All about tourist houses

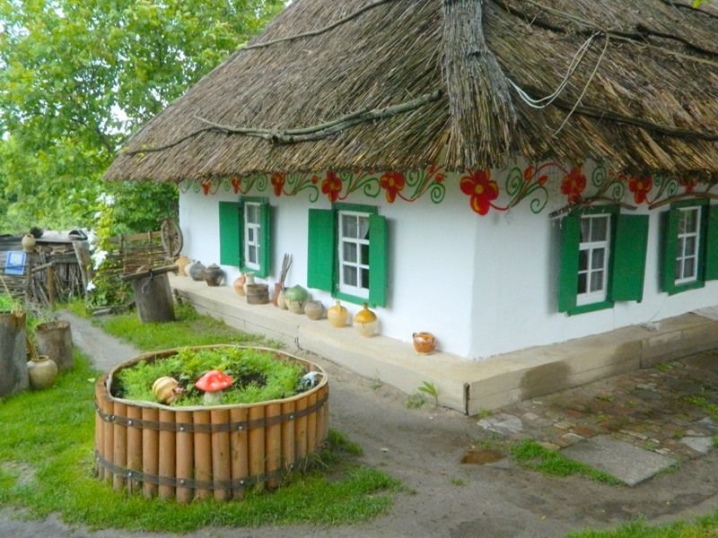
Until the 70s of the twentieth century, tourist houses were widespread in the Kuban, the Lower Volga, the Don and the North Caucasus. They are adapted exclusively for southern regions with a temperate climate and without severe cold weather. People striving to acquire new knowledge will be interested to know what a turluk is, and what it is made of, what is the difference between it and adobe. In addition, you need to figure out what the tourist huts were covered with, what are their advantages and disadvantages. Having clarified these points, you can already get acquainted with the technique of building walls with your own hands, with step-by-step technology.


What it is?
The term "tourist house" itself historically appeared in the Kuban, and outside this region is little known. Just don't think that this is nothing more than another curiosity. Similar buildings were actually built and are being built in other places. Such a dwelling began to be practiced instead of the classic huts, huts and other prototypes due to the usual lack of timber. It is interesting that modern experts classify it as a prototype of the frame type of buildings.
The only difference is that the turluk is a structure made of completely different materials.


Of course, there was no question of any ready-made house kits in the old days. Since such a house took place at a time when even the steam engine was still many centuries old.
The name of these buildings appeared due to the Turkic word "turluk". It means "wattle covered with clay". To use modern terminology, turluk is a frame structure on an unburied foundation. This is for the Cossacks. Circassians, Kabardians and other peoples of the North Caucasus erected tourist houses without a foundation at all: rammed earth served as a floor, and the ceiling and the roof itself were made of straw and reeds.


At first, the structure was built on a lightweight wicker frame - a structure made of tree branches was coated with clay mixed with straw, sometimes with manure... Gradually, however, the dwelling improved and the availability of durable wood increased. From it, they began to make turluchny frames. Of course, the buildings immediately became more reliable than the previous incarnations. The structure was fine-tuned to such an extent that it was intensively practiced in rural construction work all the time until the 70s of the twentieth century.
Similar structures were built along the coast of the Sea of Azov and on the Don. They were built even in settlements with the status of a city.


Advantages and disadvantages
When characterizing a tourist house, you need to pay attention to its pros and cons.
Let's start with the merits:
-
excellent energy saving - in the natural and climatic conditions of the Kuban, even relatively hard frosts do not care;
-
reasonable costs - publicly available materials are used, which are practically waste;
-
lack of artificial components;
-
ease of design in any direction you choose by attaching the appropriate finishing materials;
-
maintaining an excellent local climate in winter, only with constant heating;
-
good sound insulation, including near the railway;
-
moisture absorption by clay in humid weather and release in hot weather - in other words, climate systems and ambient humidifiers are not required.

