Diseases and pests of garlic

For a long time, garlic has been considered an indispensable product in the diet of a person who cares about strong immunity. Farmers who grow this plant on a large scale often face various fungal and viral diseases that affect the crop. Not only large plantations are exposed to such a scourge - diseases can also affect every summer cottage, garden or vegetable garden. To be able to deal with an ailment, you need to know its signs, so in this article we will describe the symptoms of infections and tell you how to deal with them.

Review and treatment of diseases
Spring garlic yields very quickly - if you plant it in spring, you can cut off the first juicy leaves in summer. In addition, such a plant has winter varieties, which allows you to get a harvest immediately after the end of winter. People highly value the properties of this greenery, therefore they take care of the health of young shoots, preventing their infection.
Agrarians divide garlic diseases into two main types: fungal and viral, sometimes a bacterial infection occurs, but this is extremely rare. The future harvest is most vulnerable at the time of germination - young shoots are easily affected by diseases if they are not treated with special preparations. It is very important to notice and respond correctly to the first signs of infections in time. We propose to consider the varieties of diseases of garlic, as well as ways to treat them.

Fungal
The causative agents of this type of disease are fungal spores, which play a role in maintaining the ecosystem of our planet. Parasitizing weak plants, these microorganisms play the role of natural selection among plants. For farmers, gardeners and gardeners, the noble mission of disputes is an unpleasant disease that destroys crops. Each season, the fungus reminds of its existence, affecting the plantations of young garlic.

Knowledge of the signs of infection and the correct response to them will help to save the future supply of food. Let's consider the most common fungal diseases of garlic.
- Fusarium... Fusarium spores can be stored in soil for several years without showing any signs of their presence. Fusarium rot of the bottom of garlic often worries gardeners - they are afraid of this disease every spring. The southern regions of the country are most susceptible to fungal infection, in which a warm and humid climate creates favorable conditions for the development of mycelium. To prevent massive contamination of the crop, people use various methods of prevention, but even in such conditions, isolated cases of infection appear. Fusarium begins to develop actively after a summer rain, when a short cold snap is replaced by a warming.
Spore-infected plants can be distinguished by several characteristics: leaves turn yellow; the base of the feathers and roots are covered with a beige-pinkish bloom with veins; the teeth become soft. Most often, gardeners notice Fusarium only after harvesting, so it is very important to carry out prevention on time. Diseased garlic is unsuitable for food - it releases toxic elements that can seriously harm the human body.
To prevent fusarium infection, farmers treat the seeds before planting with Maxim, they also disinfect them in the garden and cover the soil with mulch.

- Peronosporosis... The people often call this infection downy mildew, its first signs are round and oval specks of light green, yellowish and gray shades on the green feathers of the plant. After the appearance of infected areas, the leaves begin to dry out and twist into spirals. The disease affects individual plants, next to which a healthy crop grows. The contrast created by dried garlic against a bright green background should raise suspicion among gardeners. Plants with downy mildew symptoms should be removed from the plantation, and healthy plants should be sprayed with Polyhol and Bordeaux liquid. For prophylaxis, before planting, place the green seeds in the Tiram solution.

- Rust... When a bed of greenery is affected by Melampsora or Puccinia fungus, an orange-brown bloom begins to cover the leaves of the plants, reminiscent of metal corrosion. Fiery red dots spread over the feathers, gradually changing their color. After some time, the disease completely devours the young seedling, leaving no chance of life. The farmers have a chance to save the plantation - they need to cut off diseased feathers and spray the entire crop with fungicides such as Syngenta, Fitosporin, or Quadris.
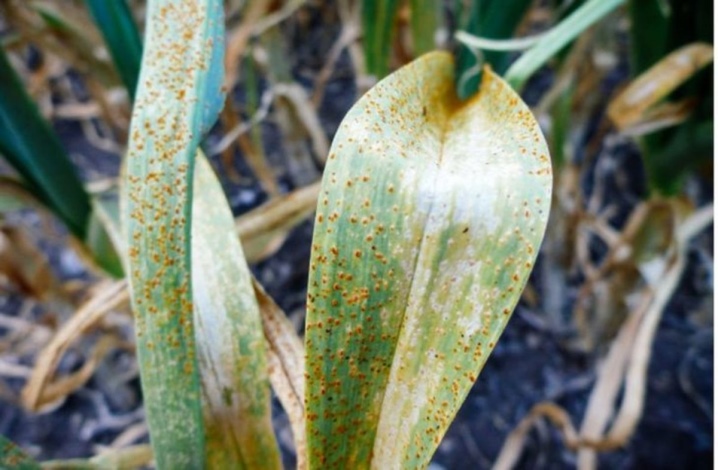

