What are the facade profiles and how to choose them?
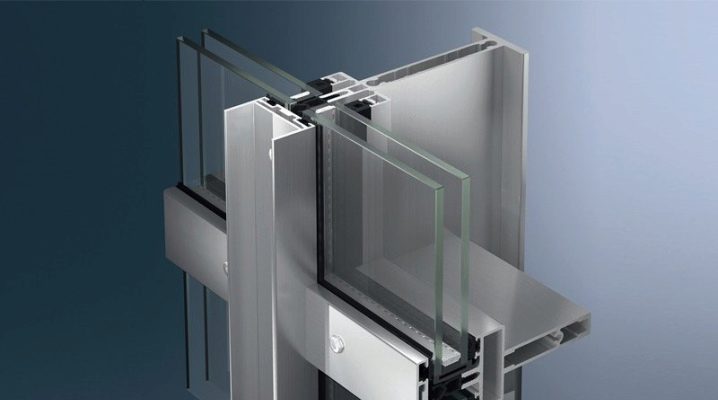

The purpose of the facade profile is to create an air layer that ventilates the walls of a building or structure. The first thing that comes to mind in this case is vinyl siding, which is extremely difficult to install on a brick or gas / foam block wall without U-shaped and corner guides.


Species overview
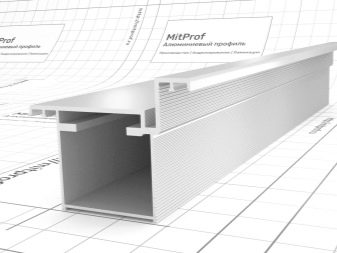
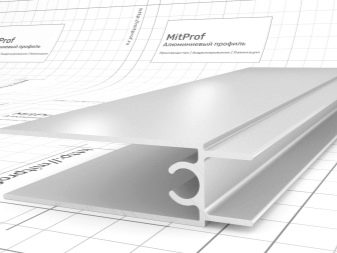
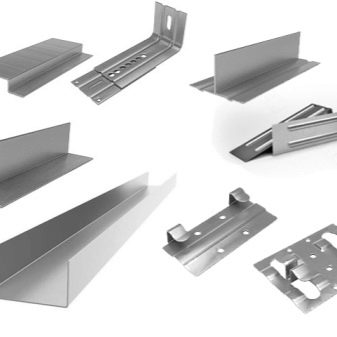
Facade profiles for fixing panels - means (consumables) for creating a supporting structure for plastic or composite cladding. L-shaped and U-shaped (in section) metal profile is the most demanded building material for exterior decoration of buildings and structures. One of the typical sizes is 40x40 mm in section. The thickness of the steel (walls) is no more than 1 or 1.5 mm, thicker corners are already referred to as simple professional steel, designed to create not vertical, but combined supports (structure skeleton), and not only for facing. For fences, a metal profile for siding is not suitable - it is easy to bend it, and after covering it with, for example, the roof of a gazebo, you cannot walk on it - it will bend.


The ventilated facing facade has an expansion joint - a number of gaps that save steel and vinyl (or composite) from buckling in the heat (in hot weather) and excessive stretching in the cold in cloudy weather. The fact is that all solid bodies expand-contract with an increase and decrease in the ambient temperature. Starting to "walk" and being rigidly fixed, they deform and spoil the appearance of the cladding - next to the wall it is not so noticeable, but as soon as you get up from the end or corner, the curvature of the curved arc panel immediately catches your eye.
Despite the fact that the siding is made light or completely white (so that it does not bask in the sun, reflecting the entire visible spectrum from itself), deformation technological gaps are needed.
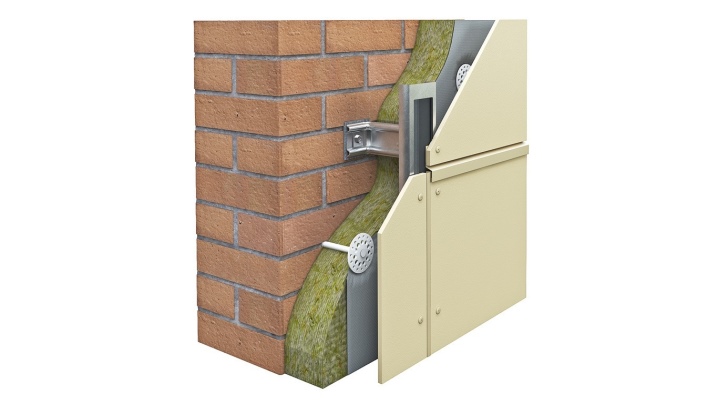

In addition to the main (vertical) profile, there is also a support (horizontal) profile. It is somewhat thicker - if, for example, a vertical one can be laid with a wall thickness of 1.1 mm, then the supporting one may need 1.5 mm. Supporting - basement and attic - the tiers are set at the same height in level, ensure the constancy of the length of the vertical guides along the entire perimeter of the structure to be faced. The height of the basement is set either flush with the blind area, or - at the level of the lower elevation of the concrete floor of the foundation, built on a strip-vertical base.
However, when the house has a basement floor, it is recommended to close the entire wall to the blind area from the outside, having previously put insulation and hydro-vapor barrier around the basement perimeter.
Varieties of the L-shaped (corner) profile - V-shaped and L-shaped segments. The first serif (fold) is made from the side of the shorter edge, while the second has both longitudinal serifs. If the bend angle of the L-profile is always straight, then at the “V” profile it can turn out to be both blunt and sharp, and the longitudinal sides are left bent inward or bent outward. The latter option makes it easy to attach the V-section to any surface. The reinforced profile has not only these bumpers, but also a maximum - up to 1.5 mm - wall thickness, as well as additional spacer components that enhance its rigidity (diagonal elements).


