Description and use of protective suits L-1

Now, on many sites, you can easily find a detailed description of light protective suits and the nuances of use, as well as the correct storage of L-1 kits. In this case, we are talking about effective means of protecting open areas of skin, clothing (uniforms) and shoes. These suits are relevant in the event of the negative effect of solid, liquid, aerosol substances that pose a potential danger to human life and health.


Features and purpose
The lightweight and moisture-proof set of the L-1 series belongs to the means of skin protection and is intended for the so-called periodic wear. Such suits are used in areas contaminated with various harmful substances, including poisonous ones. Taking into account the technical characteristics, they are used at chemical industry enterprises and in the implementation of measures of varying complexity, within the framework of which degassing and disinfection are carried out.

It is important to remember that the manufacturer focuses on the impossibility of using this category of chemical protection on fires.
Comparing the described suit with the standard OZK set, it is worth focusing, first of all, on the ease and ease of use of the first one. It should be noted that with all its advantages, it is made of materials that are not heat-resistant. It is important to take into account that the described chemical protection can be reused with an appropriate level of contamination and correct processing.


The described means of protection is most often used in combination with a gas mask. The operating instructions are worthy of special attention in such situations. It is also important to take into account the properties of toxic and chemical substances and the level of contamination (pollution) of the area. The use of kits is strictly prohibited if the exact composition of the aggressive environment is not known.


Analyzing the features of the suits under consideration, the following important points should be noted:
- long-term wearing is quite problematic due to tight fit and poor ventilation;
- L-1 is of little use for other purposes (for example, when used as a raincoat, the jacket will be short);
- operating temperature range - from -40 to +40 degrees;
- set weight - from 3.3 to 3.7 kg;
- all seams are qualitatively sealed with a special tape.

Equipment
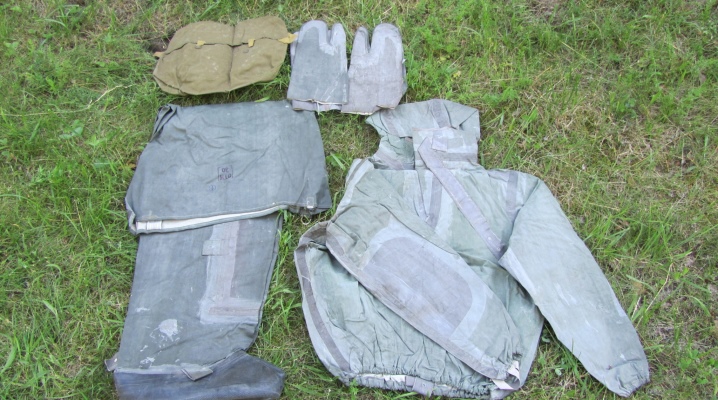
The delivery set of lightweight chemical protection consists of the following items.
- Semi-overalls, equipped with zip ties, which also has reinforced stockings that are worn over the shoes. In addition, the jumpsuit has cotton straps with half rings made of metal and designed to fasten the legs. In the area of the knee, as well as the ankle, there are “fungus” fasteners made of durable plastic. They provide maximum fit to the body.
- Top part, which is a jacket with a hood, as well as neck and crotch straps (straps) and two thumb loops located at the ends of the sleeves. The latter are equipped with cuffs that fit snugly around the wrists. For high-quality fixation of the hood, there is a strap with a fastener in the form of a "fungus". In low temperatures, it is recommended to wear a comforter under the hood.
- Two-fingered glovesmade of UNKL or T-15 fabric.They are fixed on the hands with the help of special elastic bands.
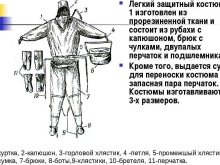


Among other things, the described set of a protective suit includes 6 pegs, called pukles. They are made of plastic and serve as fasteners. Also L-1 is equipped with a bag.
Dimensions (height)
The manufacturer offers lightweight chemical protection suits of the following heights:
- from 1.58 to 1.65 m;
- from 1.70 to 1.76 m;
- 1.82 to 1.88 m;
- from 1.88 to 1.94 m.
The size is indicated at the bottom of the front of the jacket, as well as at the top and left of trousers and on gloves. If the parameters of a person do not match the size (for example, the height corresponds to the 1st height, and the chest girth - the 2nd), you should choose a larger one.