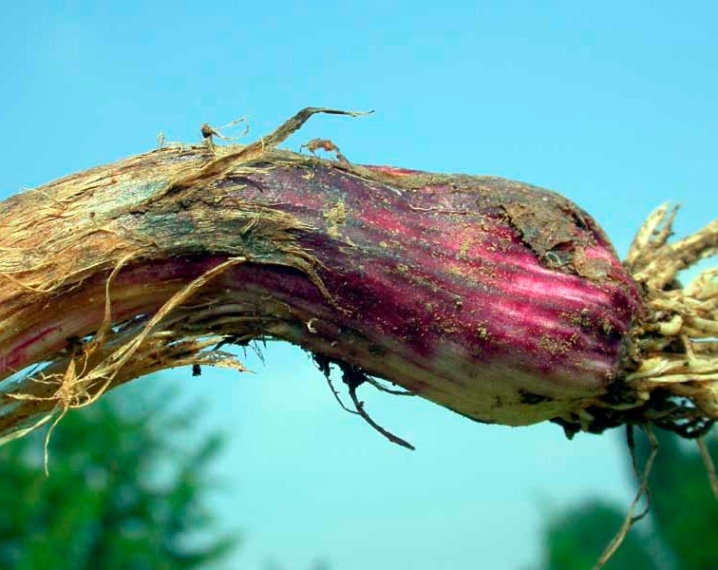
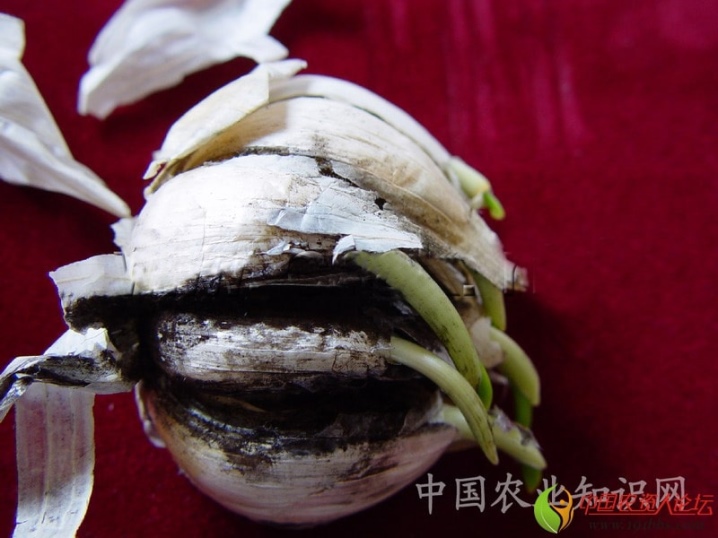
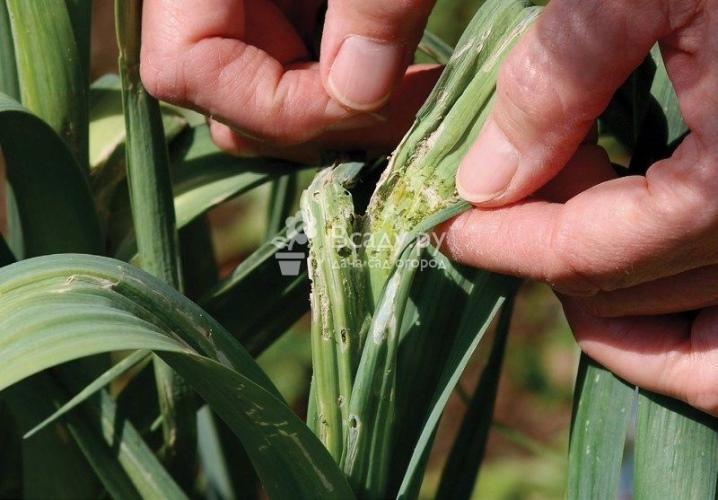
- White rot. A good environment for the growth of mycelium in the soil is created in the fall after harvest or in early spring. The top of the soil infected with mycelium is not suitable for growing garlic, but it is impossible to know in advance about the presence of mycelium. The spores of fungi are brought by the wind, and at a temperature of + 10 ° C and good humidity, the white rot mycelium begins to actively grow. The disease affects the crop, covering the bottom and roots with a white coating. The teeth begin to rot, gradually losing their elasticity, they darken and become watery. The part of the plant that is located above the ground will soon completely die.
If the diseased cloves are stored, white rot will seep inside the head and completely destroy the crop. The most important thing when dealing with white rot is growing healthy seedlings. Seeds sprouted in clean soil have a better chance of killing the fungus. If infected plants appear on the bed, they must be removed and burned, and the remaining bed must be treated with fungicidal agents. Be sure to dry the ripe harvested crop thoroughly and quickly - this will prevent the spread of rot on the stored garlic.
To prevent infection, you can apply top dressing of the aboveground part of the plants - zinc sulfate or copper sulfate.
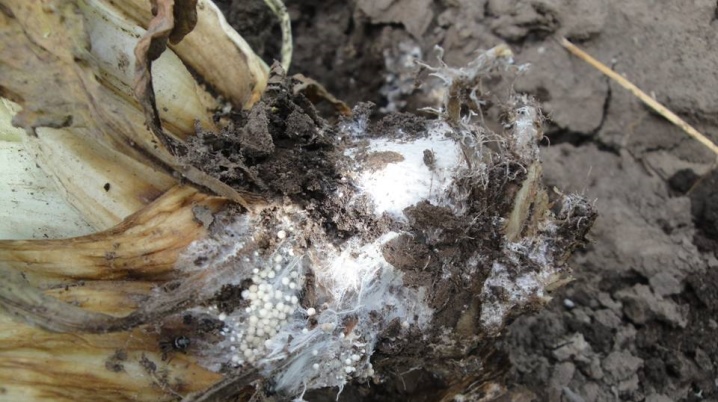