Materials (edit)
Steel is used as the basis for the ventilation facade. Complementary (decorative) elements at the ends can also be used with aluminum structures. Steel is the most durable material. To protect against high relative humidity, close to 100%, for example, in tropical and equatorial rainfall conditions, zinc plating, anodizing with aluminum and other alloys containing anti-corrosion alloying additives are used. Although the load-bearing base of the siding is closed from the rain with the same vinyl or polypropylene panels, it will not be possible to completely eliminate moisture in fog or during periods of intense evaporation against the same rainfall. Pure aluminum breaks easily, although it is stronger than many types of plastic and composite. The use of biodegradable plastic, which is destroyed by moisture, ultraviolet radiation, temperature fluctuations and microflora, which is always in the air, has not fully justified itself. Plastic cannot be considered as a full-fledged replacement for metal profiles, although developments in this direction are still underway.

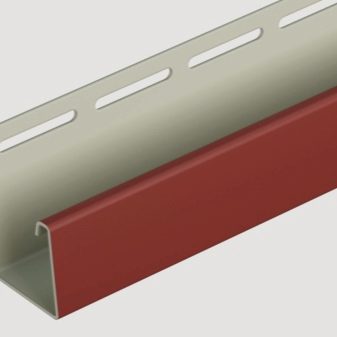
Aluminum
Aluminum is not afraid of high humidity - with the exception of acidified, alkalized or salted water, in which it would be immersed. Normal splashes and condensation mist will not corrode aluminum. Despite the fact that aluminum is more active than zinc and easily oxidizes, the dense oxide film prevents the wet aluminum profile from deteriorating further, as happens, for example, with a galvanized coating, which, when worn out, immediately causes the structure to rust. The ductility of aluminum makes it easy to file and bend the profile walls. Extension and repeated bending are unacceptable: microcracks will immediately turn into a break, and the fulcrum in this place will be lost. Aluminum is a disposable material in terms of bending, this is its main drawback. Heavy weight - for example, anodized steel siding, siding covering made of painted roofing profiled sheet - aluminum will not withstand: over the years, such a system will bend under the weight of iron.
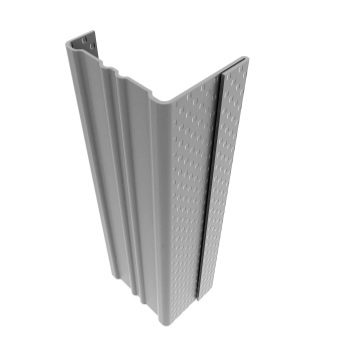

Plastic
In recent years, there has been an active distribution of plastic profiles. Disadvantages - low fire hazard: polyethylene and polystyrene profile elements are highly flammable and support self-combustion. Polypropylene, although it is also difficult to burn, even when reinforced, melts easily - although, along with vinyl, it is not brittle, it allows for kinks.


The plastic profile is not hard, durable and resistant to extreme conditions. The service life of plastic guides is 20-25 years, after which they are changed. The advantages of plastic are low thermal conductivity, as well as ease of installation by one person. The use of plastic profiles is still limited by fixing strips from below - for the same siding, platbands, longitudinal technological plugs, decorative strips. Plastic is still poor for carrying out the bearing / running function under high load conditions.

The subtype of such profiles - polymer-wooden "wood-plastic" in comparison with purely plastic guides is relatively safe for human health.
Steel galvanized
Galvanized steel (often a profile perforated at the intersection points) is the basis of a convenient geometry that is difficult to spoil even with careless transportation and improper storage: L- and V-shaped corners are easily stacked into stacking blocks by overlapping each other. Steel corners - Z-shaped, S-shaped, T-shaped (T-shaped, I-beams) - are used as longitudinal moldings and as transverse elements. They will last up to 35 years. They are often used as a profile for a plasterboard partition: it is able to withstand a ladder leaning against it at an angle of 65 degrees to the floor surface, with a person standing on it.

Components
Additional components, parts, in addition to hardware, are required. It is difficult to screw a U- or C-shaped hanger to the wall without drilling the opposite wall or without L-shaped tubular or hex keys. Brackets, corner and other similar hangers are companions of longitudinal and transverse profile guides. It is not enough to drill a wall for a dowel or anchor - this hardware must also be screwed into it until it stops so that the fixed profile does not come off the wall. Regardless of the building materials of the bearing walls - (iron) concrete, brick-cement, gas silicate-glue masonry, glued or standard timber, calibrated rounded logs, facing of brick and stone from porcelain stoneware - you cannot do without pieces of corners or brackets. Often, bearing guides are fixed to fragments of the same, but reinforced, profile, having cut out the necessary parts from it.

Selection Tips
Choose a profile for a ventilation facade with a margin of wall thickness. It is better to overpay for 1.5 mm instead of 1 mm and larger hardware than in 3-10 years to remake the rickety, slipped siding again.
Do not mount front and interior decorative panels on a single plastic profile or aluminum. Try to reinforce them with steel at least according to the principle "through one".
Instead of galvanizing, you can also choose a painted profile.


Make sure that the polymer coating on it is not worse in quality and durability than, for example, on the roofing profiled sheet.
Do not choose plastic profiles for rooms with high temperatures, as well as in the case when the siding does not come to the north side of the house (in Russia).















The comment was sent successfully.