over time it becomes thinner, which negatively affects its thermal insulation properties.Finally, glass wool fibers have cutting edges. They penetrate the skin, causing irritation.
In addition, when rising into the air, glass wool particles enter the upper respiratory tract and on the surface of the mucous membranes, also causing swelling and irritation. To work with insulation, you need to purchase a special suit, glasses, gloves and a respirator.


Basalt wool is more attractive in terms of installation and technical characteristics. It is also called stone, which is explained by the peculiarities of its composition. Cotton wool is made from molten rocks (basalt, dolomite). The heating temperature reaches 1300-1500 degrees. Fibers are also drawn from the molten raw material, from which mats are formed.Those, in turn, are subjected to pressing and additional heat treatment to obtain strength and geometric accuracy of shapes.

Basalt wool is superior in thermal efficiency to fiberglass of similar density. Stone wool is distinguished by excellent vapor permeability and high water resistance (due to the special impregnation of fibers). Despite the density of the mats, they are easily cut with a construction knife. In this case, the adhesive can be applied directly to the cotton wool, as well as the plaster layer can be laid (after the wool is reinforced).
Basalt insulation fibers are less brittle, do not split. It is easier to work with the material, although you should not give up a respirator. Like all mineral wool insulation, stone wool forms dust during the installation process, which negatively affects the state of the respiratory system.


Liquid products
When applied, liquid insulation looks like paint. However, they contain evacuated voids, thanks to which stunningly low values of thermal conductivity are achieved (by fractions of a thousandth they are superior only to the thermal conductivity of vacuum).
It is worth noting the ease of application and good adhesion to most building materials. The formulations are applied as paint coatings using brushes or rollers. Setting time is on average 6-8 hours. After that, an attractive, fire-resistant, environmentally friendly surface is formed. The liquid coating also protects walls from negative weathering and has anti-corrosion properties.


Loose species
Used to fill wall cavities or create mortars with thermal insulation properties. The oldest free-flowing heat insulator is expanded clay, which is "balls" of fired clay of different fractions. Due to its porous structure, the material has good thermal insulation properties. During the sintering process, it gains surface strength. In combination with low weight, this expands the scope of expanded clay.
The advantage of the material is its non-hygroscopicity (despite its porous structure), fire resistance (does not burn, does not emit toxins during heating), biostability (does not become a habitat for any of the life forms, a home or food for rodents), environmental friendliness and an affordable price. When using expanded clay, it is important to fill it with a thick layer, use a multi-layer structure or large hollow blocks. This is the only way to achieve high-quality insulation.

A more modern bulk insulation is vermiculite. It is based on hydromica, which is subjected to high-temperature firing. As a result, it swells, turning into layered granules with a large number of pores.
It has a low coefficient of thermal conductivity, fire resistance and durability. The only drawback is the high cost (on average, 7000-10000 rubles per m3 of vermiculite). The optimal solution in this regard is to add granules to the plaster mix to obtain a "warm plaster". Due to its high vapor permeability, such plaster is successfully used on various types of surfaces.


The use of expanded perlite sand is no less effective. The raw material is volcanic glass, which, after firing, forms fine and light porous sand.
The finished product is characterized by high values of thermal insulation (due to its low density and gas content), fire resistance. The composition of perlite contains fine powder, which is why it is quite difficult to work with it - the process promises to be troublesome and dusty. The best solution is to mix it into concrete or masonry mortars.
The use of the latter provides high-quality thermal insulation and reduces the risk of the formation of "cold bridges", since the solution penetrates into the joints between bricks or blocks, fills cracks and voids. Perlite is also used in the composition of "warm plasters", the application of which not only copes with the function of thermal insulation of the house, but also acts as the finishing of the facade.

Criterias of choice
In addition to low thermal conductivity, insulation for external walls must be characterized by high fire resistance. The optimal materials are those that belong to the class NG (non-combustible materials) or have a low flammability class (G1, G2). Fortunately, most materials are self-extinguishing, that is, they do not burn with an open flame.
However, modern synthetic-based heaters (and there are most of them) can emit hazardous combustion products when smoldering. According to statistics, it is they who become the cause of human casualties in case of fire. In this regard, it is important to choose not only a fire-resistant material, but also to make sure that it does not emit toxic elements during combustion.

