All about lags

When choosing logs for the floor and ceiling, pay attention to the length and section of the timber. In more rare cases, logs are made from calibrated or rounded logs, but fixing, installing such a base is somewhat more complicated.


What it is?
Lags in the construction of country and country houses, like other structural components from which a specific structure is built, require accurate calculation at the design stage. In addition to the initial and calculated data, knowledge and the ability to apply technologies used in the installation and finishing of floors will be required.
The main requirement is that these elements, like the subfloor itself, must withstand the load from their own weight of all elements and the additional load from people, furniture and equipment, including a two-three-fold margin in case of increased overloads.


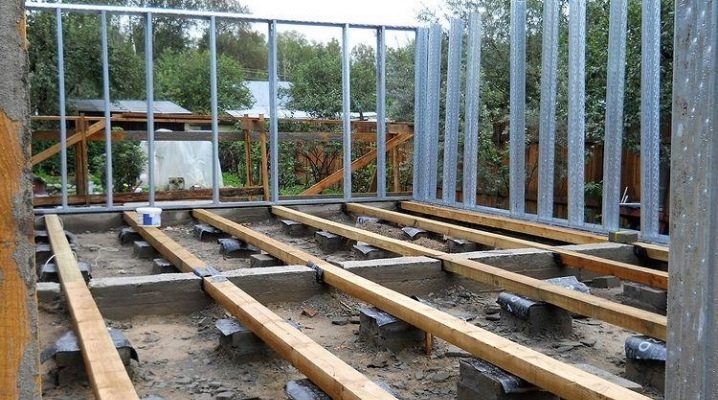
Simply put, logs are installed on the rough floor - for example, on a reinforced concrete base of the first or any of the floors. On them, the flooring is laid perpendicularly from a simple edged or grooved board, which forms the final floor. In other words, the joists are between the floor and the top deck. This component solves three problems: the creation of additional support in order to reduce the sagging of the finished floor, ventilation of the underfloor space and the provision of a heat-insulating ceiling that separates the finished floor from the cold along the perimeter of the premises.
And also lags help to hide engineering communications and small imperfections of the subfloor, for example, a not completely homogeneous concrete surface, during the leveling of which some errors were made. Finally, when laying all technological layers of the "pie" almost complete sound insulation is provided.


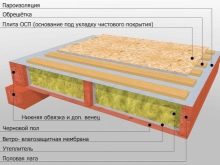
The most demanded material for arranging a log is wooden bar... A board placed on an edge is rarely used. A square bar can replace a rectangular one, in which the section length is much greater than its width, for example, 200x170 mm. The use of a 200x100 mm beam in this example will significantly reduce the stiffness of the log, and 200x40, for example, is already considered a board.
Avoid wood that contains a lot of knots. Knots often fall out, and the holes formed by them reduce the safety margin of the lag by several times.


Views
It is recommended to use mainly wooden logs for the floor. However, in a bath, these logs can be made, for example, of solid MDF material that does not have voids - this material does not absorb moisture. A channel can be used as a metal channel, but not, for example, an ordinary or professional pipe made of steel, the wall thickness of which is less than a few millimeters. The use of aluminum or plastic logs is not allowed: aluminum bends easily, and plastic, for example, high-pressure polyethylene, will not work, since, even having relative unbreakability, it will "play" under load. It is also not allowed to use composite materials that combine, for example, plastic and aluminum - they do not have the declared stiffness, and bend easily at the slightest extreme load. The size of a wooden beam for a lag is most often chosen within 12x12 cm.


A near-limiting value, for example, when organizing an interfloor base (on a concrete floor), a value is selected, for example, 25x20 cm.There is no point in increasing the dimensions of the transverse size and further - values of the order of 30x25 cm, even in the absence of a concrete floor with a span of 60 cm, are able to provide the required margin of safety, while the floor and ceiling can be fixed on the same logs. This solution is a way out in a situation when, for example, a two-story wooden house is being built.
On the balcony, the size of the lags can be much smaller - about 10x10 cm in cross section.


