Pallas spurge: description and cultivation at home

Pallas spurge belongs to the succulent plants of the Euphorbia family. It received its generic name due to the release of thick juice, similar to milk, when the stem is broken. And he acquired his full name in memory of the merits of the naturalists P. Pallas and F. Fischer who studied it, because it is also called Fischer's spurge. This plant grows in Mongolia, China, Transbaikalia and Eastern Siberia on rocky slopes, in the steppe or on the plains.

Description
Pallas spurge belongs to perennial herbaceous plants, it is quite rare. For its healing properties and the unusual structure of the root, the people awarded the flower with many names:
- "Man-grass";
- "Root man";
- "Exile";
- "Sungazer";
- "Damn milk".


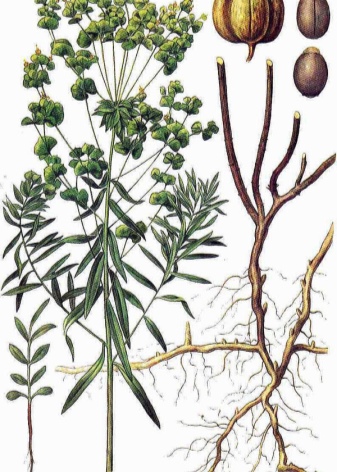
The stem of the plant is simple, leafy, 30-40 cm high. Matte leaves vary in size, depending on the distribution on the stem. The lower leaf plates have a scaly shape and a brownish tint, the middle ones are brown-green, oblong and dense in structure. The leaves are collected in small whorls.
The root of the milkweed is thick and branched, and can be up to one meter long. In shape, it is very similar to the root of a ginseng, and also similar to a human figure, but significantly predominates in size. In May, an umbrella inflorescence appears on the plant. Due to its somewhat unusual appearance, some gardeners use this herb in flower beds, in flower arrangements, but most consider Pallas' euphorbia a weed. The root, which is difficult to extract from the ground, presents difficulties for gardeners and is highly regarded by herbalists.
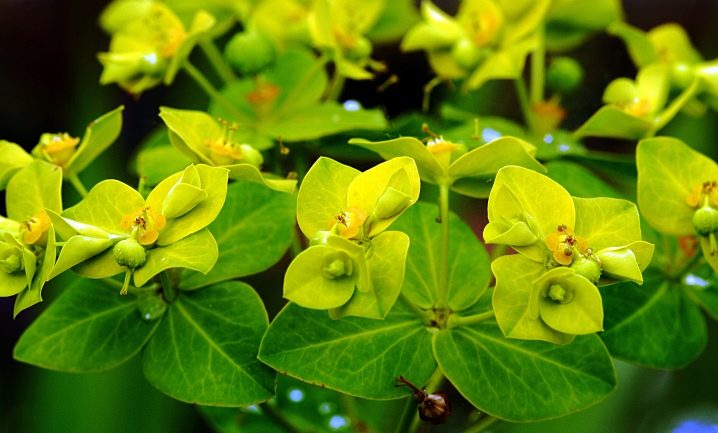
The juice exuding from the stem and leaves is poisonous. Due to the deep green color of the leaf plates with an unusual matte surface, the plant was classified as decorative.


How to grow?
Although the Pallas spurge is classified as endemic, it can also be cultivated at home: as a houseplant or on a plot. In fact, he is undemanding and unpretentious to care for. For good growth, he needs a little.
- The substrate should be sandy-peaty with the addition of sod and deciduous soil. The presence of a small amount of stones in the ground is also highly desirable. It should be as similar as possible to the natural soil in which spurge grows in nature.
- The growing container is deep, but not very wide. Planters are the ideal solution.
- The plant is not too light-loving, therefore, it must be protected from direct sunlight. In summer, you can plant it in open soil, but the landing site should be shaded and not too hot.
- Suitable temperature is from +17 to +20 degrees.
- The amount of watering depends on the season. In spring and autumn, the plant is moistened once every two weeks, in summer it is watered once a week, and in winter, watering is reduced to once a month.
- For growth and development, milkweed needs fertilizers. You can use top dressing for cacti. It is applied every two weeks, except for the winter season, during this period it is not necessary to fertilize the plant.