- Neck rot. It enters the garden in the same way as white rot, gradually infecting the soil with mycelium. The fungus remains unnoticed until the aerial part of the crop dies. Inside the head of garlic fills the body of the disease - friable gray dust, gradually killing the entire plantation. When the cervical rot completely consumes the root, the stem of the plant dies and breaks off near the head. The disease is indicated by a white line with a green edge remaining at the site of the stem fracture. To prevent the spread of neck rot, the harvested crop must be sorted out - burn all affected tubers, and dry the clean ones thoroughly. For prevention, treat new seedlings with Fundazol before planting in the ground, and pour the garden with a solution of water and Homa.
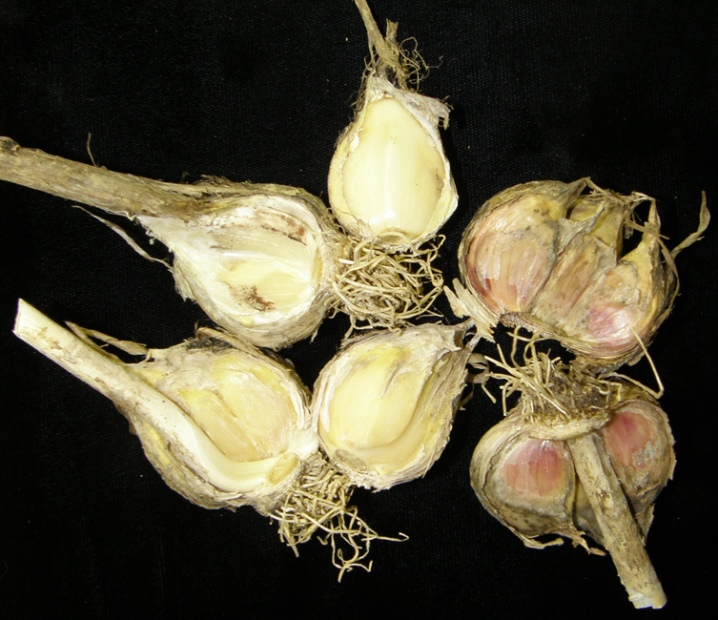