Despite the absence of a metal-plastic composite for organizing ceilings, another type of composite materials can be used - WPC, which also includes wood. The disadvantage of WPC is that, being in a full-bodied version, it is impossible to use these logs as load-bearing ones even with minimal transverse distances of spans. Try to use only wood and steel structures. For an apartment and a house, the use of lags is based on approximately the same calculations: there is already an interfloor as a subfloor. Ceiling logs, unlike floor ones, may be 1.5 times smaller: if for the floor, for example, the use of a 15x15 bar is sufficient, then for the ceiling in the same house on the lower floor, 10x10 or 10x7 cm pieces of timber are used.
The disadvantage of lags is a decrease in the height of the premises by an amount equal to the height of these elements.


How to process?
Rotting caused by the multiplication of microorganisms, fungus and mold can be easily prevented before laying the lag elements, pre-covering the wood with an antiseptic. Antiseptics, water-based or oil-based, are common. For example, kerosene-based formulations are in great demand. A typical composition of an antiseptic contains, in addition to kerosene, fungicidal additives and additives. It provides the most complete protection against the penetration of mold spores, microbes and fungi for 7 years, while observing the temperature and chemical parameters of the environment at a level corresponding to real conditions in the room and outdoors.


Additional accessories
An adjustable support is, in the simplest case, a concrete base, under which layers of plywood or fiberboard are laid. They are needed to set lags by level.... The pads are used to straighten possible zones of curvature of the timber, which, when dried, can lead in different directions, bend slightly, while cracks may form on its surfaces. Having detected this curvature, the master, setting the horizontal along the level gauge, eliminates the zones of possible backlash with the help of these pads, slipped under the beam used as a lag base.
If irregularities are found after tightening the sections of the bar, they can be smoothed out using an electric planer, and then re-impregnated with an antiseptic composition. The use of a wooden sub-floor as a basis, which was obtained, for example, during the construction of a wooden house, makes it possible in some cases to do without logs by installing the final floor on an already fitted log flooring.


Studs or brackets, brick pillars and other elements are used as accessories... The logs are attached to the concrete base mainly using self-tapping screws with a thickened section, specially made slots, combined with both "cross" and flat screwdrivers. The length of a self-tapping screw screwed into concrete reaches 220 millimeters or more, taking into account the height (thickness) of the lags. The requirement is that the end part of the self-tapping screw goes into the concrete base by at least 8 cm. An anchor - a bolt with a spacer, which is held by the walls of the base hole due to the expanded double-leaf element, serves as an improved replacement for the self-tapping screw.
The brackets have one feature - the cantilever structure. They fix the lags, while they themselves are located strictly vertically.They are used to fix the lag to the support pillars. In practice, for example, cruciform parts are used, which have fixed strips, between which pieces of timber are placed in width.


If a strip foundation is used, then brick columns are erected for reinforcement. In addition to fulfilling their supporting function, they protect wood from the destructive effects of moisture. Over time, the lagged elements are partially deformed, sagging slightly downward. The cross-section of the posts is at least two bricks laid next to each other. These brick assemblies are assembled by laying the rough base on a strip foundation or monolithic concrete base. In an area where groundwater rises to the surface of the earth quite high, such a measure will help protect the logs and the finished floor from dampness.
The material of the bricks is fired clay with a small sand content, but not silicate bricks: that, in turn, easily crumbles under the influence of moisture. It is impossible to mount brick supports on loose and creeping soil - it will go away, and the support itself will shift with it. Corner supports are fixed counter-parallel to each other. They are replaced by the P-profile, which more reliably fixes the bars to the floor.


Mounting
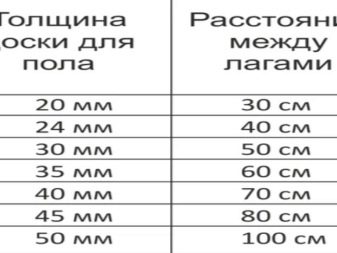
In the case when additional finishing is performed on top of the overlying flooring, the direction in which the logs are laid is not decisive. Then the step (span) between the lags is calculated, their number based on the area of the room to be finished. So, for the thickness of the board from which the flooring is laid, the step between the logs is 30 cm, and for 5-centimeter thick floorboards, a one-meter span is taken. The cross-section of the timber for the lag varies from 11x6 to 22x18 cm.
The deliberate reduction in the step between the lagged elements will significantly increase the strength of the finished floor being equipped in the room.