Minuses:
-
the high cost of repairing floors, foundations, walls and ceilings;
-
technical difficulties and small possibilities of such repair work;
-
cold, almost always blown floor;
-
difficulties with electrical wiring;
-
the ability to mount radiators exclusively on the floor, but not on the walls;
-
the inability to use hinged pieces of furniture;
-
problems with fastening door and window structures;
-
low strength;
-
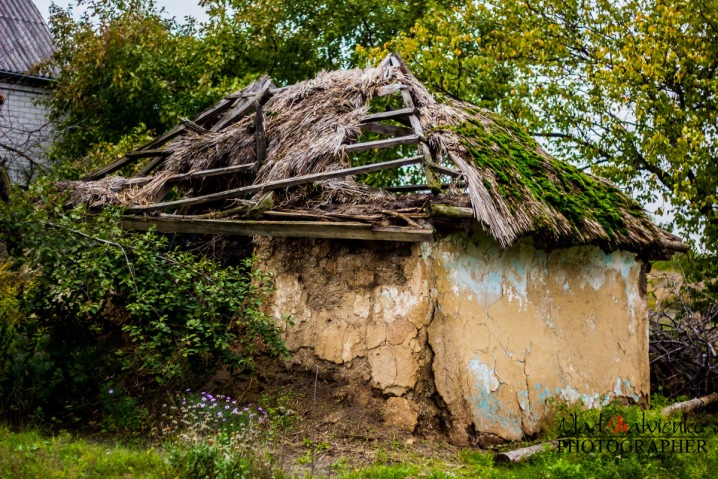
rapid destruction without constant heating in the winter.

How is turluk different from adobe?
For turluk, first of all, a frame is erected: for each wall, 2 parallel lattices of laths, branches are connected, the space is filled with straw or reeds, and then covered with clay. To form coziness and aesthetic comfort, the walls are whitewashed. The house was installed on an unburied foundation made of hammered stakes, corner stones, and the like.
The methods and techniques used in the construction of an adobe house have significant differences from the turluch construction. The difference is that in this method, clay blocks are already practiced, which are laid according to the technology of brickwork. The adobe block includes clay, straw, sand, and water. Sometimes earth is mixed into this material. As a result, a rather strong block comes out, the level of thermal insulation of which significantly exceeds the level of thermal insulation of standard lime-sand bricks.
When building from adobe, a frame is not needed. The adobe is mixed and formed by hand. In Russian villages in the last century, any such house was erected by the entire settlement. Moreover, they managed pretty quickly, in one summer. And already in the fall, the owner of the dwelling celebrated the move to a new house.
Such buildings are still standing, while they are in excellent condition.


Construction technology
The technology of erecting a tourist house is the installation of a frame in which a mixture of sand, clay and lime is placed layer by layer. Similar buildings have stood in Russian villages for many decades. And they are perfectly preserved, of course, with the proper care of the house.
The construction of a tourist house, like any other building, is carried out in a certain sequence. Clearing and leveling the construction site is required, as with any construction work. But specialized equipment is not needed - this is an obvious positive point. At the construction site, recesses are dug in the corners for the pillars. Instead of pillars in the old days, stakes were practiced, only in our time this is unacceptable.


The stakes should be 3-5 centimeters thick. The length reaches 4 meters. As a result, walls up to 3 meters high can be made without any difficulties. However, it will be necessary to forget about the construction of even a lightweight attic.
It is necessary to dig a drainage ditch and replace ordinary soil with sand - in this case, water damage will be less likely. Unfortunately, in such a design it is not worth talking about the strength of the foundation.
The wattle can be made from hazel or willow rods. The rods themselves are thoroughly soaked for maximum plasticity.


The choice of vertical or horizontal weaving method is determined by personal comfort. The roof, as a rule, is made on the basis of a shield from the same rods.
It should be braided from the thick end of the bar to the thin end. In the process of working with wattle, this direction is changed. Windows and doors will also need to be woven. The roof is tied to the walls with a bast or rope. For the winter period, an external wall with cavity filling is required.
Nowadays, such houses, as a rule, are protected from external factors by ventilated facades made of siding (plastic or metal), they are plastered for painting, they are covered with bricks, and they are insulated with penoplex. Inside, they are covered with primer and plastering solution is applied or sewn up with drywall.


About what turluk is, see below.












The comment was sent successfully.