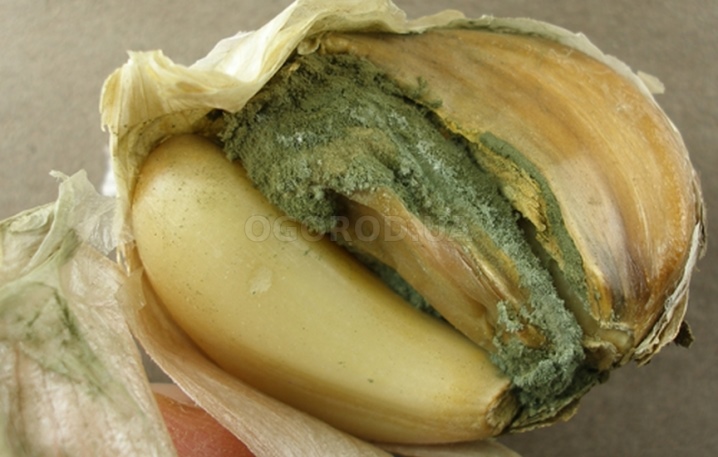
- Penicillosis... Among farmers, this fungus is also called blue or green rot. The soil infected by the mycelium of penicillosis causes less inconvenience than other diseases - the spores die rather quickly and after a year the soil is again clean of microorganisms. Nevertheless, the harvested sick garlic poses a danger to a healthy harvest - the mycelium will destroy all the heads that are located nearby. A sign of penicillosis is depressed, rotten circles covered with a green or blue coating. To prevent fungal contamination of the crop, treat the seeds with Maxim before planting.If some sprouts show symptoms of penicillosis, dig them out and irrigate the plantation with Shirlan, Kwardis or Bumper Super fungicides. After harvesting, do not cut the neck too close to the tubers as this can cause infection.
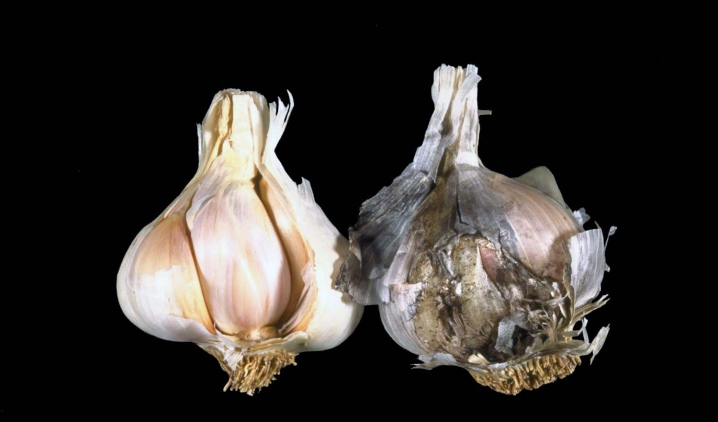
- Aspergillosis... The disease, also called black mold, manifests itself as a moist black coating between the cloves of garlic. First, it penetrates into the head through the junction with the stem, then, spreading down the root and along the sides, covers the surface of the crop under the scales. In the early stages, aspergillosis is invisible, but when there is a lot of fungus, it begins to show through the skin. The mycelium rapidly spreads through the body of the garlic, causing rotting and death of the plant. To prevent spoilage of the crop, it is necessary to process the garden with Bordeaux liquid 20 days before harvesting the garlic.

Viral
Currently, viral plant diseases cannot be cured - there are no drugs to treat infections. However, garlic is less susceptible to infection than other crops - it can only pick up yellow dwarfism and mosaic. Gardeners solve the problem of viruses by properly destroying diseased shoots and timely prevention.
In addition to viral diseases, there is another disease that can affect a green plantation - bacterial rot. The infection is one of a kind - except for it, no other bacteria can destroy garlic. Sometimes the cause of viruses and diseases in the soil is the use of contaminated garden utensils - gloves, scissors, rakes or shovels.
To clean the instruments, you must disinfect them with soap and water, or ignite them.

