Pear Bacterial Burn
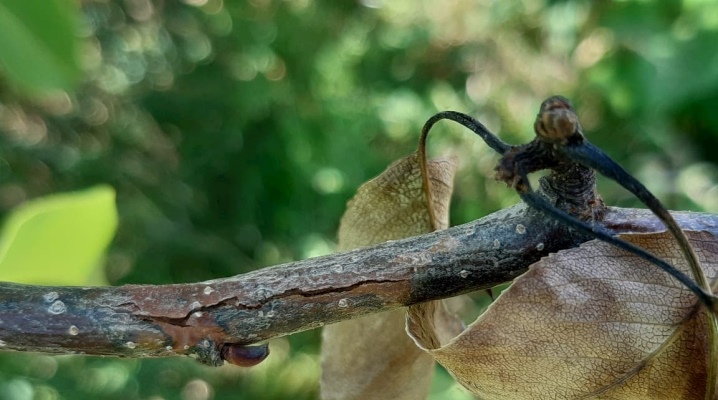

Bacterial burn is an infectious disease that often occurs in fruit orchards. If you ignore it for a long time, then you can lose not only a good harvest, but also the tree itself. We will describe below what this disease looks like, why it appears and how to deal with it.


Causes and signs of appearance
A bacterial burn is an infection that often affects garden trees. Among them there is also a pear.
First of all, you can find out about the appearance of this infectious disease by looking at the branches of a tree. In the spring, the buds growing on it will develop rather slowly. The leaves of the plant, if they had time to appear by the spring, will turn black and dry, remaining in this form on the tree and not falling off. The same situation can be observed with branches.
If the disease occurs during the fruiting period of the pear, then it will also quickly turn black and dry. During the flowering of a diseased tree, the flowers will soon also turn black, and fruits will not form on the affected branches.
In the future, if you do not take action, the disease affects the trunk of the pear tree. Its bark begins to soften, then whitish spots appear on it, which soon turn black. Over time, brown streaks begin to form around the same area. Ultimately, the diseased parts of the fruit tree flake off, and large ulcers appear in that place.


Having started an infectious disease before the trunk of a tree is damaged, trying to treat it will be a pointless exercise. In this case, the pear is simply eliminated, and as soon as possible so that the infection does not spread to healthy plants. After the tree is uprooted, it is burned.
If we talk about the causes of the disease, then the bacteria Erwinia amylovora become its causative agent. They are actively spreading in a favorable environment for them. This is the average temperature of air masses and a high level of moisture.
- So, the plant can become infected due to the wind. The bacterium that triggers fire blight releases thin threads. In windy weather, they actively spread throughout the site, finding themselves on the branches and leaves of trees. Most often, the pathogen begins to multiply in the flowers of the plant, through which infection occurs, after which the disease spreads to the rest of the fruit tree.
- Often, infection occurs after precipitation. Strong gusts of wind help the causative agent of the disease to be transferred along with raindrops to another plant and settle there.
- Gardening tools are another reason. If it is poorly disinfected, then there is a high risk of introducing an infection, transferring it from one plant to another. Most often, infection occurs during pruning or grafting.
- Sometimes pollinating insects that are useful for the plant also become the cause of the disease. Most often, in such cases, bees are the main carriers.
- In addition, it sometimes happens that the disease has arisen due to an infected seedling. To prevent this from happening, plant seeds must be carefully examined, acquiring them only in proven places.


Note that fire blight is a problem mainly in young pears. For old plants, the infectious agent is almost completely harmless.
Resistant varieties
Unfortunately, not a single pear variety has 100% resistance to fire blight. However, at the present time, those are still bred that fall ill at times less often than other varieties.
So, the most resistant to this infectious disease include the following varieties:
- Williams;
- "November";
- "Maria";
- "Carmen";
- General Leclerc;
- Bere Durando.


Processing time
Treatment is recommended to be carried out several times in one season.
So, it is necessary to spray the plant with special agents during the period of bud swelling and during their blooming, at the end of the flowering phase and 14 days later, as well as after the final harvest of the fruits.
Especially careful processing should be carried out in summer, which is characterized by high temperatures and dryness. It is best to do this in the evening so as not to harm the plant.


How to treat?
There are always several options for saving a tree.
Antibiotics
Antibacterial drugs are used not only for treating pears, but also for prophylactic purposes. However, in order for the effect to be noticeable, when processing plantings, the funds must be regularly changed so that the pathogen does not develop immunity to them.
Antibiotics are available at your regular pharmacy. Gardeners most often take funds such as Ofloxacin, Levomycetin, Genamycin and others.
It is recommended to treat trees with "Ofloxacin" and other preparations in the spring, 14 days before the flowering phase. The medicine is applied to all areas of the pear.

Please note: in order to completely cure a tree, it is necessary to strictly observe the dosage and follow the instructions, otherwise it is possible to bring the plant more harm than good.
Chemicals
Chemicals are another way that you can fight the pathogen and save the plant. However, you shouldn't use them regularly. First, toxic substances in large quantities are harmful to the plant and tend to accumulate in fruits. Secondly, during processing there is a chance to harm oneself, in addition, the environment can also suffer from this. Thirdly, when treated with chemicals on an ongoing basis, the disease can mutate, which makes getting rid of it in the future several times more difficult.
Most often, such funds are used in the early stages of the disease. However, drugs that do not contain copper will be ineffective. Before you start treating a tree, you need to get rid of its diseased areas, after which you can start spraying the plants, paying attention to healthy trees.
Most often, among the chemicals are "Skor", "Previkur", "Energi". They are mainly used in combination with antibacterial agents. You can also use Bordeaux liquid at a concentration of 1%. But copper sulfate is dangerous to use in its pure form, as it can cause a burn of foliage.


When using chemicals, it is necessary to strictly observe safety measures, follow the instructions and use personal protective equipment.
Bacteriological methods
Bacteriological methods of control involve the use of biological products. Their advantages include high efficiency and, most importantly, the safety of most of them both for humans and for the tree itself.
Most often, "Gamair" is used to fight infection. It is made on the basis of bacteria. A solution is prepared from it at the rate of 2 tablets per 1 liter of liquid. You can start spraying the plant with it in the spring, when buds are blooming. This is done 3 times at intervals of 7 days.
Another remedy is Fitosporin. It is used mainly in the most advanced cases. It is not recommended to use it annually, it is advisable to do it with certain pauses.If we talk about the preparation of a solution based on it, then for this you will need 1 or 2 liters of water, depending on the neglect of the situation, and 1.5 g of the product. Next, the mixture should stand for about 3 hours, after which the solution can be applied to plants.
This drug is completely safe for humans, but harmful to pollinating insects, and therefore it is better not to process them during the flowering of the tree.

In addition, it is not recommended to use it in hot and windy conditions.
Prevention measures
To avoid the appearance of an infectious disease or to eliminate it in time, preventive measures must be followed.
- First of all, they include the iron rule of any gardener - regular inspection of trees. Thus, if something happens, you can identify the disease at the earliest stages and quickly eliminate it. If an affected area is found, it must be immediately eliminated, after which the area with healthy tissue must be processed.
- For planting plants, it is necessary to take varieties that are highly resistant to diseases. In this case, you need to try to take seed in proven places. In this case, immediately before the very planting of trees, the seeds must be treated with special means.
- Trees should be planted so that there is no excessive planting density that interferes with normal air circulation.
- For prevention, it is recommended to regularly treat plants with antibacterial drugs.
- In addition, it is imperative to remove old plant residues after each harvest by burning or sprinkling them with soil.


For a bacterial pear burn, see the video below.













The comment was sent successfully.