Another important criterion is the vapor permeability of the insulation. When insulating walls, it is important to bring the "dew point" to the outer layer of insulation. This point is a linearly changing boundary, which accounts for the transition of moisture from one state of aggregation to another, or rather, from vapor to liquid. The liquid, in turn, leads to wetting of the walls and insulation, after which the latter ceases to cope with its functions.
The walls get wet, erosion and other destructions occur on them, zones of high humidity are found inside the house, which leads to dampness of the walls, the appearance of mold, and insect nesting. Avoiding such troubles allows the choice of insulation with high rates of vapor barrier and moisture resistance and, of course, the competent organization of the heat-insulating "pie" with the obligatory use of a vapor barrier film or membrane.

When choosing a heater, it is important to consider the cladding material. So, for brick walls, you can purchase polystyrene foam, while it is imperative to provide a ventilation system. Stone wool or expanded polystyrene is traditionally used under a wet facade. For hinged facades - mineral wool insulation, as well as for wooden buildings.
It is also important to take into account the features of the operation of a suburban building. So, as a heater in the country, where you live only in the summer, extruded polystyrene foam is quite suitable. If you finish it with plaster, it will turn out to be cheap and beautiful to equip the facade.
But for the insulation of walls made of aerated concrete, polystyrene cannot be used. A good solution would be the use of mineral wool insulation and further siding. By the way, this option is also optimal for cinder block houses and expanded clay concrete walls. An arbolite house built from blocks with a thickness of 30 cm or more does not need to be insulated. An exception is living in a region with a harsh climate.
Preparatory work
Preparatory work involves the selection and purchase of insulation. It is important to correctly calculate its amount (volume), as well as the thickness. If the thermal insulation is carried out independently by the owner of the house, you should achieve the evenness and smoothness of the walls.
To do this, communications are dismantled from their surface, protruding elements are knocked off, cracks are filled with cement mortar. After that, the facade is primed in 2-3 layers. When organizing a ventilated system, a crate is mounted. When facing with bricks, the foundation is strengthened.
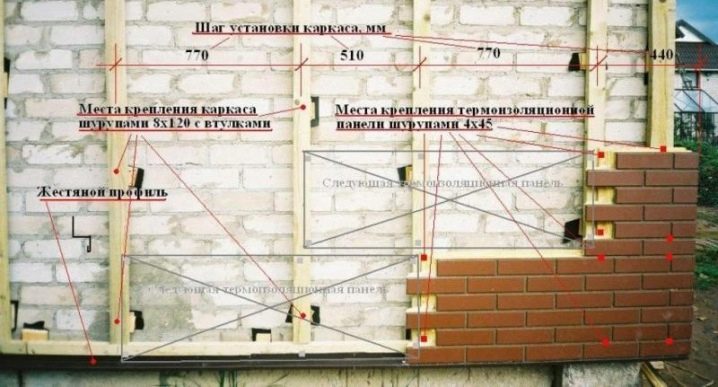
Thickness calculation
With thermal insulation, it is important not only to choose the right insulation, but also to calculate its required thickness. Using an overly thin layer will not solve the heat loss problem. An unreasonably thick layer will lead to excessive stress on the walls, an irrational increase in the cost of work.
There is a special formula for calculating the thickness of the insulation, but it can be difficult for a non-professional to work with it. Knowledge of the regulatory requirements for wall thickness helps to simplify the calculation process. So, for brick walls, this thickness is 210 cm, for wooden walls - 53 cm. Next, you need to find out the thickness of the walls in your own house, by subtracting to determine how many cm are not enough to meet the standard indicators.

Installation technology
Most modern heaters are versatile and are suitable for fastening from the street to stone, concrete, wooden surfaces, block bases. As a finish, both decorative compositions and tiles, panels and siding for tiles and natural finishing materials are used.
The installation technology differs depending on the features of the organization of the facade system and the materials used. Slightly above, it has already been said about 3 possible methods for arranging an insulated facade:
- thermal insulation for plastering;
- ventilated facade;
- three-layer facade.
When insulating walls, it is important to take care of insulating its basement part. It is through the base that most of the heat loss occurs. Foamed polystyrene foam, polyurethane foam, basalt insulation are suitable as insulation.
The surface of the basement is cleaned of facade coating, dirt, if necessary, reinforced, necessarily leveled, primed. Next, the insulation is fixed in accordance with the technological recommendations for its installation.


For information on how to properly insulate the walls of the house from the outside, see the next video.













The comment was sent successfully.