Let's take a closer look at garlic diseases caused by viruses and bacteria.
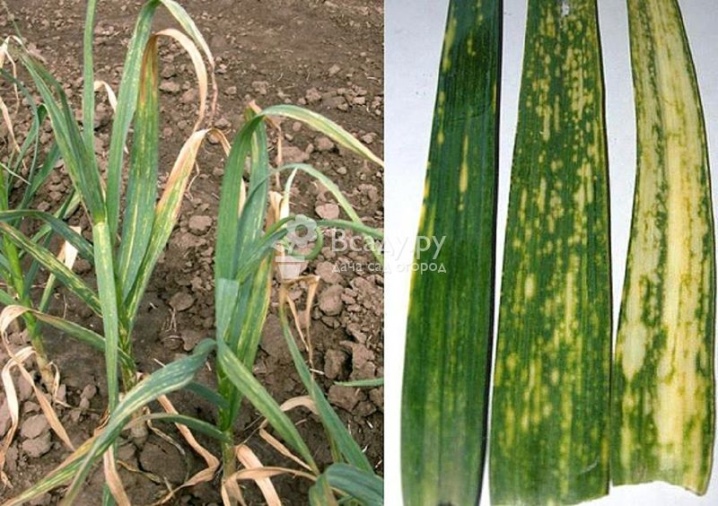
- Viral mosaic. Infection allium virus (Allium virus) enters the soil through vectors - ticks, begins to be active on hot summer days, when the soil is saturated with moisture after rain. Infection is clearly visible on the aerial part of the plant - the feathers fall and wither, becoming covered with white stripes and spots of yellow or brown color. To stop the spread of the allium virus, it is necessary to collect and burn the affected sprouts. And you also need to clean the soil - treat it with copper sulfate, acaricidal or insecticidal poison. By following these precautions, you can prevent the virus from emerging next year.

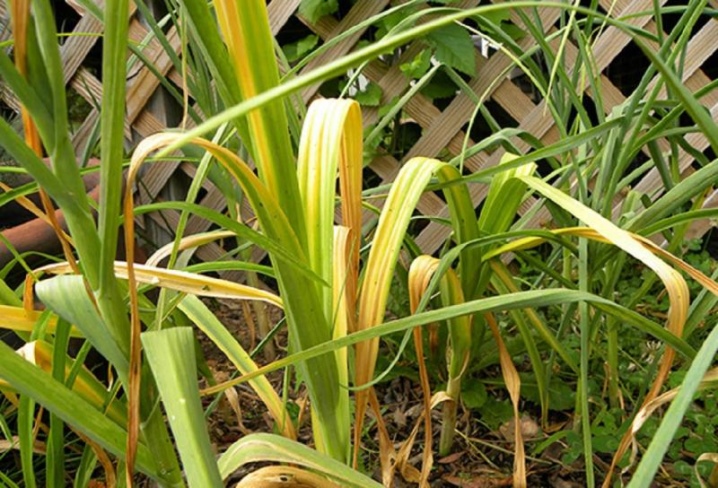
- Viral yellow dwarfism... The carriers of this virus are harmful insects - nematodes, ticks and aphids. The infection cannot live in the soil - it retains its vital activity only in the tubers. It takes about 2 weeks from the moment of infection to the appearance of its signs. The virus is recognized by the following symptoms: the feathers of greenery are deformed and turn yellow, the cloves stop growing and dry out. Having found traces of yellow dwarfism, you need to collect and burn the infected plants, then treat the remaining plantation with a fungicidal agent. For prophylaxis, corn can be grown in the beds a year before planting the garlic.

- Bacterial rot. The crop plantation can be infested with bacteria through groundwater or insect vectors. A favorable time for the development of bacteriosis is warm and damp weather. Rot becomes noticeable only after harvest - yellow-brown ulcers begin to actively cover the teeth, making them soft and watery. Mucus begins to accumulate inside the neck, softening the scales of the plant.
To stop the spread of bacteriosis, the crop must be treated with fungicides and copper sulfate. And also take preventive measures: dry the garlic and store it in a cool, dry place.

Description of pests and control of them
Everyone knows about the beneficial properties of garlic - it is used not only to maintain immunity, but also to repel annoying insects.Nevertheless, plantations of healthy greenery can also be affected by harmful bugs. To save the harvest from uninvited guests, you need to know the signs of the appearance of parasites and take timely measures to combat them. We propose to consider several types of parasites dangerous for garlic.
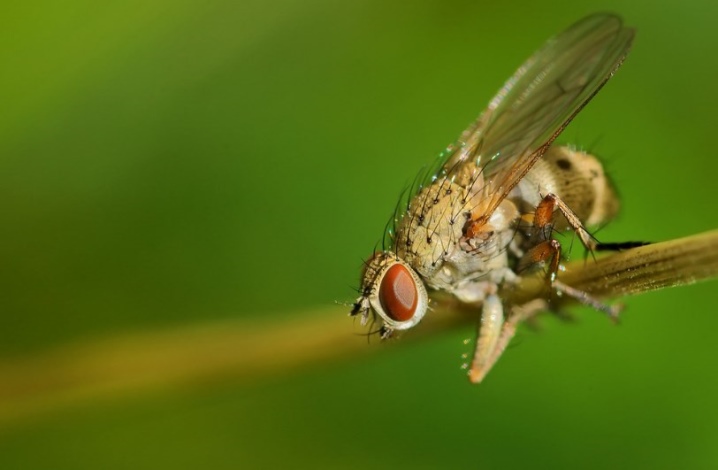
- Onion fly... Winged parasites prefer to live near sandy or loamy soil. Flies overwinter in the ground, at a depth of 20 cm, wrapping themselves in pupae. During spring warming, insects climb to the surface, the adult individual reaches 8 mm in length. When the onion fly finds garlic shoots, it lays eggs on the stem, closer to the tubers. Within a week, the larvae are born, which go down to the head and eat the cloves. Pest control will help the treatment of the plantation and soil with tincture of tobacco mixed with ground black pepper and laundry soap.