By foundation
If a strip-monolithic foundation is used at the basis of a country house, then after the construction of the walls and roof of the building, the arrangement of window and door openings, the usual mounting of the lag is used with the help of self-tapping screws for concrete and / or anchors. In the case when the foundation is buried under the basement floor, but there is no floor slab, an assembly structure is used based on thicker masonry pillars or elements completely cast from reinforced concrete... At the same time, their location is the same as in the case when the foundation is somewhat recessed, but there is no basement floor underground - there is only a small space of several tens of centimeters that fences off the floor lying above from possible flooding.


On the ground
To create a reliable fastening of the lag along the ground, first, a columnar base is installed, extending as far as possible beyond the deep freezing of soil layers.
If this requirement is not met, then the heaving of the soil in the first severe frost will significantly displace the support, and the logs will either sag or, conversely, bend upwards.

If a country house or a temporary house that performs its functions is installed in advance on a soil-brick base, then the installation of a log in such a house is not required. The rough and final floor in the finished house structure assembled, made as an all-season insulated or seasonal (for summer residence) container house, has already been assembled, and additional logs will not be required to be placed on brick pillars (or self-assembled lining supports).
The device of a lag in a capital structure, whose foundation level has already coincided with the level of the soil nearby, is carried out in the same way - as in a house where the level of the foundation is raised by several tens of centimeters above the ground level of the adjacent site. The logs are attached to the concrete base by means of self-tapping screws for concrete or anchors, to wooden beams on the second floor - by means of ordinary self-tapping screws, but here it is also permissible to use anchor bolts.


On the floor slab
An interfloor reinforced concrete floor slab, including one with voids, is also drilled for self-tapping screws or anchor bolts - similar to a monolithic reinforced concrete coating. The use of brick pillar supports, studs and brackets when arranging a lag is not justified.
Craftsmen can fix the logs both with through-drilled bolts or self-tapping screws, and with the help of sections of an angle profile. Both methods of fastening to a concrete floor are quite reliable.
If a discrepancy is found in the horizontal position, the rigidly fixed logs must be leveled by slightly grinding off the wood on the upper edge.


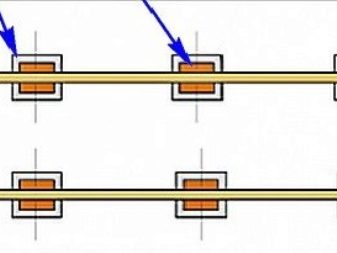
In all cases, the logs are laid in the following sequence: the distance from the nearest wall to the extreme element is no more than a few centimeters... If the size of the last span turns out to be significantly less than the others (between the central and extreme lines of two adjacent lags), then they are dislocated so that they are located strictly evenly. If the same distance turns out to be greater, then an additional lag element is introduced, and the resulting amount of lag, as in the previous case, is distributed similarly (over the resulting span).
Before installing the lag, the concrete or wooden base is covered with an additional layer of a protective agent ("concrete contact"), antiseptic impregnation, then a layer of roofing material is placed on top. For a concrete base, it will serve as a reliable waterproofing agent, thanks to which the logs will be protected from dampness. The logs, pre-coated with an antiseptic, are laid on roofing material and fixed using self-tapping anchor and stud fasteners.

How to enhance?
The already existing base for the logs can be strengthened in the following ways.
-
Installation of several additional supporting elements. In this case, the leveling of the base is carried out, for example, additional compaction of the soil.
-
Installation on both sides of the lag steel platesfastened by means of a nut-bolt connection with a set of appropriate washers.
-
Change of a punctured segment to an equivalent analogue, which is a welded assembly of reinforcement or a section of a channel.
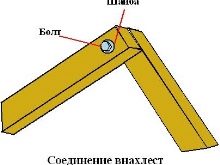
If the area of the room is large, then the lags can be spliced. The peculiarity of this measure is that the timber is most often released in 6-meter segments, and the length of a room or hall may be, for example, equal to 7-12 m. The parts of the log are spliced "in half a tree", "in a paw" or with an overlap. Fastening is done with hardware and carpentry (for example, epoxy) glue.
The parts of the log should be connected, for example, on a brick post, and not outside it.











The comment was sent successfully.