Fischer's spurge normally withstands the proximity of other flowers and grasses when planted in flower beds. At home, east or south windows are well suited for him. In May, the plant produces a small umbrella-shaped inflorescence, yellow-green in color, and at the end of August, a three-root fruit appears in its place. This box contains three smooth, round seeds.
Reproduction
Pallas spurge reproduces, like most houseplants, in several ways:
- stem cuttings;
- leaves.
Each breeding option has its own nuances, observing which, you can plant a plant without much difficulty. The first method is used in the spring, when the flower is in the stage of active growth:
- from the upper part of the milkweed, pinch off small cuttings about 12 cm in length;
- the segments are immersed in a bowl of warm water so that the milky juice flows out;
- the sections are treated with crushed coal;
- after the appearance of a protective film on the damaged area, the cutting is moistened or sprinkled with a growth stimulant, for example, "Kornevin", and planted in a sandy-peat substrate.


After about two weeks, Pallas spurge begins to take root.
With leaf cuttings, a leaf is pinched off from a mature plant and kept a little so that the juice comes off. After that, they are treated with any rooting agent, planted in special mineral wool cubes and placed in a bowl with coarse sand. The sprouts are watered and covered with polyethylene, which is periodically removed. After about a month, roots appear.
If this method seems too difficult to someone or there is no special mineral wool, you can use the previous breeding option, only instead of cutting from the stem, take a leaf. In both cases, the cuttings must be pinched off, not cut off. Cut off shoots will not take root. When working with Fischer's milkweed, you need to protect your hands, since the plant sap is toxic and causes skin damage. This variety of milkweed does not propagate by seeds at home.

Diseases and pests
Despite the release of harmful sap, the flower can be attacked by pests, while plant diseases are directly related to improper care of it. If the plant loses leaves but is not affected by pests, there is a possibility of drafts or sudden temperature changes. In this case, it is necessary to pick up the flower from the windowsill and control the temperature. In the event of an unpleasant odor and foliage falling off, it is necessary to establish an irrigation system, since these are signs of root rot.
The appearance of dry brown spots indicates the natural aging process of milkweed. If the plant is young, it marks the penetration of direct sunlight. It is necessary to rearrange the flower in a less illuminated place or shade a little. When the tips of the shoots dry out, it is worth increasing the humidity level in the room. Euphorbia is regularly sprayed and the humidity of the room is increased.
A black bloom on the leaf plates manifests itself as a sooty fungus, and this is also a consequence of the vital activity of aphids or whiteflies. As a result of the disease, the plant weakens and withers. Euphorbia eliminates pests, and the fungus is washed off with soapy water.



Pests affecting Pallas spurge include aphids, scale insects, whiteflies, and root mealybugs.
- Aphids destroy the tops of the shoots, and in the presence of large colonies can destroy the entire flower. A small amount of aphids can be neutralized with water and laundry soap. If the lesion is strong, use insecticides: "Decis", "Inta-Vir". The plant is treated twice, with an interval of a week.
- The scabbard multiplies quickly, and in a short time can completely infect the plant, after which it dies. It manifests itself as yellow spots on the plates. It is very difficult to remove an insect. Mechanical cleaning and insecticides are used against it.
- The whitefly, like its larvae, feeds on the sap of the plant, attaching itself to the lower part of the leaf plates. Affected leaves turn yellow, curl and fall off. Pest control consists of treatment with soapy water and, if necessary, insecticidal preparations.
- The root mealybug also draws juices from the roots of the milkweed, which leads to its decay and subsequent death. The danger lies in the fact that the existence of the pest may not be known before the flower is transplanted.To get rid of the worm, the plant is removed from the soil, the roots are dipped in an insecticide solution, and transplanted into a new substrate.



Pallas spurge will not only decorate the apartment with its unusual appearance, but will help improve health, because it has powerful healing properties.
For the medicinal properties of milkweed, see the next video.























































The comment was sent successfully.