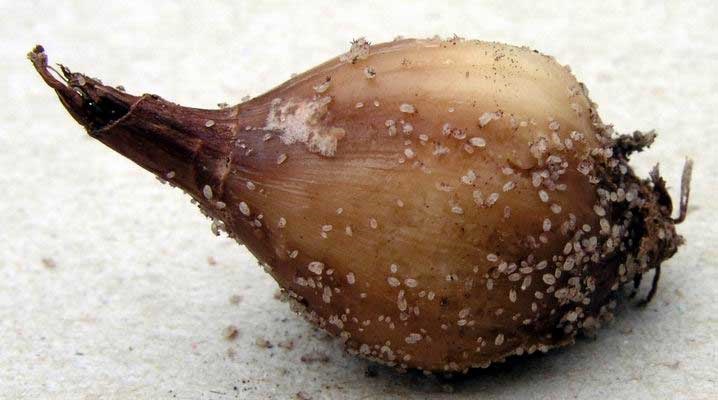
- Root mite. This miniature pest is not easy to detect - its size does not exceed 0.7 mm, there are only 4 legs on a tiny translucent body. A tick from egg to mature individual grows within 30-40 days, and several generations of beetles can develop during the season. The soil is the natural habitat of these insects, so they easily get to the tubers of garlic and gradually eat the cloves, leaving only whitish dust. To get rid of root mites, it is necessary to treat the upper part of the plantation with a solution of Neoron or Actellic in June.

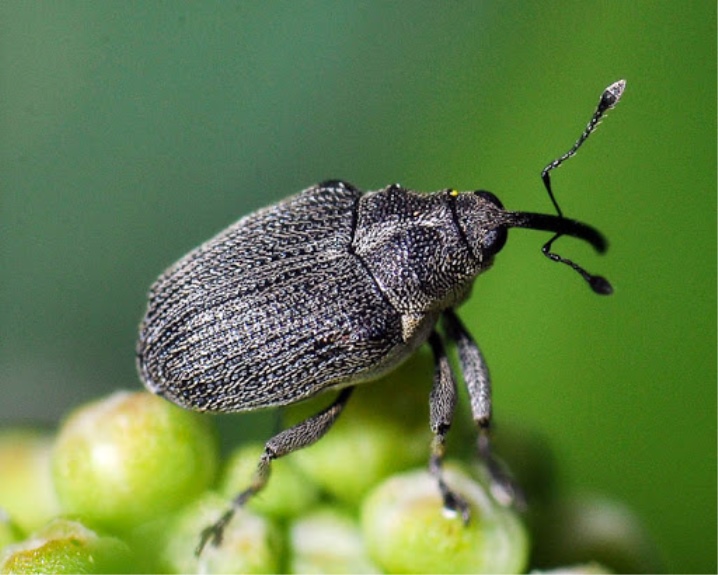
- Weevil... Small insects that grow no more than 3 mm in length, which wake up in early spring along with many other pests. Adults lay eggs on the leaves of garlic, then larvae appear, which eat the green feathers. The affected parts of the plant gradually turn yellow and die. Symptoms of infestation by larvae of weevils are white stripes on the aerial part of the greenery. To stop the spread of insects, use Karbofos or Gin. For prevention, many farmers add dry mustard or ash to the beds.