Selection Tips
When choosing personal protective equipment, you need to pay special attention to 3 key points.
First of all, we are talking about a supplier of lightweight chemical protection kits. It is highly recommended to give preference to the manufacturers themselves. If it is not possible to order directly, it is worth contacting stores with an appropriate reputation. As a rule, trusted suppliers try to avoid image risks.
The second whale on which the correct choice of LZK stands is the availability of documents drawn up at the manufacturing plant.


In this case, we are talking about a valid certificate of conformity, as well as a technical passport with an OTK mark, a consignment note and an invoice.
In addition to all of the above, do not forget about such an important point as a careful personal check of all the elements of the kit. During the inspection, special attention should be paid to the completeness, integrity and condition of the fasteners.


User manual
One of the important points is to prevent overheating of the body during the use of L-1. For this purpose, the rules define the maximum duration of continuous wearing of protective clothing. The following terms of work are meant:
- from +30 degrees - no more than 20 minutes;
- +25 - +30 degrees - within 35 minutes;
- +20 - +24 degrees - 40-50 minutes;
- +15 - +19 degrees - 1.5-2 hours;
- up to +15 degrees - up to 3 hours or more.
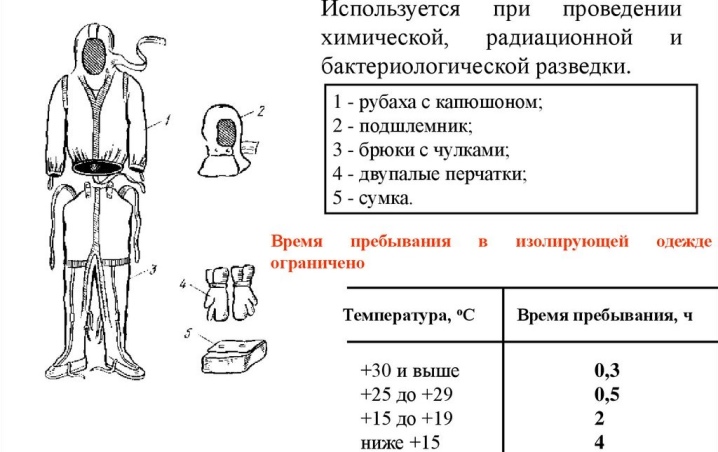
It is important to take into account that the above time intervals are relevant for performing work in direct sunlight and medium physical exertion. We are talking about such actions as a march on foot, processing of various equipment and devices, the actions of individual calculations, and so on.



If manipulations are carried out in the shade or in cloudy weather, then the maximum time spent in L-1 can be increased by one and a half times, and sometimes even twice.
The situation is similar with physical activity. The larger they are, the shorter the periods, and vice versa, with decreasing loads, the upper threshold for using the protective kit increases.

Terms of use, service life
After applying the LZK in conditions of contamination with harmful substances, regardless of the degree of aggressiveness of the environment, it must be subject to special treatment without fail. This allows the L-1 sets to be operated many times. The duration of the protective action, that is, the shelf life of the chemical protection, is directly determined by the operating conditions. An equally important point will be the methods of the aforementioned processing of sets. So, the maximum period of validity of chemical protection, taking into account OV and hazardous chemicals, is:
- chlorine, hydrogen sulfide, ammonia and hydrogen chloride in a gaseous state, as well as acetone and methanol - 4 hours;
- sodium hydroxide, acetonitrile and ethyl acetate - 2 hours;
- heptyl, amyl, toluene, hydrazine and triethylamine - 1 hour;
- toxic substances in the form of steam and drops - 8 hours and 40 minutes, respectively.

According to the current GOST, a lightweight suit is able to provide effective protection against acids with a concentration of up to 80% in terms of H2SO4, as well as alkalis with a concentration exceeding 50% in terms of NAOH.
It is also about waterproofing and protection against the penetration of solutions of non-toxic substances.
In addition to everything already mentioned, a light suit should have the following properties:
- acid resistance - from 10%;
- acid resistance for at least 4 hours;
- resistance to direct action of acids and open fire - up to 1 hour and 4 seconds, respectively;
- tensile load that the seams must withstand - from 200 N.

Putting on and taking off
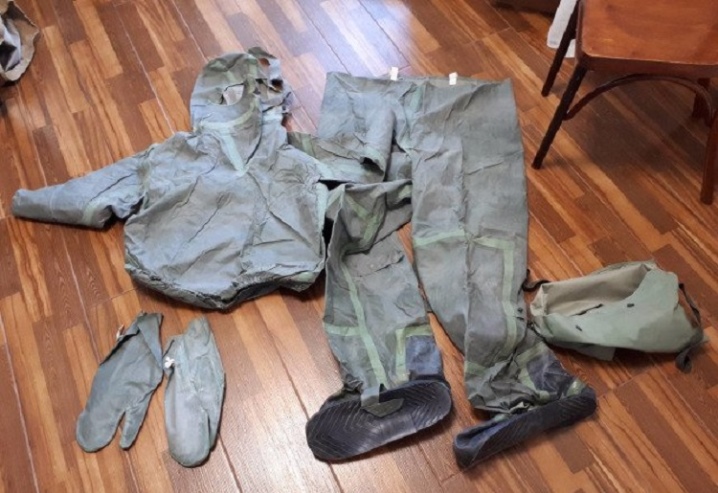
According to the current rules of the mechanism for the use of LZK, there are 3 of its provisions, namely marching, ready and directly combat. The first option provides for the transportation of the set in the stacked state. In the second case, as a rule, we are talking about the use of a kit without respiratory protection. The transfer to the working state, that is, the third, from the indicated positions is carried out after the corresponding command. In this case, the rules provide for the following algorithm of actions:
- take off all equipment, including headgear, if any;
- remove the kit from the bag, fully straighten it and place it on the ground;
- put on the lower part of L-1, fixing all the straps with "mushrooms";
- throw the straps crosswise over both shoulders, and then fasten them to the stockings;
- put on a jacket, throwing its hood back and fasten the crotch strap;
- put on and fasten the equipment, if any;
- put on a gas mask;
- place the previously removed headgear in the L-1 carrying bag and put it on;
- put on a gas mask and a hood over it;
- carefully straighten all the folds on the jacket;
- wrap the neck strap tightly but neatly around the neck and fix it with a fastener in the form of a fungus;
- put on a protective helmet, if one is included in the equipment set;
- put on gloves so that the elastic bands tightly wrapped around the wrists;
- hook on the special elastic bands of the sleeves of the L-1 suit on the thumbs.

Take off the suit outside the contaminated area.
In this case, contact with the infected tissue surface must be avoided.
If, after removal, it is required to reapply the kit, which has been exposed to harmful substances, without treatment, then the following steps must be performed:
- remove the top;
- carefully remove contaminated gloves;
- lower the straps without unfastening them;
- holding the straps, as well as the stockings themselves, remove them with the utmost care;
- wrap the straps themselves and the clean surface of the stockings inside;
- place trousers near the stacked upper part of the set;
- put on gloves, taking only the inside and clean part of the leggings;
- make tight rolls from both parts of the kit and place them evenly in the carrier;
- fix the valves with a special tape and perform a thorough surface treatment;
- take off the gloves, trying to avoid touching the outer surface, and place them on the tightened valves;
- close the lid tightly and fasten both buttons.

After all the steps described above are completed, the bag should be placed where the risk of inhalation of harmful substances and their vapors on people will be minimized. Then it remains to carefully process your hands.

Storage
One of the key points in the context of the proper storage of the chemical protection in question is its proper installation. After removing the suit and processing it, you must:
- make a roll out of a jacket by folding it in half lengthwise;
- perform similar actions with trousers;
- place all the elements of the kit evenly in the carrier.
Store protective equipment to prevent overheating and direct sunlight. It is removed from the carrying bag and put on the suit only before the very beginning of work. It is important to remember that the main properties and all performance indicators of the described personal protective equipment directly depend on the state of the material of its components and fasteners.


How to put on a protective suit L-1, see below.













The comment was sent successfully.