- Garlic nematode... Nematodes are miniature worms that do not exceed 1.5 mm in length. Sitting in a garden bed, the nematode does not eat the plant itself - it feeds on juice. Having lost life-giving moisture, the above-ground part of the plant first becomes covered with whitish stripes, then dries up and curls altogether. Infected plantations begin to exude an unpleasant rotting smell, and the spicy tubers gradually dry out. To cure the crop, use Fitoverm insecticide or potassium permanganate solution.
To prevent the appearance of nematodes, it is necessary to correctly observe the change of crops and process the seeds before planting.

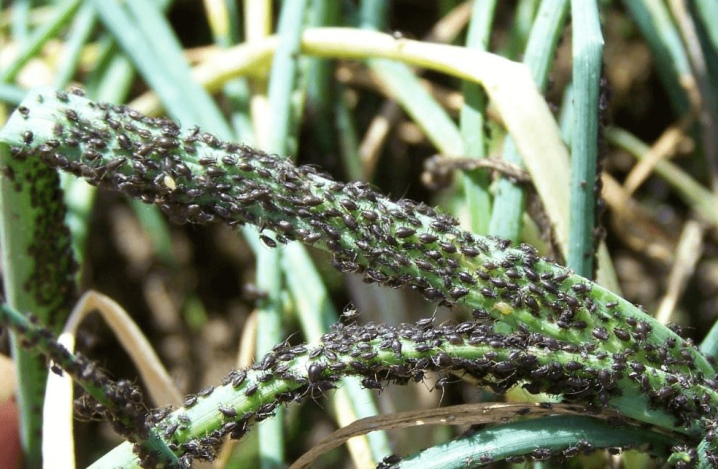
- Aphid... Small yellow parasites with black paws are densely located on the garlic from the neck to the arrows. When miniature bugs create colonies, there is practically no free space on the plant. Insects suck nutritious juices from the crop and eat leaves, depleting entire plantations. Aphids reproduce at an incredibly fast pace - from early spring to late autumn, they are able to breed an entire generation several times. The period of greatest activity of parasites is in the summer, when young shoots are just beginning to grow actively.
When infected with aphids, the feathers of young garlic turn yellow, shrivel and curl, the tuber stops growing completely. In addition, parasite colonies are carriers of most fungal diseases. First of all, to destroy pests, it is necessary to water the beds with water, salt and laundry soap, then spray the above-ground part of the crop with special insecticides. A good preventive measure is to regularly remove weeds from the garden.
Interesting observation: aphids do not infect garlic that grows next to mint.

Prevention measures
The appearance of pests, fungi or viruses on the plantation is a serious problem for every gardener or gardener.If you do not take action in time, there is a possibility of losing most of the crop. The most reliable protection for a garlic plantation is correct and timely disease prevention. To prevent the harvest from getting sick, it is effective to use various agronomic tricks: correct crop rotation, care and location, prevention and preparation of seeds for planting.

It is much easier to keep the crop healthy by applying advanced techniques than to then treat sick plants with dubious folk remedies, using kerosene or alcohol to destroy pests. We suggest that you familiarize yourself with the agronomic tricks tested by generations of farmers in more detail.
- The right choice of location. Well-positioned beds can help prevent many crop problems. To create favorable conditions for the growth of garlic, choose an area of land with good sunlight. The bed should not be located in a depression, otherwise excess moisture will become a good environment for the development of fungal infections.

- Crop rotation... Correct crop rotation on the site is an excellent disease prevention. Good precursors for garlic are such crops: melons, cucumbers, zucchini, cauliflower, any beans. Garlic is not recommended to be planted in the soil after any onion crops. It is necessary to plant other crops 3-4 times and only then in the same place can spicy greens be grown again.

- Seed preparation for planting. The processing of the cloves is perhaps the most important preventive measure, because they can contain various infections. There are several ways to disinfect future crops. The first is fungicide treatment. The modern market provides a huge range of products for plant protection, for example, "Planriz", "Gamair" or "Maxim". The main rule for using these substances is strict adherence to the instructions for use. The second way to cleanse seeds is to soak in a weak solution of potassium permanganate for 9-12 hours.
The method very effectively removes all pathogens and bacteria from the teeth.

-
High-quality crop drying... You can grow and harvest an excellent crop, and then, without observing the rules of drying and storage, completely lose it in the battle with the fungus. Drying is very important to ensure long-term storage of garlic. It is also very important to collect ripe tubers, because unripe crops can also cause a lot of trouble. During storage, injured and poorly dried plants are the first to fall ill, transmitting the infection to healthy garlic.

About diseases of garlic and methods of dealing with them, see below.













The comment was sent successfully.